FALSESUM : Generating Document-level NLI Examples for Recognizing Factual Inconsistency in Summarization
논문 정보
- Date: 2023-04-20
- Reviewer: 전민진
-
Property: Text summarization, Data augmentation
-
Abstract
-
abstractive summarization model의 경우 원문과 factually inconsistent한 요약을 생성하는 경향이 있음
-
이전까지는 이러한 factual inconsistency를 인식하는 task를 NLI의 downstream application으로 소개
-
하지만 SOTA NLI model도 target task에 일반화할 수 있는 능력이 부족해, 위의 task에서는 성능이 좋지 않음
-
본 논문에서는 training data을 task에 맞춰서 augmented해 NLI모델이 이 task에 효과적일 수 있다는 사실을 밝힘
-
FALSESUM: data generation pipeline leveraging a controllable text generation model to perturb human-annotated summaries, introducing varying types of factual inconsistencies
- 이전에 소개된 document-level NLI dataset과 달리, 본 연구에서 생성한 데이터셋은 다양하고 inconsistent하지만 plausible한 데이터들을 포함함
-
-
FALSESUM-augmented NLI dataset에 학습한 모델이 factual inconsistency를 감지하는 task에서 SOTA 달성
-
-
Introduction
-
NLI dataset의 경우 abstractive summarization에서 자연스럽게 발생하는 entailment 현상만 포착하고 있지 않음
-
또한, 우선 input granularity의 관점에서 discrepancy가 존재
- 예를 들어, consistency classification task에서 premise는 여러 문장으로 이뤄져 있지만(원문), 보통의 NLI dataset에서는 한문장의 premise를 가지고 있음
-
본 논문에서는 이러한 차이를 해소하고자, document와 gold summaries가 positive pair로, 생성된 inconsistent summaries와의 pair를 negative examples로 하는 NLI dataset을 만드는 data generation pipeline, FALSESUM을 제안
- 여기서 inconsistent summaries를 만드는 generator에서 생성된 output에서 보이는 factual error의 type을 결정하는 input control codes을 변경할 수 있음
-
본 논문의 contribution은 다음과 같음
-
document, gold summary pair를 input으로해 factually inconsistent한 summary를 만드는 novel한 training pipeline을 제안
-
이렇게 생성한 dataset의 유용함을 증명
- 사람이 쓴 요약문이랑 구별하기 어려우면서, 있을법한 inconsistent summary
-
-
-
Related Work
-
ground-truth summary text와 generated summary에서 relation tuples를 추출하는 information extraction model을 사용해 overlap되는 부분을 세서 factuality의 지표로 씀
-
QA모델을 바탕으로 document와 summary를 context로 사용해 predicted answer를 매칭함으로써, factual inconsisteny를 감지하도록 함
- 같은 질문에 대해 summary를 context로 줬을 때, document를 context로 줬을 때, 요약이 doucment와 factually consistent하다면 유사한 답변이 나올거라고 가정
-
factually consistency문제를 NLI로 해결하려 함
-
NLI model을 바탕으로 entailment label에 배정될 확률을 사용해 summary candidates를 re-rank
- 하지만 consistency error가 개선되진 않았음
-
inconsistency detection을 binary classification setting으로 두고 NLI모델을 바로 사용했을 땐, 다수결보다 조금 나은 성능을 보임
-
FactCC - transformation rules(sentence negation, entity swappinng 등)을 바탕으로 inconsistent summary의 example을 얻는 synthetic NLI data generation process
-
NLI모델이 여러 summarization model의 결과를 manully annotating해 얻은 현실 test case에 대해 좋은 성능을 보임
-
하지만 rule-based 특성 때문에 다양한 consistency error type을 만들진 않고, 더 abstractive할 수록 error distribution이 잘 align되지 않음
-
-
-
-
FALSESUM Approach
-
Design Overview
-
input으로 source document D와 그에 따른 reference sumary S+를 input으로 받음
-
이후 preprocess와 format과정을 거쳐서 나온 D와 S+를 generation model G에 넣음
- G의 결과는 factually inconsistent summary S-
-
각 summarization example에 대해서, positive와 negative NLI를 가짐
- (D, S+, Y=1), (D, S-, Y=0)
-
FALSESUM의 목표는 S+와 대조되는 자연스러운 S-를 만드는 것
-
즉, S+와 S-는 표면적인 특징에서는 구별 불가능해야함(style, length, vocabularies)
-
오직, D에 관해서 factual consistency만 달라야 함
-
-
이는 NLI모델이 surface feature를 기반으로 구별하는게 아니라 정확한 factual consistency의 개념을 학습하게 함
-
또한, 자연스러움에 더불어 다양한 consistency error type이 나오도록 해야함
-
consistency error typology를 바탕으로 error를 크게 2가지로 분류
-
intrinsic : source document에서 잘못된 정보 통합으로 인한 오류
-
extrinsic : source document에서 직접적으로 추론할 수 없는 새로운 정보를 가정함으로써 발생하는 오류
-
-
-
-
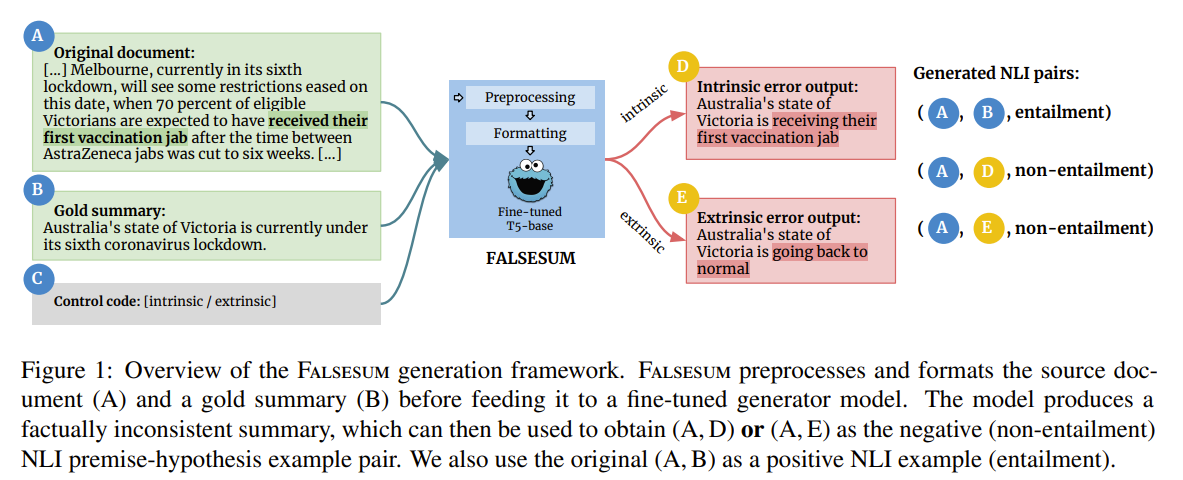
- 위 그림과 같이, generation model G는 summarizatoin model의 consistency mistakes를 모방하도록 학습
- source document에서 잘못된 정보를 original summary의 random span에 삽입
- summary에 source document에 없는 새로운 fact를 넣음
- 이를 위해, framework는 generator에서 이용가능한 source document의 information이나 fact가 무엇인지, 어디에 틀린 정보가 gold summary에 삽입될 수 있는지를 식별해야하는데 이를 input preprocessing과 formatting 단계를 수행
- 모델 G를 학습하는 seq2seq 태스크를 다음과 같이 정의
- Given a list of shuffled and formatted pieces of information extracted from source document and gold summary and a partially masked gold summary, fill in the blanks and generate the original gold summary
-
Input Preprocessing
-
source document와 gold summary에 있는 fact는 OpenIE tuple로 정의될 수 있음
-
문장에서 찾은 predicate와 argument structure를 표현
-
각각의 relation tuple를 (ARG_0, PRED, … , ARG_n)으로 표기
-
PRED는 event를 표현(What happend), ARG는 event의 who, to whom, where, how를 나타내는 semantic argument를 표현
-
즉, predicate는 보통 clause의 핵심 동사
-
predicate와 argument는 token의 span을 구성
-
-
-
-
OpenIE를 사용해 source document와 reference summaries에서 relation tuple를 추출
-
랜덤하게 tuple에서 argument하나를 선택, 제거해 추출한 “fact”를 corrupt시킴
- 멀쩡한 fact가 generation model에 들어갈 경우, consistent한 summary를 만들 수 있음
-
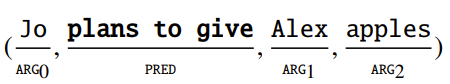
- 예를 들어 위와 같은 relation이 있다고 하면, 랜덤하게 apple를 선택해서 tuple에서 제거해 버림
- 혹은 각 argument와 predicate span의 dependency root word를 lemmatize
- e.g., plans to give ⇒ plan to give
- 이렇게 하면 모델이 grammaticality에 대한 correct를 학습할 수 있음
- 모든 span이 추출되고 처리되면, 2개의 list로 grouping하고 shuffle
- predicates와 argument에 대한 list
-
Input Formatting
-
P = (PRED_1, … , PRED_n), A = (ARG_1, … , ARG_m)
- sorcue document D와 summary sentence S+에서 추출한 unordered list
-
여기에 masked summary sentence M, control code variable c \in {extrinsic, intrinsic}
-
Generator G는 p(S+ P,A,M,c)를 계산하도록 학습됨 -
모든 conditional variables를 다음과 같은 format으로 encode
- Predicates: P; Arguments: A; Code: c; Summary: M
-
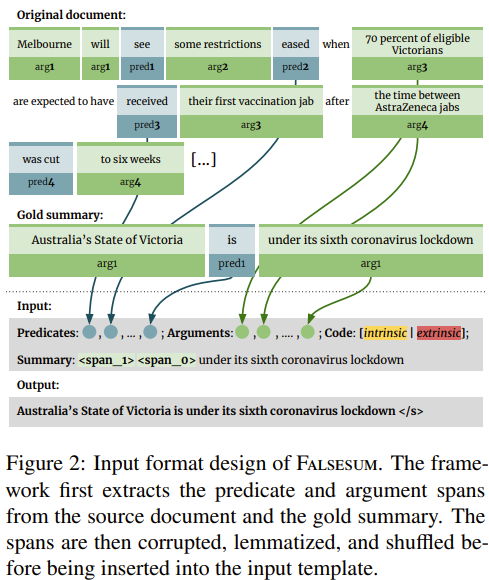
- step 1 : Span Removal(핵심 span삭제)
- 처음엔 gold summary에서의 predicate, argument span을 포함하고, 이를 사용해 S+를 reconstruct
- 하지만 test time땐, gold span을 제거해 G가 consistency mistake를 하도록 유도
- 혹은 control code extrinsic으로 G를 학습할 때도 제거
- 그럴듯한 unseen span을 예측하도록
- gold summary에 있는 pred, arg가 input document에도 있을 수 있는데, 이 경우 간단한 휴리스틱을 통해 제거
- step 2 : Span Reduction(랜덤 span 삭제)
- G가 fine-grained error을 생성하도록 하기 위해, incorrect modifier를 P와 A의 span으로 hallucinate하도록 학습
- 완전하지 않은 list를 바탕으로, 그럴듯하게 만들기 때문인 것으로 추청됨
- 이를 위해, gold predicate와 argument span의 10%정도 랜덤하게 adjectives와 adverbs를 drop
- 예를 들어, “recently elected prime minister”이라는 argument span이 있을 때, 여기서 minister를 제거
- 이를 통해, 모델이 formatted input만 context로 제공될 때, span의 남아있는 부분을 생성하도록 함
- step 3 : Control Code
- G에서 생성된 consistency error의 종류를 control하기 위해, “code:”라는 string을 다음에 “intrinsic” 혹은 “extrinsic”을 input token에 추가
- 이 코드는 0.5의 확률로 랜덤하게 선택됨
- 코드가 선택되고 나면 아래 그림(table 1)과 같이 남은 formatting step을 수행
- step 4 : Sumamry Masking
- 랜덤하게 선택된 predicate와 argument의 span을 special token로 교체해 masked summary M을 만듦
- special token <span_i>, where i = 0 is reserved for the predicate and i > 0 for their arguments
- 이러한 token들은 generator model에 의해 original sumamry에 틀린 정보가 삽입되도록 함
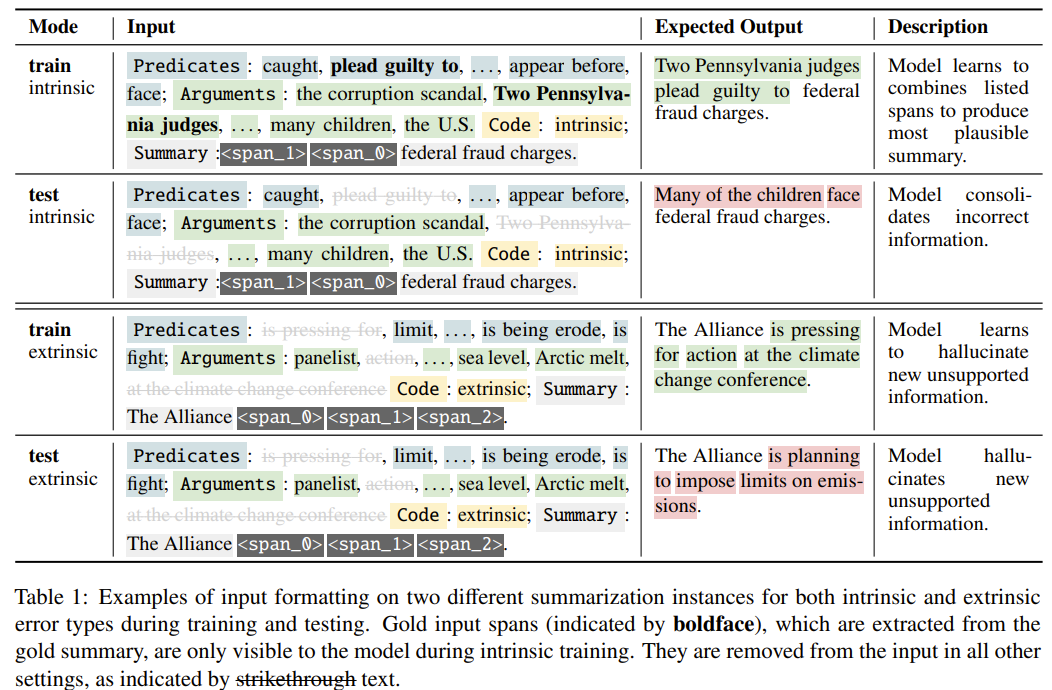
- gold input span은 intrinsic training할 때만 볼 수 있음
- 위의 표를 보면, intrinsic을 학습할 때는 summary를 randomly masking해 주어진 listed spans를 통합해 그럴듯한 요약문을 생성하도록 함
- 이와 달리 extrinsic을 학습할 때는, gold input span을 삭제함에도 원문 요약을 생성하게 함으로써, hallucinate을 유도
- test시에는 두 가지 code 모두 gold span삭제 후 생성
-
Training FALSESUM
-
CNN/DM corpus의 train split에 대해 FALSESUM data generation pipleline을 학습
-
CNN/DM은 원래 QA를 위해 데이터를 수집했지만, summarization으로 reformulated됨
-
dataset은 영어 기사와 사람이 쓴 요약문이 pair로 존재, 각각은 여러 문장으로 구성됨
- summary를 한 문장씩 쪼개서 document text and a single sentence summary의 pair로 만듦
-
각 document-summary pair에 대해 preprocessing과 formatting 단계를 거침
-
formatted된 input과 target output의 pair는 train 394774, test 262,692개
-
-
T5-base모델을 사용해서 G를 seq2seq task에 fintuning
-
“Given (♦i) a list of shuffled and formatted pieces of information extracted from source document and gold summary and (♦ii) a partially masked gold summary, fill in the blanks and generate the original gold summary.”
- **fine-tune된 generator를 사용해 전처리되고 포맷팅 된 test split에 대한 NLI example를 생성**
- 본 논문의 실험에서는 100,000개의 FALSESUM example를 샘플링해 NLI dataset을 보강(augmented)
-
Experimental Settings
-
FALSESUM-generated document-level examples for NLI dataset augmentation의 효과성을 입증하는게 목표!
-
NLI 모델의 downstream performance를 평가하기 위해 generated summaries의 factual inconsistency를 결정하는 여러 벤치마크들과 비교
-
Training
-
NLI models
-
RoBERTa-base를 MNLI에 fine-tuning
-
MNLI dataset는 392702개의 train instances로 각 라벨은 entailment, neutral, contradiction 중에 하나로 되어 있지만, NLI data의 application을 가능하게 하기 위해 binary formulation을 사용해 neutral, contradiction을 non-entailment로 통합
- sentence pair로 구성되어 있음
-
-
Document-lebel NLI dataset
-
augmentation 비교를 위해서 요약 혹은 news 도메인의 multi-sentence NLI dataset사용
-
ANLI : 대부분 Wiki data, 소수의 news text로 구성됨. paragraph-level NLI dataset.
-
DocNLI : QA examples 혹은 news summaries을 NLI로 번형한 데이터셋. news summaries의 단어와 문장을 LM을 사용해서 교체. document-level NLI dataset
-
-
-
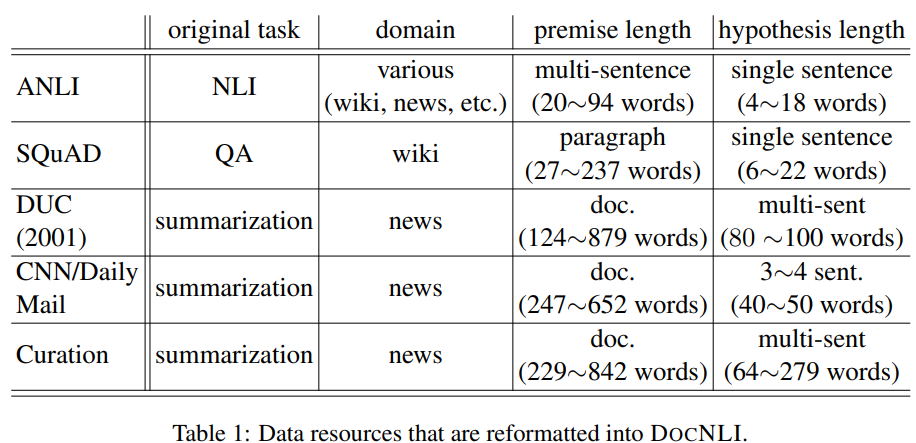
- FactCC : summary factual correctness classification model을 학습하기 위해 생성된 large-scale dataset. FactCC의 positive는 CNN/DM의 news story를 back translation해서 만듦. negative는 predefined rules를 사용해 sentence를 perturbing.
- 형평성을 위해 랜덤하게 100000개의 데이터만 샘플링 해 사용
-
Benchmark Datasets
-
NLI model을 평가하기 위해 abstractive summaries의 factual consistency를 분류하는 4가지 벤치마크에 사용
-
기존에 consistent, inconsistent로 라벨링 되어있던 것을 NLI모델을 평가 하기 위해 entailment, non-entailment로 mapping
-
FactCC : 1431개의 document와 single-sentence summary pair로 구성됨. CNN/DM에 대해 학습한 abstractive summarization모델이 생성한 summary를 사용.
-
Ranksum : 107개의 문서와 sumamrization model이 beam search로 생성한 5개 순위의 summary candidates가 pair로 구성됨. task는 list를 re-rank하는 것으로 top-1 summary가 factually consistent함
-
Summeval : 7개의 extrative model이 생성한 summaries와 16개의 abstractive model이 생성한 summaries를 포함. 각각은 3명의 notator가 5-Likert scale를 사용해서 consistency를 판단. 5점일 경우에만 consistency하다고 라벨링.
-
QAGS : XSUM에서 239개의 test set instances과 CNN/DM(multi sentence summaries를 single-sentence summary test instance로 쪼갠 후의 개수)에서 714개의 instences로 구성된 dataset. 각 instance는 source document와 single-sentence summary의 pair로 구성되어 있고, 다수의 annotator가 선택한 label이 data의 label이 됨
-
-
Results and Discussion
-
Main Results
-
FactCC, QAGS, SummEval에 대한 성능은 balanced accuracy를 사용해 측정됨
-
balanced accuracy는 class imbalanced settings에 적합한 방식
- consistency에 대한 acc와 inconsistency에 대한 acc를 평균내 계산
-
몇몇 벤치마크 데이터셋에서는 consistentcy가 다수의 라벨이기 때문
-
다수의 label에 대한 voting이 50%의 점수만 얻도록 2 class의 average recall로 정의됨
-
라벨 각각에 대한 예측률의 평균
-
-
Ranksum에서 ranking performance를 측정하기 위해서, average Precision@1을 계산
-
각 test instance에서 factually consistent summary가 가장 높은 순위를 차지한 비율
-
모델이 매긴 순위를 바탕으로, 1위가 실제로 consistency라벨인 경우
-
-
random seed 5개에 대한 성능을 평균내서 사용
-
-
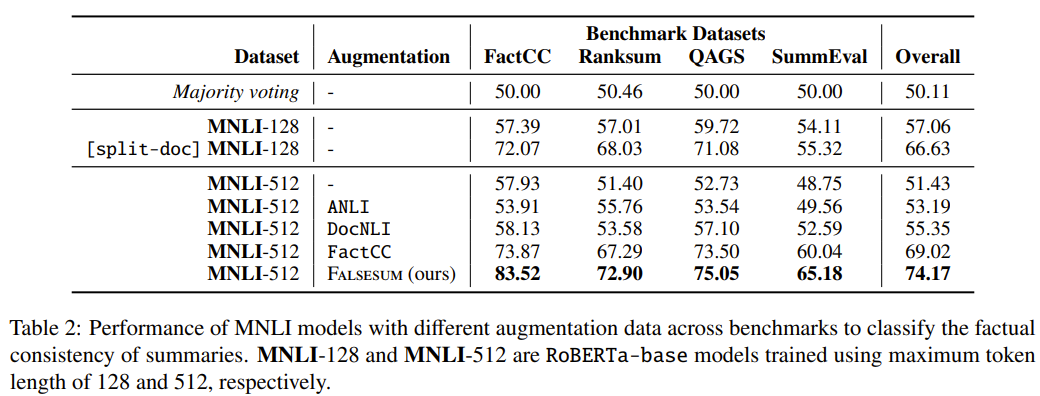
- FALSESUM을 사용해 학습한 모델이 제일 좋은 성능을 냄
- sentence-level MNLI dataset로 학습한 모델의 경우 max-seq을 128에서 512까지 늘려도 document-level benchmark에서는 성능이 안좋음
- 하지만 document를 문장별로 쪼개서 sentence-wise prediction을 하면 나아짐(하지만 계산량이..)
- 다음과 같은 방식으로 classification
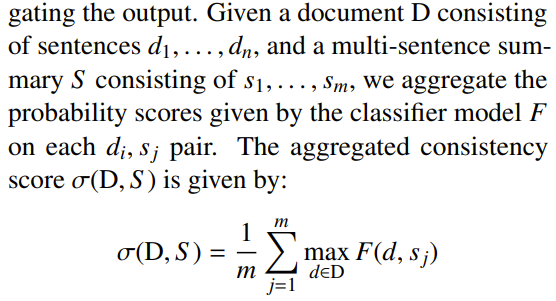
- DocNLI와 ANLI는 더 긴 premise sentences를 가지고 있지만 성능이 좋지 않고, 이는 length match가 주요한 원인이 아님을 보임
-
Ablation Anaysis on FALSESUM Data
-
NLI examples에서 얻은 (D,S+)에서 constrative property를 제거하기 위해 positive 혹은 negative 둘 중에 하나를 제거하거나, negative pair만 가지고 type에 따라 dataset을 분류
-
이렇게 쪼갠 데이터를 -contrastive, -intrinsic, -extrinsic 으로 표기
-
각각의 학습 데이터는 100000개로 샘플링해서 맞춰줌
-
-
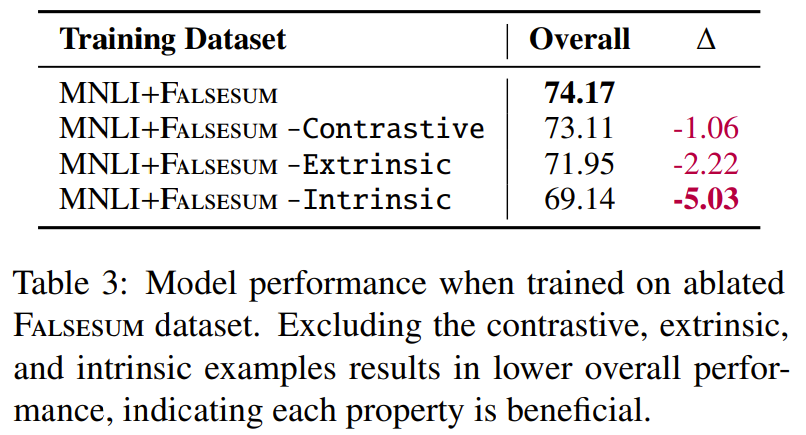
- 보면 intrinsic을 제거했을 때 가장 성능이 저하됨
- 즉, 벤치마크에서 intrinsic consistency error가 지배적이라는 걸 알 수 있음
-
Fine-grained Evaluation
-
이전 연구에 따르면, NLI모델은 entailment label을 lexical overlap과 연관시키는 안좋은 휴리스틱을 가지고 있음
-
factual consistency task에서 모델이 highly extrative summaries을 consistent label과 연관시키는 것과 유사
-
과연 이러한 경향이, FALSESUM에서 줄어들었는지를 비교 분석
-
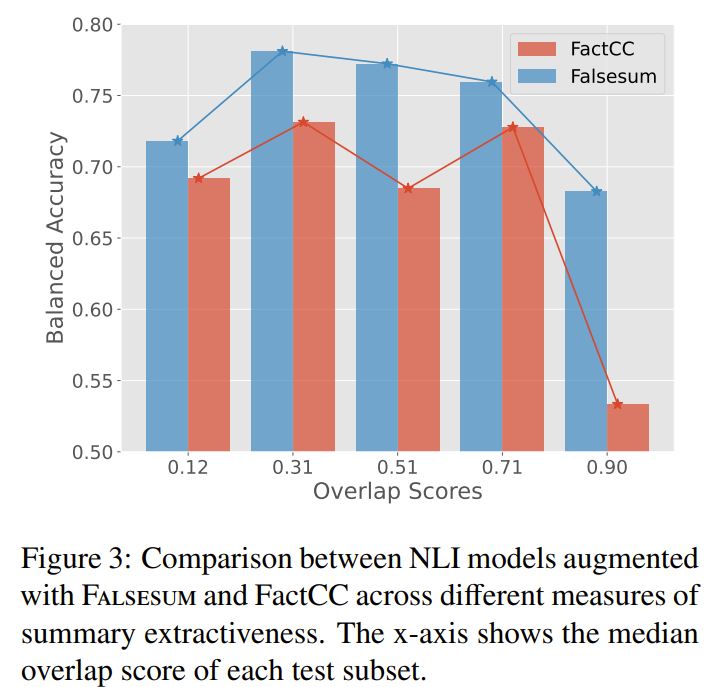
- 이를 위해 FactCC test examples을 lexical overlap정도에 따라 5가지로 분류, 각각의 balanced accuracy를 측정.
- overlap은 Normalized coverage and Density summary extrativeness score로 계산
- 1은 summary의 모든 단어가 source document에 존재함을 의미
- 즉 summary가 거의 source document의 일부를 copy해서 나온 결과라는 뜻
- overlap = normalized coverage x density로 계산
- 측정 결과, FALSESUM으로 학습한 모델이 모든 subset에서 우수, 특히 0.9 overlap subset에서는 큰 차이를 보임
- 즉, FactCC는 overlap정도가 심하면 모두 consistent하다고 예측해 majority voting performacne인 50%에 가깝다는 것을 알 수 있음
- 하지만 FALSESUM으로 학습할 경우, overlap정도와 상관없이 꾸준한 성능을 보임
-
Data Quality Analysis
-
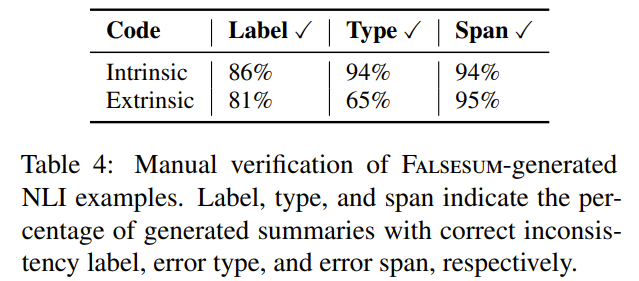
FALSESUM-generated dataset에서 manual, automatic quality evaluation을 진행
-
우선 200개의 negative example을 샘플링한 뒤, 직접 1) 이 요약이 정말 factually inconsistent한지, 2) consistent error가 지정한 control code와 맞는지 3) incorrect “fact”가 특정 missing span에 삽입되었는지를 확인
-
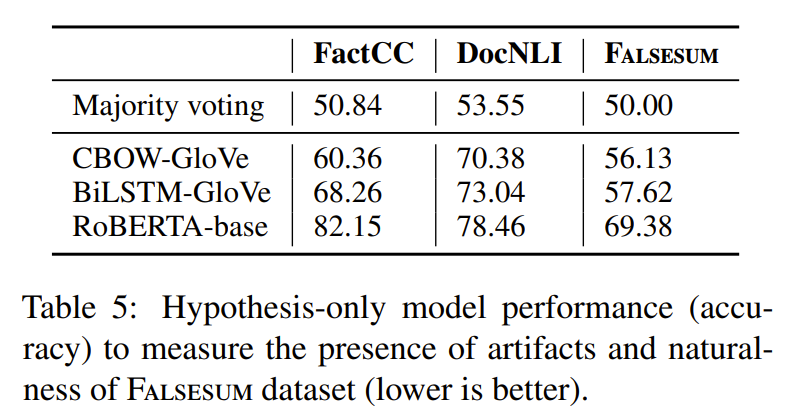
- 생성된 dataset의 자연스러움을 평가!
- CNN/DM의 positive examples과 FALSESUM의 negative examples을 사용해서 NLI model을 학습
- 모델은 premise없이 semantic plausibility 와 spurious surface features(예를 들면 문법적 오류나 유창성 오류)를 보고 entailed과 non-entailed hypotheses를 구별해야함
- FALSESUM에 대한 low acc를 보이는 것으로 보아 FALSESUM이 자연스러운 negative를 만든다는 것을 알 수 있음
-
Conclusion
-
FALSESUM이라는 data generation pipeline을 제안해서, large-scale document-level NLI dataset을 manual annotation없이 렌더링
-
본 논문에서 제안한 방법으로 더 자연스럽고 다양한 factually inconsistent summaries를 생성하도록 학습할 수 있었음
-
NLI dataset을 augmenting해 이를 바탕으로 학습한 모델이 4가지 summary factual inconsistency benchmark에 대해 SOTA를 달성함
-