Learning to Tokenize for Generative Retrieval
논문 정보
- Date: 2023-12-19
- Reviewer: 건우 김
- Property: Retrieval
Abstract
-
본 연구에서는 generative retrieval 계열의 방법으로 document semantics을 docids로 encoding하는 과정을 학습하는 GENRET을 소개함.
-
당연하게도 GENRET는 IR에서 SOTA를 보이고, 특히 unseen doc에 있어 높은 성능 향상을 보임.
Introduction
최근 Information Retrieval에서 generative retrieval을 활용하는 연구들이 많이 진행되고 있다. 우리가 흔히 알고 있는 dense retrieval 방법들과 다르게, generative retrieval은 end-to-end 방법으로 주어진 query에 대해 ranked list of docids를 LM이 생성하게 함.
docid를 할당하는 것은 document가 semantic space에 어떻게 분포되어 있는지 정의하는 과정이기 때문에 중요함. 이전에는 주로 title 혹은 URL과 같은 meta data를 사용하거나 off-the-shelf document embedding에서 clustering 결과를 활용하는 rule-based 방법을 사용해서 training에서 본 것들에 대한 document들은 잘 retrieving 했지만, 이것들은 ad-hoc하고 generalize 못하다는 단점이 있다.
위 문제를 해결하기 위해 연구를 진행함
-
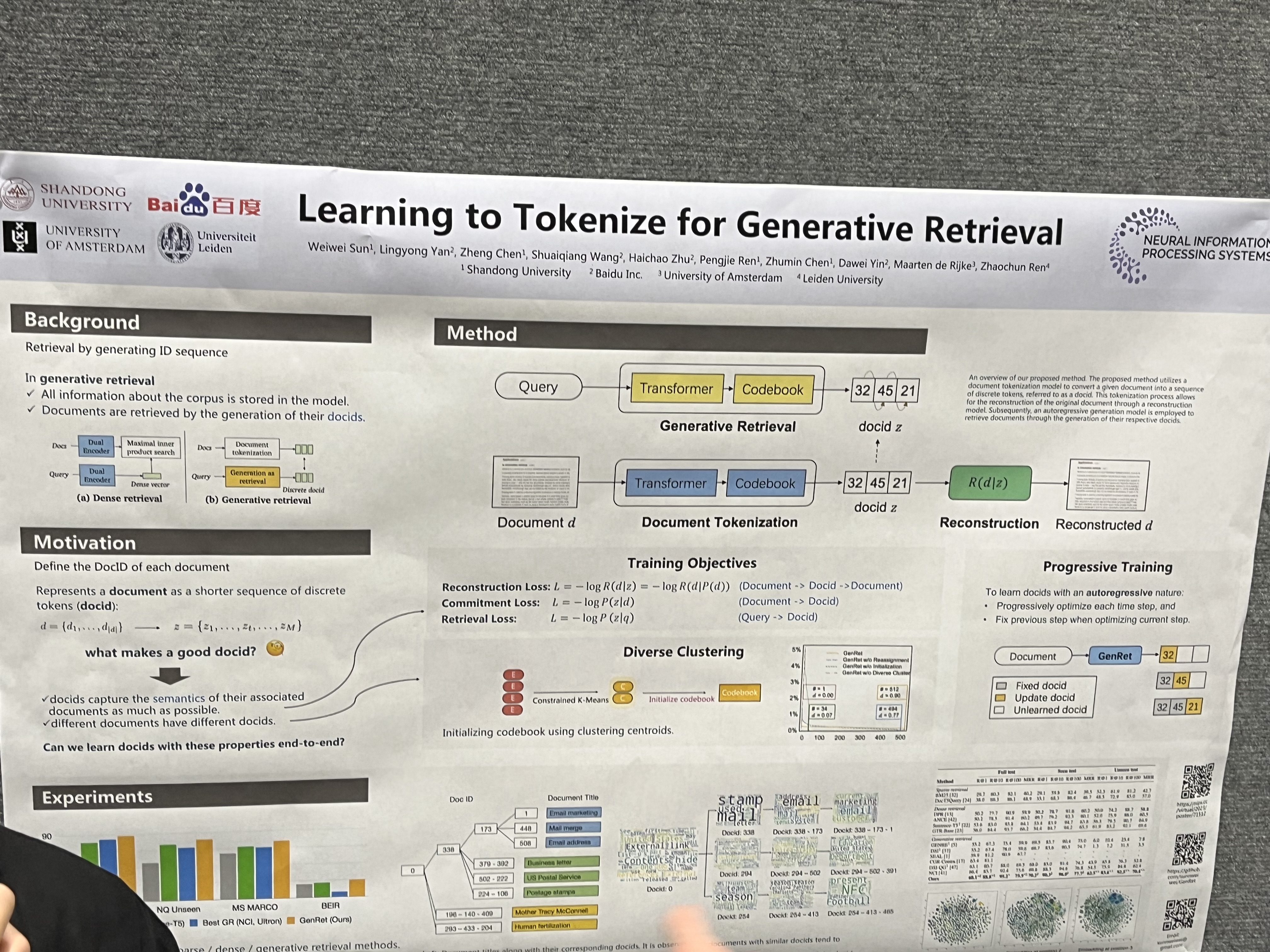
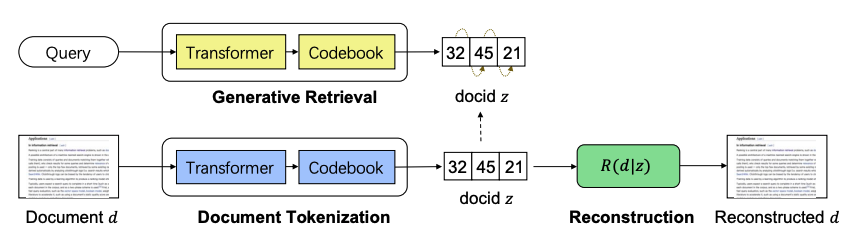
GENRET: a document tokenization learning framework that learns to tokenize a document into semantic docids in a discrete auto-encoding scheme
-
shared seq2seq-based document tokenization model
-
generative retrieval model
-
reconstruction model
-
-
auto-encoding을 이용하여 generative retrieval model을 optimize하는데 아래와 같은 issue 존재
-
docids with an autoregressive nature
- 이 문제를 해결하기 위해 progressive training scheme 제안
-
docids with diversity
- 이 문제를 해결하기 위해 parameter initialization strategy와 docid의 re-assignment 제안
-
-
Contributions
-
처음으로 tokenization learning method를 document retrieval에 적용한 GENRET 제안
-
학습의 안정화를 위해 progressive training scheme 적용
-
SOTA 달성 및 unseen documents에서도 잘 함 (dense retrieval baseline은 가볍게 부숨)
-
Preliminaries
document tokenization: generative retrieval은 original document를 직접 생성하는 것은 길기 때문에 inefficient. document tokenization은 document를 sequence of discrete tokens (docid)로 표현함.
-
D: collection of documents
-
d: each document
-
d : total number of tokens in document -
M: length of docid
-
z: sequence of discrete tokens (docid)
-
z_t: K-way categorical variable
- 위 그림에서는 M=3, K=64인 case
docid인 z는 아래 두가지 조건을 만족해야함.
-
different documents have short but different docids
-
docids capture the semantics of their associated documents as much as possible
Tokenization model: Q:d\to z, document d를 docid z로 mapping
Generative retrieval model: **P:q \to z****, **query q와 관련된 문서 docid z를 autoregressive하게 생성하며 학습함
Method
document tokenization은 주로 fixed pre-processing step으로 사용됨
- e.g.) document의 title이나 BERT로 얻은 hierarchical clustering results
→ 이런 ad-hoc한 방법은 document의 semantic을 잘 잡아내지 못한다는 단점이 존재함.
-
web page의 title이 없는 경우
-
web page title의 의미가 page contetn랑 관련이 적은 경우
-
clustering-based docids가 document를 discrete space에서 정의하는 경우
GENRET: Semantic docid를 학습하는 discrete auto-encoding 기반의 tokenization leraning method
크게 세가지 components로 구성이 됨
-
seq2seq based retrieval model: **P(z q)** -
document tokenization model: **Q(z d)** -
reconstruction model: **R(d z)**
Overview process
→ document tokenization model Q가 document d를 unique discrete variables z로 변환시키고, retrieval model P가 given query q에 대해 z를 생성하도록 학습이됨. 추가로 Reconstruction model R은 docid z에서 original document를 생성하도록 학습이됨 (original document의 semantic을 파악하기 위해)
Architecture
Document Tokenization Model
-
enc-dec Transformer: input text d가 있을 때, T5-based tokenization model이 d와 a prefix of docid z_{<t}를 인코딩하여 hidden latent vector d_t 생성.
- D: hidden size of model
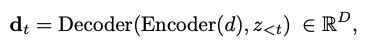
-
tokenization model은 d_t를 기반으로 각 document에 대한 token을 생성
-
각 timestep t 마다, codebook을 정의해줌
-
E_t^{K*D}: E는 external embedding matrix (codebook)을 의미하고 K는 discrete latent space의 size를 의미함
-
e_{t,j} \isin R^D, j \isin [K]: K개의 embedding vectors
-
-
codebook embedding matrix E_t와 latent vector d_t를 dot-prodcut softmax 취하여 j \isin [K]에 대한 t 시점에서의 확률값 계산,
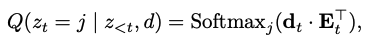
Reconstruction Model
-
tokenization model Q가 생성한 docid는 semantic 정보를 담아야하기에, auto-encoding training scheme 사용
- R: z \to d는 Q: d \to z 로 하여금 original document로 reconstruct할 수 있는 z를 만들게 함
-
Input: docid z
- embed z into representation matrix z={(z_1,…z_M) \isin R^{M*D}} (tokenization model에서 사용한 codebook)
→ 아래와 같이 표현
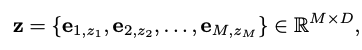
- output: document d
Retrieval-based reconstruction model
- docid z와 target document d 간의 relevance score는 다음과 같이 정의함
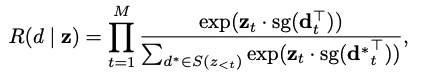
-
S(z{<t}): z{<t}와 동일한 docid prefix를 갖는 sub-collection of D
-
d^* \isin S(z{<t}): sub-collection S(z{<t})에 있는 document
-
d_t,d_t^{t}: representation vectors
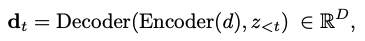
- sg(*): stop gradient operator (gradient back propagation 방지)
| → R(d | z)는 S(z{<t})에서 각 timestep t 마다 특정 document를 retrieve함. 이 score를 활용한 loss function은, model로 하여금 previous docid z{<t}에서 잡지 못한 residual semnatics을 학습할 수 있게 해줌. |
Optimization
Document tokenization model, generative retrieval model, reconstruction model을 한 번에 auto-encoding을 활용하여 학습시키기에는 다음과 같은 이유로 어렵다.
-
Learning docids in an autoregressive fashion
-
t 시점의 zt를 생성할 때는 previously predicted docids z{<t}를 이용해야하는데, 학습 초반에는 under-optimizaed 되어 있어 학습이 어려움
-
z를 simultaneously optmize시키면 unique docid를 할당하는 것에 있어 어려울 수 있음
→ GENRET 학습을 안정화 시키기 위해 progressive training scheme 제안
-
Generating docids with diversity
-
auto-encdoing으로 학습하면 unbalanced docid assignment가 될 수 있음 → model distinguishability에 영향을 줌 (잘못되면 docids의 길이가 너무 길어지는 문제가 생김)
→ docid diversity를 위해 2가지 diverse clustering techniques 제안
Progressive training scheme
- M번의 learning steps을 갖는 전체 learning scheme에서 docid z_T은 T \isin [M] 시점에 학습이 됨. 이후 시점에서는 이전 시점의 docid z_T와 parameters들은 fixed됨.
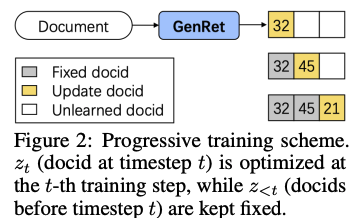
-
아래 3가지 loss function을 통해 학습이 이루어짐
- **Reconstruction Loss: **Reconstruction model R을 활용
→ main goal: docid를 생성할때 semantic 정보를 최대한 많이 담기위해 auxiliary model로 사용
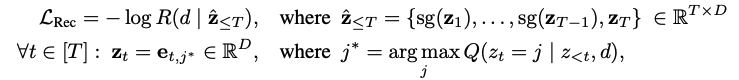
- 위 수식에서 non-differentiable operation (argmax)가 존재하여 straight-through gradient estimation을 사용

- **Commitment Loss: **Tokenization model Q 사용
→ main goal: predicted docid가 embedding에 대응되고, previous docid를 까먹지 않기 위해
(말은 이렇게 해도 걍 docid 생성하도록 학습하는 Cross Entropy Loss)
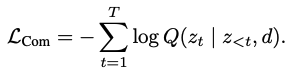
- **Retrieval Loss: **Generative retrieval model P 사용 + Q를 함께 사용
→ main goal: P가 query q가 들어올때 관련 documents d의 docids를 생성하는 것을 학습
- (q,d) pair 주어지고 아래와 같이 loss 정의
- q_T, d_T,d_T^*: query, document, in-batch document의 latent vector
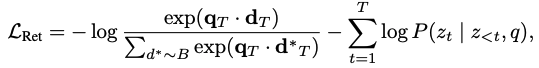
- first term: ranking-oriented loss
- second term: CE loss, generating docid z based on q
→ step-T에서 final loss는 아래와 정리됨
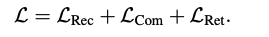
Diverse clustering techniques
docids의 diversity를 보장하기 위해 아래 두가지 clustering techniques을 각 progressive training step에 적용함.
- Codebook Initialization
→ main goal: increase the balance of semantic space segmentation
(MEMTO와 거의 판박이로 비슷함ㅋㅋ)
-
warm-up: docid representation z_T을 사용하지 않고 d_T를 바로 reconstruction model에 사용
-
L(Rec) + L(Com)만 사용함
-
documents에 대한 continuous vectors d_T 수집후 → K groups으로 clustering (Constrained K-Means)
-
cluster의 각 centroid는 codebook E_T를 initialize하는데 사용
-
Docid re-assignment
→ main goal: increase the balacne of docid assignments
아래 dot-product results를 modify하여 different doc에 대응하는 docid가 distinct하는 것을 보장
- D: continuous vectors of batch of documents
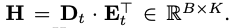
-
re-normalization vectors (u and v) 사용
- Sinkhorn-Knopp algorithm을 통해 u and v vecotrs가 계산됨
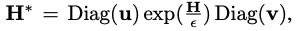
- calculated H*는 Softmax에 들어가 확률 생성
Experimental Setup
-
enc-dec: T5-base
-
retrieval model과 tokenization model에 사용되는 enc-dec, codebook 각각은 shared
-
K number of clusters: 512
-
M length of docid: 문서의 개수에 따라 달라짐
Experimental Results
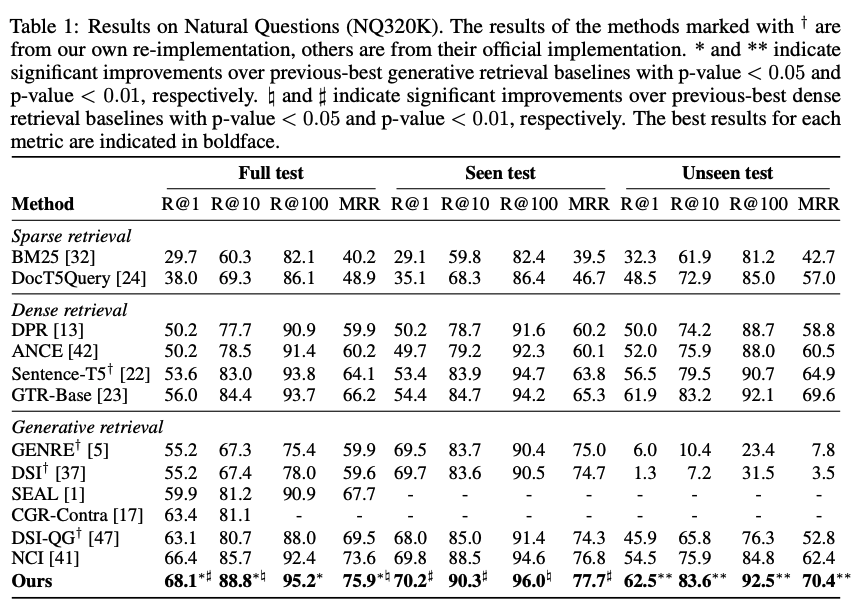
NQ320K results
-
strong pretrained retrieval GTR + previous SOTA in generative retrieval보다 우수한 성능 보임
-
Seen + Unseen dataset에서 우수한 성능 보임
→ 실험 결과는 GENRET이 dense + generative retrieval의 장점을 결합한 방법임을 강조함
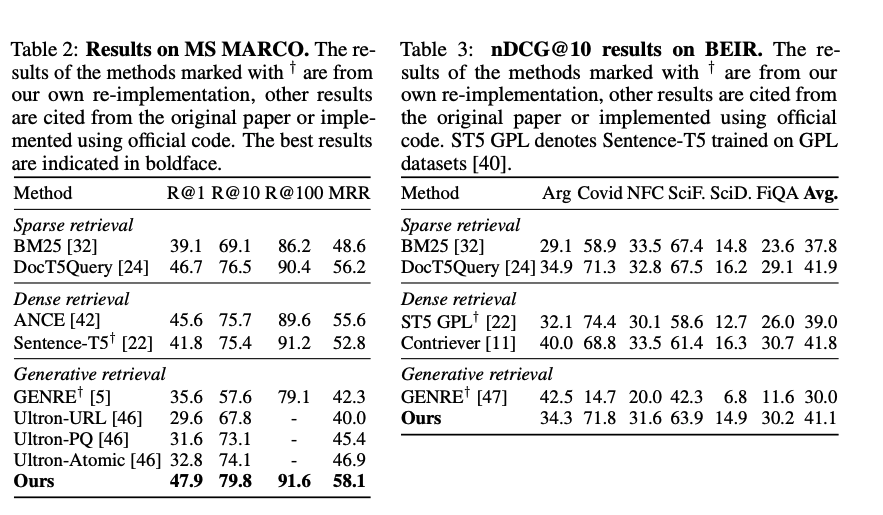
MS MARCO + BEIR results
-
MS MARCO
-
URL이나 title같은 meta data를 사용하는 generative retrieval model인 GENRE, Ultron은 MS MARCO에서 NQ320K 대비 성능이 크게 하락함.
- NQ320K는 wikipedia를 retrieve해서 meta data가 content와 밀접하지만, MS MARCO는 web search dataset이기 때문
-
그치만 semantic docids를 생성하도록 학습한 GENRE는 roboust한 성능을 보여줌
-
-
BEIR
-
특히 BM25가 잘하는 dataset인데, 보다 높은 성능을 보여줌
-
title을 docid로 사용하는 generative retrieval model인 GENRE는 BEIR-Covid, BEIR-SciDocs에서 성능이 낮은데, 이는 documents의 titles이 content의 semantic을 담지 못함.
-
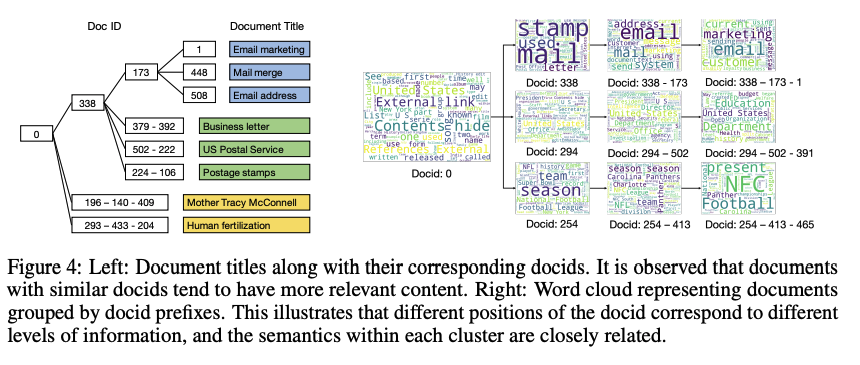
Qualitative analysis
NQ320K dataset에서 GENRET이 생성한 docid에 대한 시각화
-
left: similar docids는 비슷한 content로 구성
- 338-173 branch는 email과 관련된 내용
-
right: same group에 들어가는 docid는 semantically하게 비슷함
- 338에서 173이 추가되면, 더욱 email과 관련된 내용 포함
Conclusion
본 연구에서 처음으로 generative retrieval 계열의 document tokenization learning method인 GENRET 소개함. 요약하면, generated docids가 semantics을 담게 설계된 auto-encoding 방식을 통해 documents를 discrete representations으로 tokenize하는 것을 학습함.
Dense retrieval method 보다 안정적으로 높은 성능을 보이며, 특히 unseen dataset에서도 좋은 성능을 보인 것으로 미루어 보아 generative retrieval이 앞으로 IR에서 핵심 연구 주제가 되지 않을까 싶음
더 짧은 docids로 학습 및 infer해서 효율적이지만, training process가 복잡해서 computation cost가 높을 것 같은데, 이 점에 대한 dense retreival method와 비교 실험이 없어서 아쉬움.
이 아니고 appendix에 꼭 숨겨놨었네요
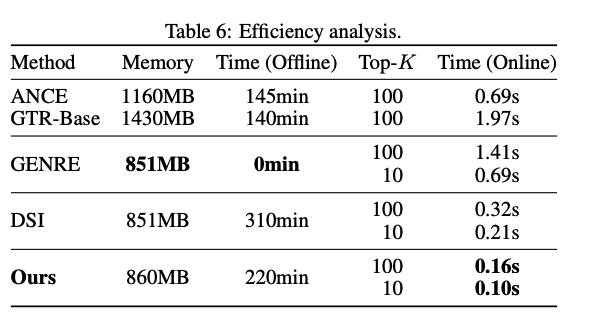
학습 속도는 느리긴 하지만, infer 속도는 가장 빠르다는 결론!
+MEMTO!