A Survey on Large Language Model based Autonomous Agents
논문 정보
- Date: 2023-10-31
- Reviewer: 건우 김
- Property: Autonomous-Agents
Abstract
이전까지 Autonomous agent는 제한된 환경에서 제한된 knowledge를 가지고 agent를 training시키는 것에 초점이 맞추어져 와서 사람이 학습하는 과정과 다른 점이 많았기 때문에, agent가 human-like decision을 수행하기는 어려워 왔음. 하지만 human-level intelligence의 가능성을 보여준 최근 LLM의 등장으로 인해 LLM-based autonomous agents들이 연구가 많이 되어 왔고, 본 연구에서는 해당 연구의 전반적인 내용을 다음과 같이 정리함.
-
LLM-based autonomous agents의 구성을 설명
-
LLM-based autonomous agents를 다양한 application에 적용한 사례
-
LLM-based autonomous agents를 어떻게 평가하는지
1. Introduction
사람들이 흔히 말하는 AGI를 달성하기 위해서는 self-directed planning과 action을 통해 task를 수행하는 autonomous agents가 필수적이라는 말이 많았음. 이전 연구들은 주로 agents가 heuristic한 policy를 기반으로 제한된 환경에서 action을 수행하는 식으로 이루어졌는데, abstract에서 언급한 내용과 동일하게 이는 human learning process와 많이 다르기 때문에 접근 자체가 잘못된다는 평가를 많이 받고 있음 → human-level decision process를 모방하지 못함
최근에 LLM 연구가 많이 진행이 되며, LLM이 human-like intelligence를 갖고 있다고 보고 있음. 이 능력을 통해 autonmous agents를 구축할 때, LLM을 central controller로 두고 아래와 같은 연구가 많이 진행됨.
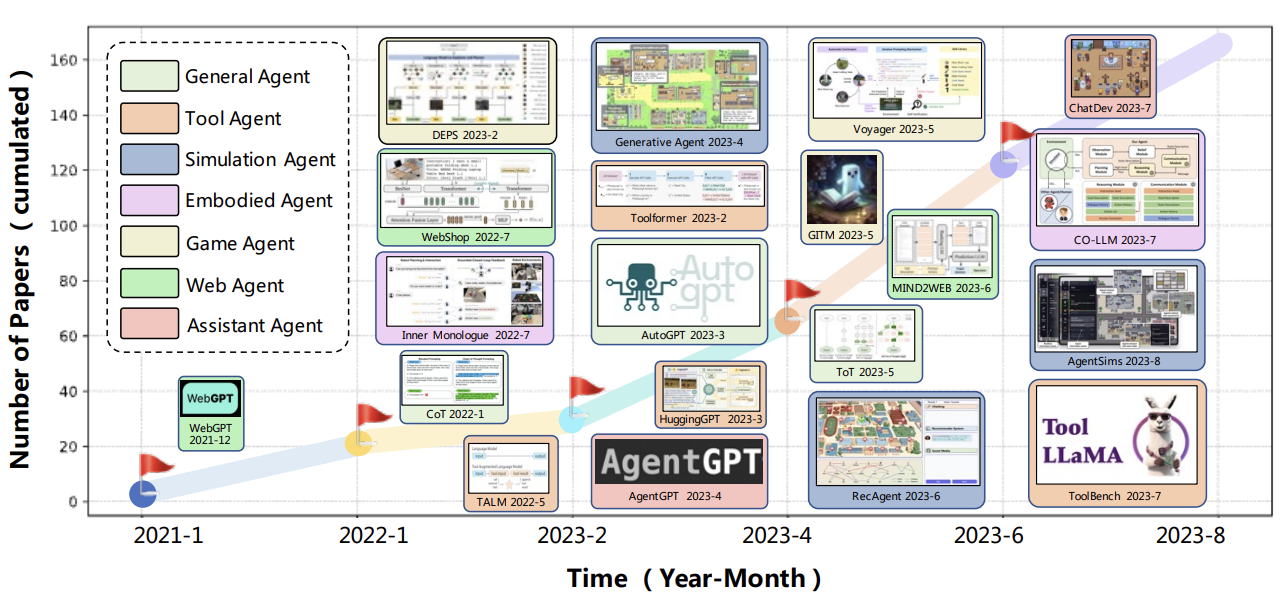
LLM-based autonomous agents들의 정리가 되었던 적이 없었기에, 본 연구에서 세가지 관점으로 다음 내용을 정리하고자 함.
-
construction of LLM-based autonomous agents
-
LLM을 보다 잘 활용하기 위해 agent architecture를 어떻게 디자인할지?
- 본 연구에서 이전 연구들을 포괄할 수 있는 unified agent framework를 제안함
-
다양한 task를 수행하기 위해 agent의 성능을 어떻게 끌어올릴지?
- 자주 사용되는 agent 능력을 얻는 strategies의 summary를 정
-
application of LLM-based autonomous agents
- social science, natural science, engineering 세가지 domain
- evaluation of LLM-based autonomous agents
- subjective / objective
2. LLM-based autonomous Agent Construction
LLM을 autonomouns agent로 사용하기 위해서 아래 두 가지 내용이 중요함
-
LLMs을 더 잘 사용하기 위해 적절한 architecture는 무엇인가?
-
특정 task를 달성하기 위해 어떻게 agent의 능력을 어떻게 끌어올릴까?
2.1 Agent Architecture Design
LLM이 다양한 task를 수행할 수 있게 하기 위해 QA format을 사용했지만, autonomous agent는 사람처럼 특정 역할을 이행하고 환경으로부터 자동으로 인식하고 학습해야 한다는 점에서 QA와는 다소 거리가 멀다.
→ traditional LLM과 autonomous agent의 이런 간극을 채우기 위한 rational agent architecture를 구상해야 하며, 최근 연구들은 LLM을 autonmous agent 역할을 수행할 수 있게 하기 위해 다양한 모듈을 개발함. 본 연구에서 이러한 모듈을 구성하는 unified framework를 제안함.
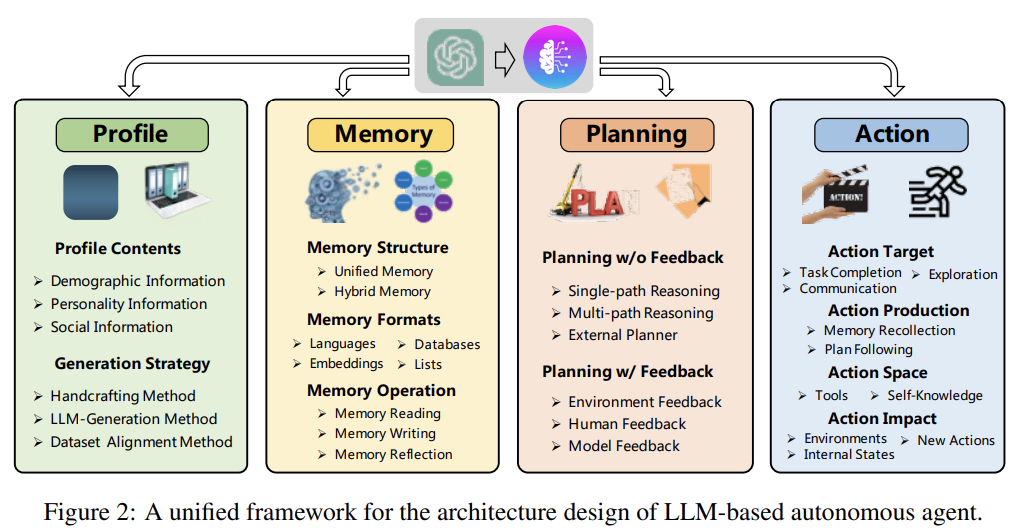
4가지 모듈이 소개되며, 각 module의 주요 기능을 간략하게 소개하면
-
profiling module: agent의 역할을 확인
-
memory and palnning modules: agent를 dynamic enviornment에 던져 이전 행동을 기반으로 미래의 action을 설계할 수 있게함
-
action module: agent의 decision을 특정 output의 형태로 반환시킴
2.1.1 Profiling Module
Profiling module은 agent role의 profile을 prompt 형식으로 나타나게 함으로써 LLM behavior에 영향을 준다. Profile은 주로 (age, gender, career, psychology info)등을 포함하며 agent의 성격과 social 정보를 형성함. → profile을 만드는데 3가지 방법이 주로 사용됨
-
Handcrafting Method: 사람이 직접 agent profiles을 구축하는 방법으로 flexible하다는 점은 용이하지만, agent의 수가 많을 때 labor-intensive하다는 단점 존재
-
LLM-generation Method: LLM을 통해 agent profile을 생성함. agent의 수가 많아도 사용할 수 있긴 하지만, generated profiles에 대한 precise control이 어렵다는 단점 존재
-
Dataset Alignment Method: real-world dataset을 통해 agent profile을 얻음. 실제 human 정보를 natural language prompt를 통해 구성하고, 이를 활용하여 agent를 프로파일링 진행
2.1.2 Memory Module
Environment에서 얻은 정보들을 저장하고 future action을 수행하기 위해 recoreded memories를 활용함으로써 memory module은 agent가 experience 혹은 self-evolve 등의 정보를 축적하고 consistent, reasonable, effective 한 방식으로 행동하게 도와줌. 이것이 Traditional LLM과 가장 다른 핵심적인 요소이며, memory module을 통해 agent의 과거 행동을 축적하며, 이를 바탕으로 dynamic environment 상황에서 agent가 새로이 학습하고 일을 수행할 수 있음.
Memory module을 구성하는 주요 요인들은 아래와 같음.
-
Memory Structures: 인간의 memory process를 다루는 방식으로 설계됨. 인간은 오감을 통해 input을 받아 들여 short-term memory와 long-term memory로 저장함. Memory structure를 design할 때, Transformer 모형의 context window를 short-term memory로 보고 external vector storage를 long-term memory로 봄
-
Unified Memory: human의 short-term memory를 이용하는 방법으로 In-context learning을 통해 prompt로 memory information을 전달함.
-
**Hybrid Memory: **human의 short-term과 long-term memory를 직접 이용한 방법으로 short-term memory는 recent perception을 조정하고, long-term memory는 주요 정보들을 계속 통합함. → short/long-term 다 사용하는 것이 agent로 하여금 long-range reasoning과 valuable experiences를 축적을 하는 것을 가능캐함 (complex environment에서 매우 중요)
-
ex) 최근 gaming agent (Generative Agent, AgentSims)가 hybrid 형식 사용
-
**Memory Formats: **Memory storage 형태에 따른 종
-
Natural Languages: agent에게 더 복잡한 내용을 singal로 줄 수 있음.
-
Embeddings: embedding으로 저장한 뒤 retrieval로 추출하여 사
-
Database: agent가 SQL 명령어를 통해 DB에 접근하여서 memory 정를 add, delete, revise
-
Structured Lists: Tree와 같은 자료구조 활용
-
-
Memory Operations: memory module이 agent가 environment와 소통하여 얻은 지식을 축적하게 하는데, environment와 소통하는 것이 주로 세 가지 operation을 통해 이루어짐.
- Memory Reading: agent의 action을 향상 시키기 위해 memory에서 의미있는 정보를 추출하는 것이 reading의 주요 역할임. 예를 들어, 비슷한 goal을 달성하기 위해 과거에 했던 유사한 action을 사용하는 것. → 여기서 핵심은 valuable information을 추출하는 것이며, 주로 recency, relevance, importance 세 가지 기준을 통해 추출함. (더 최근이고, 더 관련있고, 더 중요한 정보)
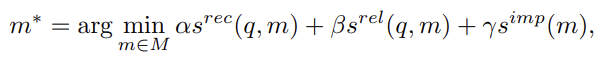
- q: query, s: scoring function, M: set of all memories, s^imp는 memory 자체의 성격을 반영하기에 query와 독립적임
-
Memory Writing: environment에서 인식된 정보를 저장하는 것이 주요 역할. 의미가 있는 정보를 저장해야 나중에 memory에서 정보를 추출할 때, agent가 더 합리적으로 동작하기 때문임. 하지만 두 가지 주요 쟁점이 있음
- Memory Duplicated: exisitng memories와 유사한 정보가 있는 정보는 어떻게 처리할지?
ex) 비슷한 정보가 있으면 최신 정보를 삽입하고 기존의 것을 삭제하기 etc.
1. Memory overflow: memory가 storage limit에 도달할 때, 어떤 정보를 지울지?
ex) ChatDB에서는 user 명령어에 따라 memories를 지움. RET-LLM은 FIFO 방식으로 오래된 정보를 overwrite 진행 etc.
- Memory Reflection: agent가 사람이 스스로의 cognitive, emotional, behavior를 평가하는 능력을 흉내를 내는 것이 주요 역할.
ex) Generative Agent에서 agent는 스스로 memory에 있는 과거의 experiences를 보다 더 광범위하고 추상적인 insight로 요약하는 능력이 있다. 처음에 agent는 최근의 기억을 기반으로 세 가지 주요 질문을 생성하고, 이것을 query로 사용해서 관련 정보를 memory로부터 가져오고, 이렇게 얻은 정보를 기반으로 더 고차원의 아이디어를 반영함.
2.1.3 Planning Module
사람들도 복잡한 문제를 만나면, 작은 여러 문제로 쪼개어 각각 푸는 경향이 있음. 이 module 역시 agent로 하여금 더 합리적으로 행동하게 하기 위해 planning을 사용함.
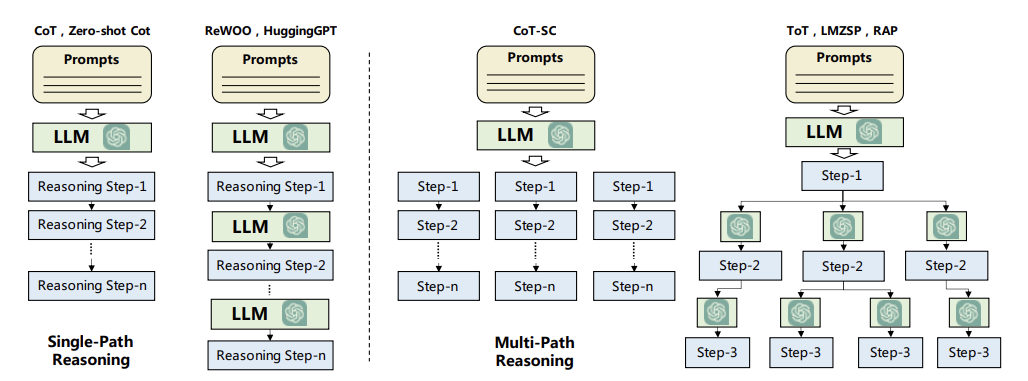
-
Planning without Feedback: future behavior에 영향이 갈만한 어떠한 feedback도 받지 않는 경우
- Single-path Reasoning: final task가 몇 가지 중간 steps으로 분해됨. steps들은 계단식 형식으로 연결이 되어 있으며, 하나의 step이 바로 다음 step에 영향을 줌. LLM이 이 step을 밟고 최종 goal에 도달함. 복잡한 문제를 풀기 위해 reasoning steps을 입력하는 reasoning task 방법.
ex) Re-Prompting은 각 step을 생성할 때, prerequisites를 만족하는지 확인하는 과정이 있고, 틀리면 자동으로 plan을 재생성함
-
Multi-path Reasoning: final plan을 위한 reasoning steps이 tree 구조와 같이 구성됨. 각 중간 step은 multiple subsequent step을 갖고 있으며, 사람이 생각하는 방식과 유사함.
-
Self-consistent CoT (CoT-SC)는 모든 복잡한 문제는 답에 도달하기 위해 여러 경로의 reasoning path가 있다고 보며, 가장 많이 나오는 답이 선정됨
-
Tree-of-Thought (ToT)는 tree구조를 갖으며 plan을 생성하는데, tree의 각 node를 중간 step의 ‘thought’로 보며 BFS 혹은 DFS를 기반으로 답을 도출
-
-
External Planner: zero-shot planning이 강력하긴 하지만 domain-specific 문제에 대해 plan을 생성하기에는 약함. 따라서 외부 지식을 사용하는 external planner를 도입하는 연구가 진행이 됨. LLM+P는 task description을 Planning Domain Defintion Languages (PDDL) 형태로 변환시키고 external planner를 사용하여, 최종 generated restuls는 다시 자연어로 변환되어 도출됨.
- CO-LLM에서 LLM이 high-level plan을 잘 생성하긴 하지만 low-level에서는 부족한 모습을 보이기에, heuristically하게 설계된 external low-level planner를 사용
-
Planning with Feedback: Real world에서 복잡한 task를 풀기 위해 agent는 long-horizon planning을 만들 필요가 있음. Feedback이 없는 planning module은 다음과 같은 문제점들이 있음
-
다양하고 복잡한 task에서 결함이 없는 plan을 처음부터 바로 생성하는 것은 거의 불가능함
-
plan을 실행하는 것은 예측할 수 없는 transition dynamics에 의해 방해받을 수 있음
→ 다음과 같은 문제를 해결하기 위해서는 action을 가한 이후에 아래와 같은 종류의 feedback 을 받는 식으로 보완 할 수 있음
-
**Environmental Feedback: **objective world 혹은 virtual environment에서 얻는 feedback. 예를 들어, RL에서 reward를 받는 것의 알림. ReAct는 prompt를 thought-act-observation triplet으로 구축하는데,
-
thougth: agent 행동을 가이드하기 위해 high-level reasoning과 planning을 가능캐 하기
-
act: agent가 취한 구체적인 action
-
observation: action의 outcome
-
다음 thought는 이전 observation에 영향을 받음.
-
Voyager도 program execution, error, self-verification results 형식으로 묶어 feedback을 받음
-
Human Feedback: 사람으로부터 즉각적으로 feedback을 받아 agent planning 역량을 향상시킴.
-
**Model Feedback: **Environmental/Human Feedback은 external signals이지만, internal feedback으로 작동되는 것과 같이 agent 스스로 feedback을 주는 방법.
- Self-refine 방법은 (output, feedback, refinement) 세 가지로 구성되며, agent가 생성한 output에 대해 LLM이 feedback과 어떻게 고쳐야 할지 guidance도 생성함. (특정 조건을 만족하면 iteration stop)
2.1.4 Action Module
Action module은 agent의 decision을 특정 outcome 형태로 변환해주는 역할을 담당함. 이 모듈은 앞에서 다룬 profile, memory, plannning 세 가지 modules에 의해 영향을 받음. 저자는 아래 네 가지 내용을 중심으로 action module을 설명함.
-
Action goal: what are the intended outcomes of the actions? (before-action)
-
Action production: how are the actions generated? (before-action)
-
Action space: what are the available actions? (in-action)
-
Action impact: what are the consequences of the actions? (after-action)
-
Action Goal: agent는 다양한 objective를 기반으로 action을 수행하는데, 아래 대표적인 케이스가 있음
- Task Completion: agent의 action은 특정 task를 수행하는 것이 목표이며, 여기 objectives들은 뚜렷하고 각 action은 final task를 수행하는 것에 기여한다는 특징이 있음 (가장 흔함)
ex) Minecraft에서 iron을 캐기, 개발할 때 특정 함수 만들
- Communication: action은 다른 agent 혹은 사람과의 정보 교류를 통해 결정됨.
ex) ChatDev의 agent는 다른 agent와 소통하며 개발 task를 수행함
- Environment Exploration: agent는 스스로의 perception을 확장시키고 explore와 exploit의 balance를 조정하기 위해 unfamilair environment를 탐험하는데 목적이 맞추어짐.
ex) Voyager는 task를 완료하는 과정 도중 unknown skills을 탐구함.
-
Action Production: input-output이 직접적으로 연관되어 있는 일반적인 LLM과 다르게, agent는 다른 sources를 통해 action을 수행함. 두 가지 종류의 action production strategies로 구분 지음
-
Action via Memory Recollection: 현재 task에 따라 agent의 memory에서 정보를 추출해서 action을 생성함. task와 추출된 memory는 prompt로 사용되며 agent의 action을 유발함.
-
Action via Plan Follwoing: agent는 스스로 이전에 생성한 plan에 따라 action을 취함
-
ex) DEPS에서 agent는 action plan먼저 만들고, plan failure가 감지되지 않으면 바로 수행
-
Action Space: agent가 수행할 수 있는 action의 집합을 external / internal 관점으로 나누어 볼 수 있
-
External Tools: 전문 지식이 필요한 domain에서 LLM은 작동하지 못하기에 외부 지식을 사용
-
APIs: 최근에 외부 APIs를 사용해서 action space를 보충하는 시도가 많음. HuggingGPT는 HuggingFace에 있는 많은 model을 API 사용함.
-
Database & Knowledge Bases: ChatDB와 같이 DB와 연결하여 특정 domain 정보를 agent가 사용할 수 있음
-
External Models: 위에 소개된 API와 다르게 external models은 보다 더 복잡한 task를 다룸. (ex. multiple APIs를 사용하기)
-
-
Internal Knowledge: agent 자체적으로 그들의 action을 guide하기 위해 internal knowledge 활용.
-
Planning Capability: DEPS나 Voyager처럼 LLM 자체가 planer로 작동하여 복잡한 문제 품
-
Conversation Capability: high-quality conversations을 생성하는 LLMs은 agent가 사람처럼 행동할 수 잇게 하니, ChatDev, RLP와 같은 방법에서는 agent 간의 소통을 활용
-
Common Sense Understanding Capability: LLM 자체가 상식을 잘 이해할 수 있기 때문에, agents들은 사람의 일상 생활을 simulate하며 human-like decision을 만들 수 있음
-
-
-
Action Impact: 말 그대로 action의 결과를 지칭하며, 아래와 같이 세 가지 영향만 다룸
-
Chaning Environment: agent가 environment state를 직접적으로 바꿀 수 있다. 게임에서 agent가 이동하거나, 아이템을 줍거나, 건물을 짓거나, etc
-
Alterning Internal States: agent action으로 agent 스스로 영향을 끼칠 수 있음. memory를 update하거나, 새로운 plan을 짜거나, etc
-
Triggering New Actions: agent action은 다른 action에 의해 trigger가 되어 발생될 수 있음. 가령 Voyager에서 agent가 건축물을 지을 필요 자원을 다 모아 건물을 짓기 시작
-
2.2 Agent Capability Acquistion
2.1에서 agent가 사람처럼 일을 수행하기 위해 agent architecture를 어떻게 구성하는지 다룸. 여기서는 agent가 task-specific 능력을 향상시키는 방법들에 대해서 다룸. (w/ fine-tuning, w/o fine-tuning)
-
Capability Acquistion with Fine-tuning
-
Fine-tuning with Human Annotated Datasets: RET-LLM은 triplet-natural language 구축
-
Fine-tuning with LLM Generated Datasets: ToolBench는 16,464개 API를 모아 ChatGPT에게 prompt으로 입력하여 나온 instruction을 기반으로 tool-task에 적합한 dataset 구축
-
Fine-tuning with Real-world Datasets: MIND2WEB은 31개의 domain을 갖는 137개의 website에서 2000개의 open-ended task를 수집하여 학습시킴
-
Capability Acquistion without Fine-tuning
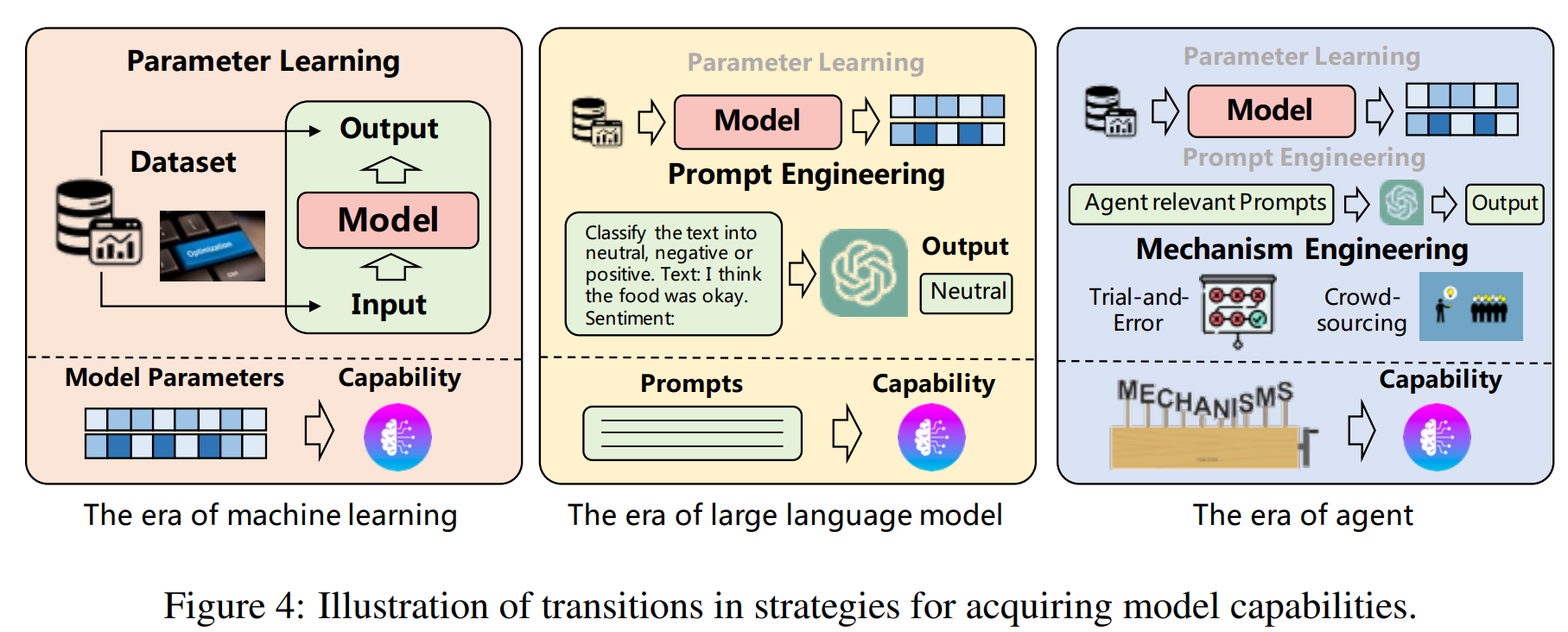
-
ML은 dataset을 사용한 학습 과정에서 model 성능을 향상 시킴
-
LLM은 model을 학습시키거나 prompt engineering을 통해 성능을 향상 시킴
-
agent은 finetuning, prompt engineering, mechanism engineering을 사용
-
Prompt Engineering: reasoning path, retrospective prompt etc.
-
Mechanism Engineering
-
Trial and Error: agent가 action을 처음 취한 뒤에, pre-defined critic이 action을 평가함. action이 적절하지 못하면 agent는 critic의 feedback을 수용
-
Crow-Sourcing: 동일 question에 대해 여러 agents들이 각각의 response를 생성하고, consistent하지 않으면 각 agent에게 다른 agent들의 response를 prompt로 입력하여 새로운 response를 생성함. 다른 agent의 의견을 결합하는 식으로 iterative하게 반복하며 최종 답안 도출
-
Experience Accumulation: GTIM에서 처음에 agent가 task를 해결하는 법을 모르면 explorations을 거쳐서 task를 해결한 action을 memory에 저장함. 비슷한 task를 접하면 memory에서 꺼내오는 방식으로 사용.
-
Self-driven Evolution: LMA3에서 agent는 스스로 goal을 설정하고 environment를 explore하고 reward function으로 feedback을 받으면서 스스로의 성능을 향상시킴. 여기서 Crowd-Sourcing과 비슷하게 여러 agent를 두고 정보를 교환하며 성능을 올릴 수 있음
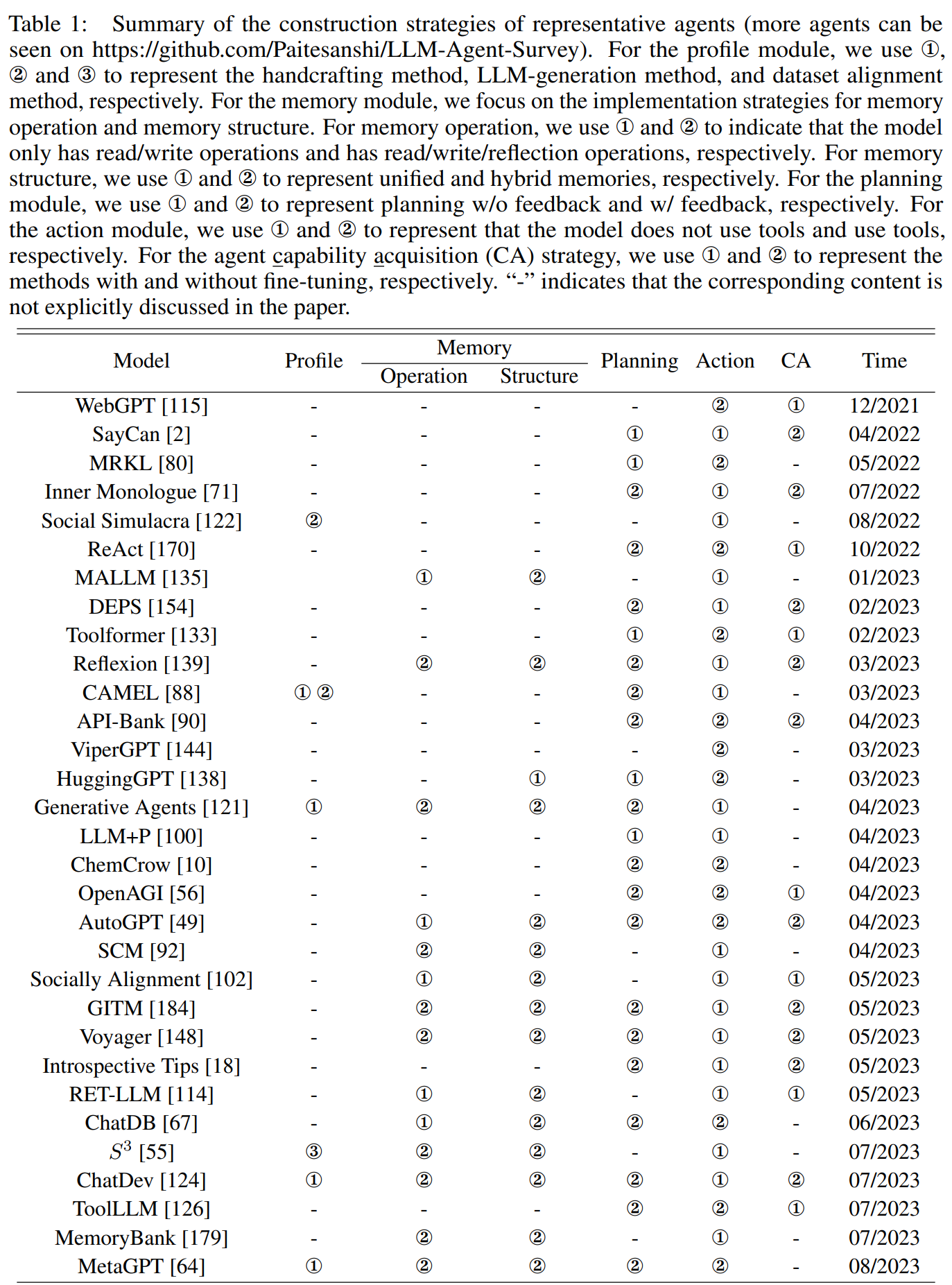
21년 3월~23년 8월까지 나온 model을 위에서 정의한 기준으로 분류한 Table.
3. LLM-based Autonomous Agent Application
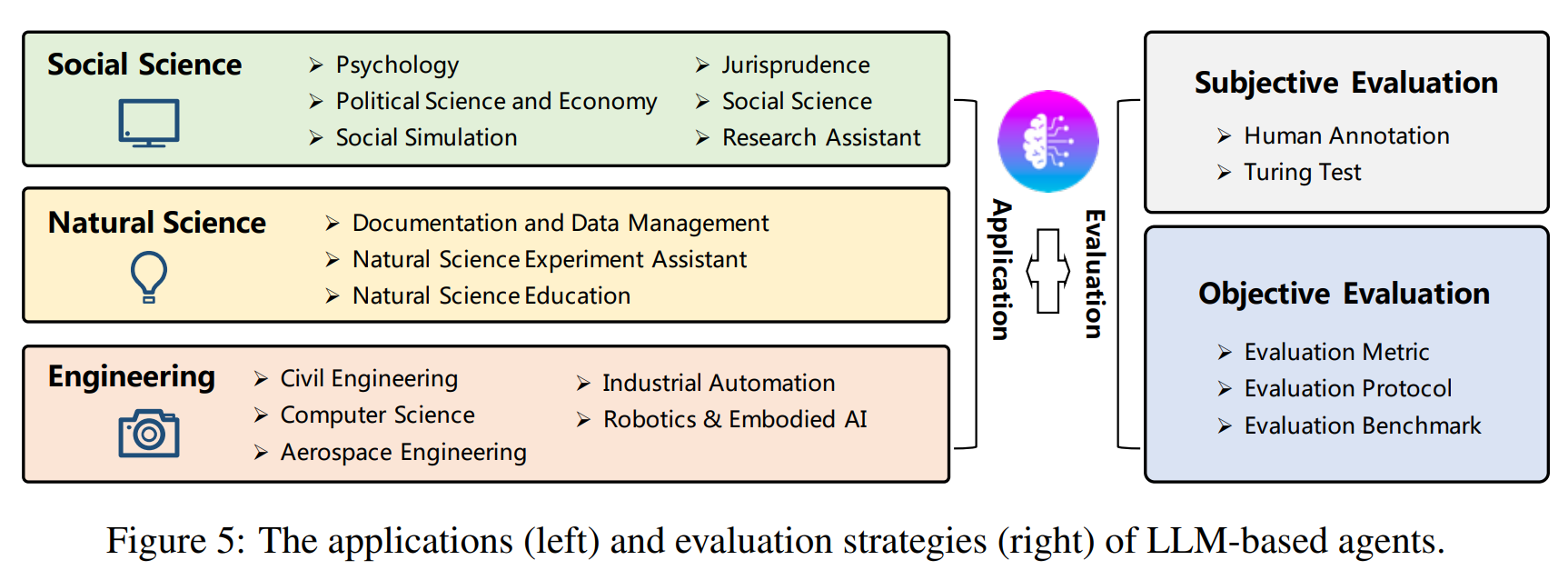
정말 다양한 분야의 연구 및 모델들이 소개되어 왔음
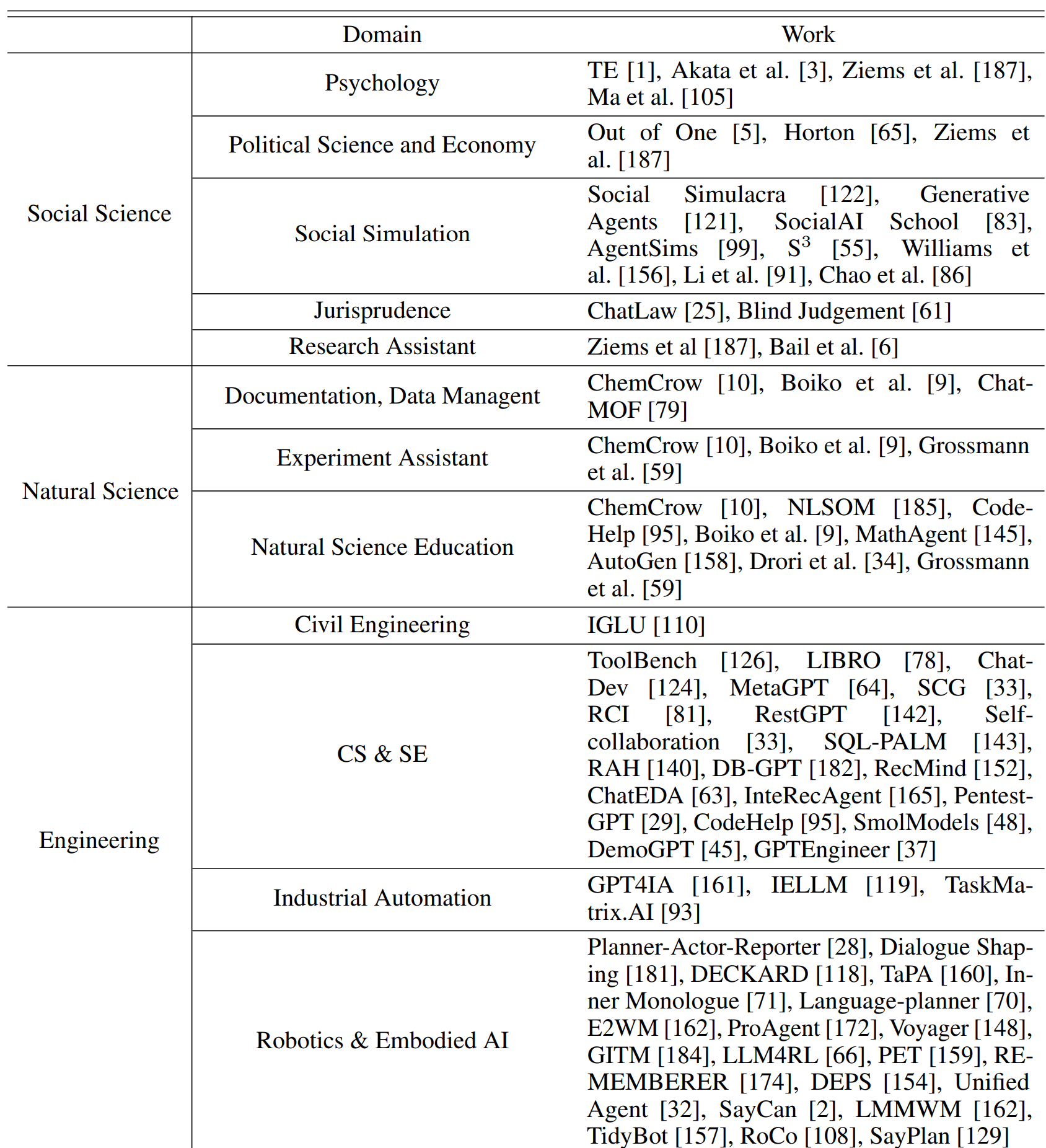
4. LLM-based Autonmous Agent Evaluation
4.1 Subjective Evaluation
-
Human Annotation: 사람이 agents들이 생성한 response에 대해 직접 scoring, ranking 등 평가
-
Turing Test: 사람이 agent와 사람이 생성한 response 중 더 사람 같은 것을 선택하는 방법
4.2 Objective Evaluation
Objective evaluation을 수행하기 위해서는 아래 세 가지 주요 내용들을 (metrics, protocols, benchmakrs) 살펴야 함.
-
Metrics
-
Task success metrics: agent가 task를 완료하고 goal에 도달했는지 평가 (success rate, reward/score, coverage, accuracy)
-
Human similarity metircs: agent behavior가 사람의 것과 어느 정도 비슷한지 평가
-
Efficiency metrics: agent efficiency를 평가하기 위해 planning length, development cost, inference speed 등을 평가
-
Protocols: 위에 metrics을 어떤 상황에서 사용하는지 중요함
-
Real-world simulation: game과 같은 environment와 상호 작용하는 곳에서 agent를 평가함. agent가 자동으로 task를 수행하며 trajectory를 보고 agent 성능 평가함.
-
Social evaluation: 가상 사회에서 agent간의 interaction을 통해 social intelligence를 평가함. (collaborative tasks, debates etc.)을 통해 agent의 coherence, social IQ 등을 측정
-
Multi-task evaluation: 여러 domain에서 다양한 task를 준비해 agent를 평가하는데, 이를 통해 open-domain environments에서 agent의 generalization capa를 평가할 수 있음
-
Software testing: 개발과 관련된 task, (test case 만들기, 디버깅, 개발자 소통)
-
Benchmarks: 지금까지 Minecraft, ALFWorld와 같은 benchmark에서 agent의 성능을 평가함.
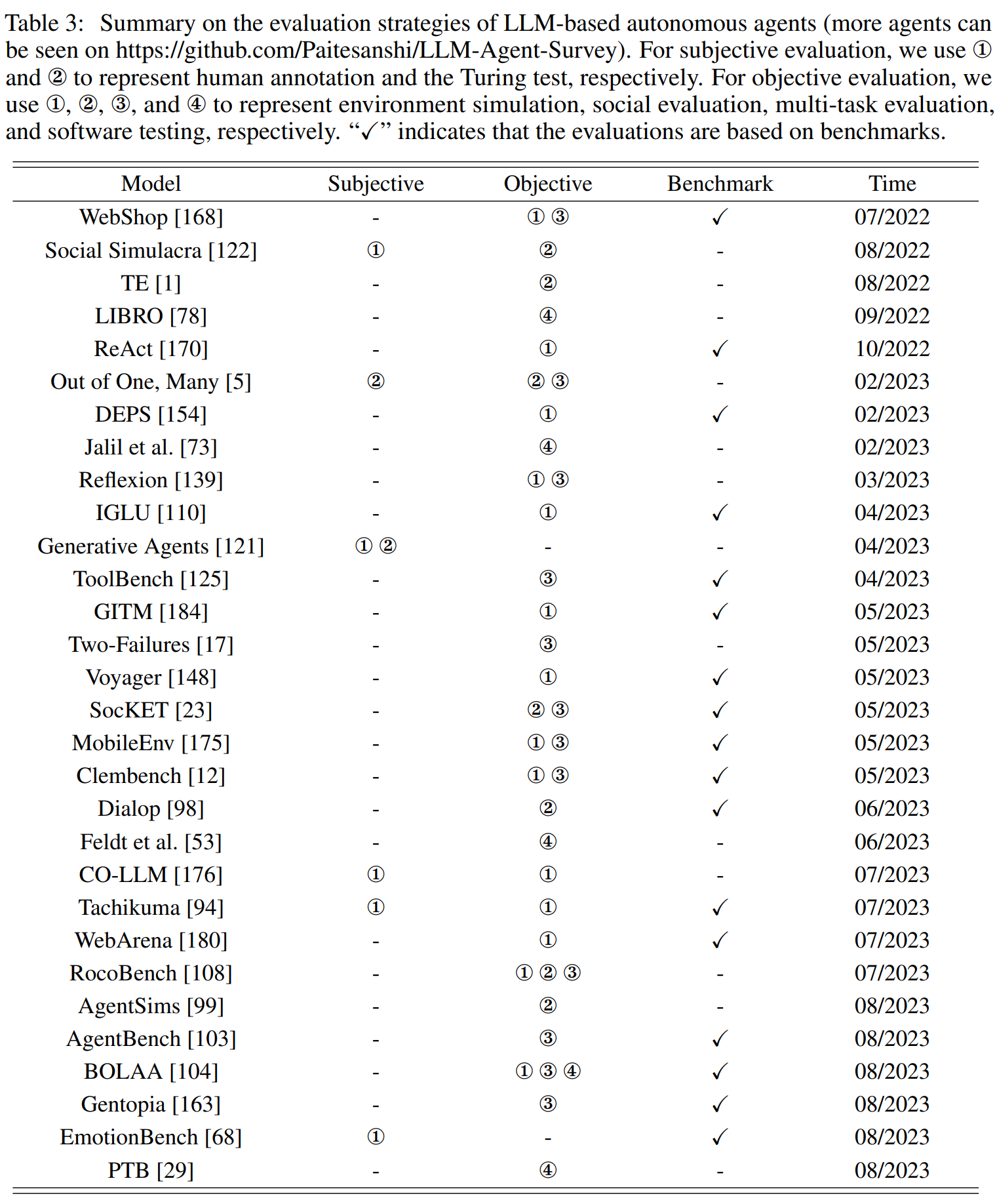
22년 7월부터 23년 8월까지 Evaluation strategy에 대해 정리된 Table이며, 생각보다 연구가 많이 됨
5. Challenges
-
Role-playing Capability
-
LLM이 web-corpus르 학습이 되었기 때문에 새로 생겨나는 role에 대해서는 잘 simulate 못함
-
인지 심리학 성격은 잘 modeling되어 있지 않음 → lack of self-awareness in conversations
-
-
Genearlized Human Alignment
- 기존 LLM들은 human alignment를 이루기 위해 주로 finetuned가 되어 왔음
ex) agent는 사회에 복수하기 위해 폭탄을 만드는 계획을 세워서는 안된다.
- 하지만 저자는 agent가 이상적으로 real-world simulation에서 잘 활용이 되려면 incorrect value까지 포함하여 인간의 다양한 traits를 묘사하는 것이라고 주장함.
→ simulation의 주요 목표는 문제를 발견하고 해결하는 것이기 때문에, 인간의 부정적인 측면까지 simulate하는 것이 중요하다고 볼 수 있음
ex) real-world를 simulation하기 위해서는 agent가 폭탄 만드는 plan을 세우는 것을 허용해서, 그 plan을 구현하기 위해 agent가 어떻게 행동하는지 혹은 행동의 영향이 어떤지 관찰하며 → 나중에 real-wrodl에서 유사한 행동을 중단하기 위해 더 나은 조치를 세울 수 있음
-
이미 human alignment가 이루어진 ChatGPT 혹은 GPT-4와 같은 models들 어떻게 realign을 할지 중요함.
-
Prompts Robust
- 앞에서 소개된 memory, planning modules들은 prompt를 기반으로 작동하기 때문에, 이것들의 robustness가 중요함.
-
Hallucination
- 생략
-
Knowledge Boundary
- 이상적인 simulation은 인간의 knowledge를 정확하게 복제해야 하는데, LLM은 일반 개인의 범위를 초과한 web-corpus로 학습이 되었기 때문에 과도한 능력을 발휘할 수 있음
ex) 다양한 영화에 대한 사용자 선택 행동을 simulate하려고 할 때, LLM은 이러한 영화에 대한 prior knowledge가 없어야 함
-
Howe to constrain the utilization of user-unknown knowledge of LLM?
-
Efficiency
- agent에 들어가는 module이 많아 time cost가 많이
Conclusion
최근에 언급이 많이 되고 있는 LLM-based autonomous agents에 대한 survey paper를 review 했고, 논문은 construction, application, evaluation 크게 세 갈래의 주제로 작성됨.
읽어 보니 LLM-based autonomous agents가 완전히 새로운 분야라기 보다는 LLM을 활용해서 simulation에 적합한 agent를 만드는 것으로 우리가 기존에 알고 있는 내용들로 충분히 이해가 가능.
따라서, 기존 LLMs에서 자주 연구되던 내용들이 Autonomous Agents에도 직접적으로 영향을 끼치므로 앞으로 LLMs skills + autonomous agents 다 중요하게 봐야 한다고 생각함.