QLoRA: Eficient Finetuning of Quantized LLMs
논문 정보
- Date: 2023-06-29
- Reviewer: 건우 김
- Property: LLM, Efficient Training
Introduction
-
Finetuning LLMs is effective way to improve performance, and to add desirable or remove undersiable behaviors
-
Expensive to train
-
16-bit finetuning LLaMA 65B: >780GB GPU memory
- Recent quantization methods can reduce the memory, but only work for inference
-
-
QLoRA: quantize PLM to 4-bit, and add learnable params LoRA weights (updated using quantized weigths) → performance degradation x
-
LLaMA 65B: >780GB → <48GB (no degradation)
-
best model (Guanaco family of models) = 99.3% level of ChatGPT
- single GPU over 24 hours
-
-
QLoRA main components
-
4-bit NormalFloat: 4-bit Integer/Float보다 더 좋은 성능을 보이는 데이터 타입.
-
PLMs의 weights는 주로 정규분포를 따르는데, 이에 맞는 데이터 타입 사용(이론적으로 가장 optimal한 quantization data type)
-
Double Quantization: quantization constant를 quantize하는 기법.
-
parameter 당 0.37 bits 크기 save
-
**Paged Optimizer: **GPU memory가 최대치에 도달할 때, 일반 memory에 data를 저장시켜 연산에 필요한 memory를 확보하는 기법
-
LoRA
-
-
-
**Additional analysis **
→ regular finetuning으로는 분석할 수 없었던 실험들을, quantization을 통해 in-depth study of instruction finetuning과 chatbot performance를 model의 scale에 따라 실험 진행
-
*Data quality** is far more important than *dataset size.
- 9k sample dataset (OASST1) outperformed a 450k sample dataset (FLAN v2) on chatbot performance
-
MMLU benchmark performance does not imply strong Vicuna chatbot benchmark performance and vice versa
- dataset suitability matters more than size for a given task
Background
-
**Basic Knowledge**
- BLOOM-176B
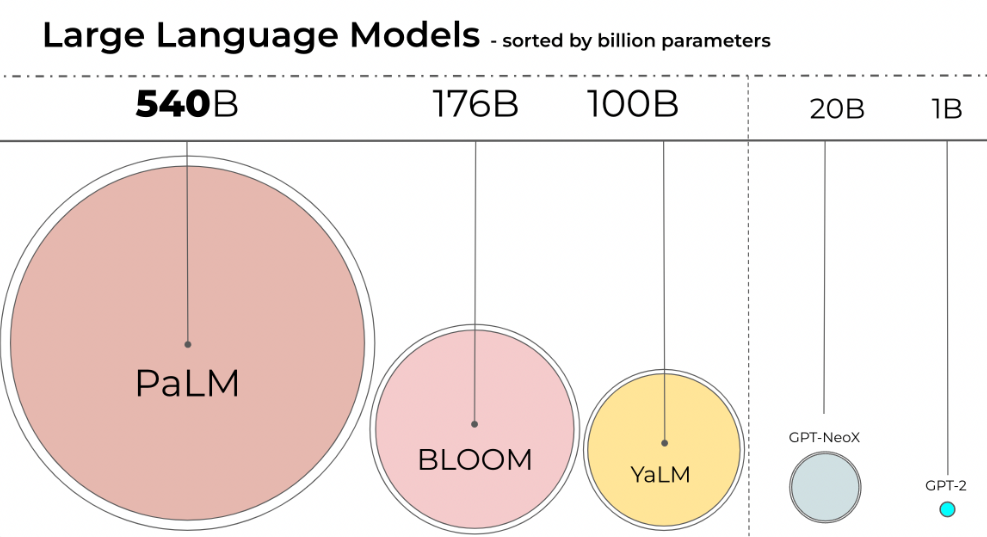
- Inference: 8x 80GB A100 GPUs
- Finetuning: 72x GPUs
-
Floating Point Formats
-
Floating point example
-
(10진법) 5.6875 → (2진법) 101.1011 → (정규화) 1.011011 x 2^2
-
sign: 0 (positive)
-
exponent (unadjusted): 2
-
mantissa (unnormalized): 1.011011
-
-
-
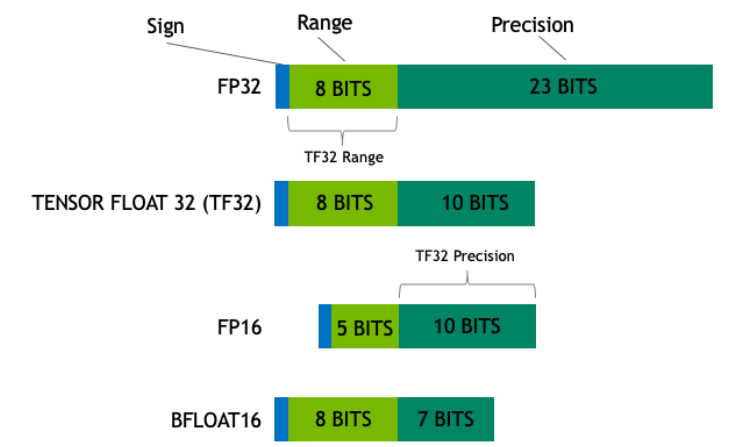
- **Float32 **(FP32)는 IEEE754에서 정한 표준 기준 (Full precision)
- 1bit: sign (부호)
- 8 bits: exponent (지수)
- 23 bits: mantissa
- FP16은 underflow/overflow 문제 有
- **FP16**: Half-precision, 16비트 부동 소수점 형식.
- Memory를 적게 사용하므로 DL에서 자주 사용하지만, precision이 낮아서 model의 성능을 보장하지 못함
- Training에 주로 FP32 사용, Inference에 주로 FP16사용
- Example
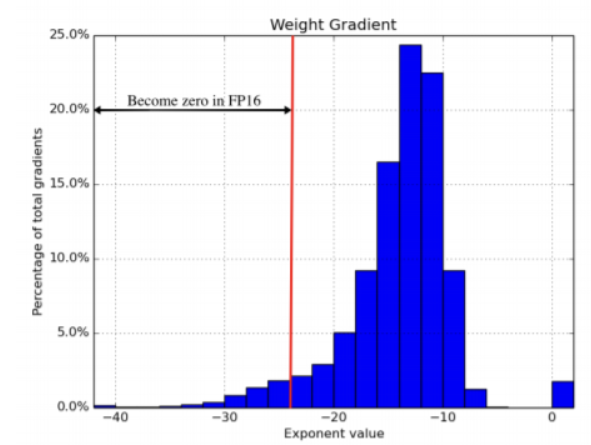
- FP32를 통해 학습시킨 network의 gradient를 ranodm하게 sampling하여 찍은 graph.
- Red line 왼쪽 graident는 FP16에서 표현이 불가능
- **BFLOAT16 **(BF16)은 FP16의 한계점을 보완하기 위해 소개됨
- 8bit를 exponent를 사용하고, 7bit를 mantissa로 사용
- FP32과 동일한 dynamic range를 갖으며 memory 사용량 적지만, precision이 더 낮음
- **Mixed Precision**는 FP16과 FP32를 혼합하여 사용
- Memory 사용량을 최적화 + 학습 가속화하며 model의 성능유지 가능
- FP32대비 1/2 memory 사용량 + 8배 연산 처리량 + 2배 memory 처리량
- Deep Neural Network에서 학습에 관여하는 4가지 tensor 종류
- Weights, Weight Gradients: FP16 범위 안에서 연산 가능
- Activation, Activation Gradient: FP16에서 0으로 변환
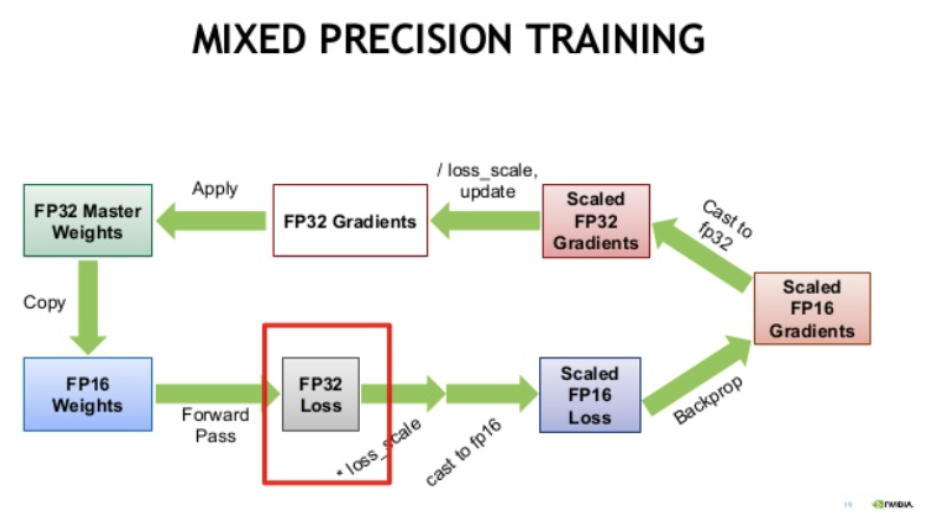
- **Process**
1. FP32 weight를 FP16 copy weight 만들어 줌
1. copy weight가 forward, backward에 사용
1. FP16 copy weight를 통해 forward 진행
1. Forward로 계산된 FP16 prediction을 FP32로 캐스팅 진행
1. FP32 prediction을 이용해 FP32 loss 계산하고, scaling factor 곱함
1. scaled FP32 loss를 FP16으로 캐스팅 진행
1. scaled FP16 loss를 통해 backpropagation 진행후 gradeint 계산
1. FP16 gradient를 FP32로 캐스팅 하고, 다시 scaling factor로 나눔
1. FP32 gradient를 통해 FP32 weight update
""" define loss scaler for automatic mixed precision """
# Creates a GradScaler once at the beginning of training.
scaler = torch.cuda.amp.GradScaler()
for batch_idx, (inputs, labels) in enumerate(data_loader):
optimizer.zero_grad()
with torch.cuda.amp.autocast():
# Casts operations to mixed precision
outputs = model(inputs)
loss = criterion(outputs, labels)
# Scales the loss, and calls backward()
# to create scaled gradients
scaler.scale(loss).backward()
# Unscales gradients and calls
# or skips optimizer.step()
scaler.step(self.optimizer)
# Updates the scale for next iteration
scaler.update()
- 학습 전에 scaler 선언하고 → torch.cuda.amp.autocast()를 통해 캐스팅하고 forward진행
- backward, optimization, weight update → scaler를 통해 진행
- batch size 2배 사용 가능 + OOM 해결 가능
- BLOOM-176B
- BF16 사용: 176 x 10^9 x 2 bytes = 352GB 필요
- **Quantization: **더 적은 memory를 사용해서 다른 data type으로 weight를 저장하는 방식
-
Block-wise k-bit Quantization
-
8-bit quantization: quarter precision을 사용하며 model의 1/4 size만 사용
-
Not jsut dropping half of the bits
-
Example
-
1st range: 10진수 / 2nd range: 4진수
-
‘4’는 0~9에서 중앙에 위치하므로, 0~3에서 표현하면 중앙값인 ‘2’로 표현
-
‘3’은 0~9에서 ‘2’와 ‘4’ 사이에 위치하므로, 상대적으로 0~3에서 ‘1’과 ‘2’사이에 위치하고 반올림하면 ‘2’로 표현
-
다른 수를 동일한 값으로 표현하는 Information Loss 발생 (Lossy compression)
-
-
-
Common techniques (8-bit quantization)
-
FP values를 더 compact한 int8 (1byte) values로 mapping시킴
-
Zero-point quantization
-
Range: -1.0~1.0 (float) → Range: -127~127 (int8)
-
원래의 값을 다시 얻으려면, int8 value를 quantization factor (127)로 나눔
-
Example) ‘0.3’은 0.3*127 = ‘38.1’이므로, 반올림 하면 ‘38’로 mapping 됨
- 원래의 값을 얻으려면, 38/127 = ‘0.2992’를 얻게 되서, ‘0.008’ qunatization error 발생 → 누적되면 성능 저하의 원인
-
-
-
Absmax quantization
-
Tensor의 absolute maximum 값을 활용하여 스케일
- no quantization error
-
Example
23.5 = 127/5.4
-
-
-
-
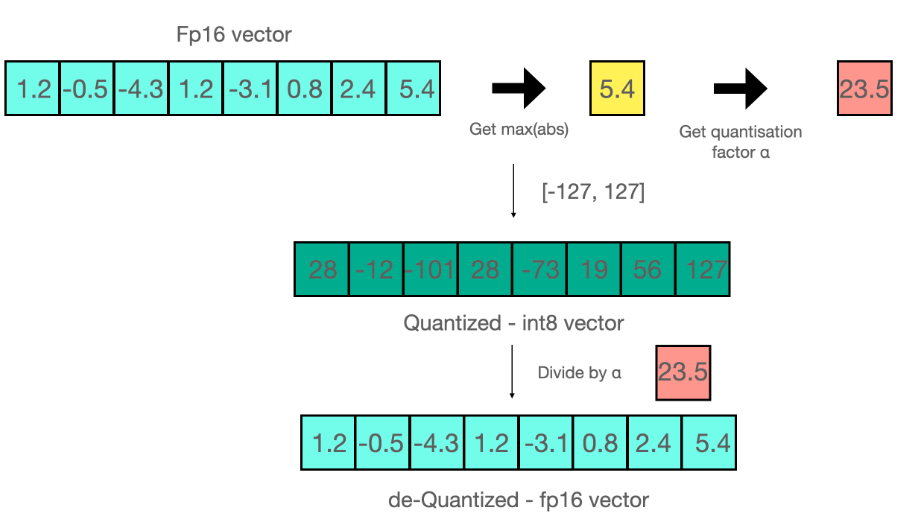
- quantizaing FP32 into Int8 [-127,127]
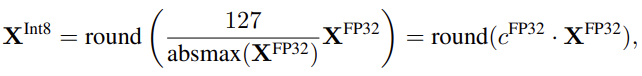
- dequantizing
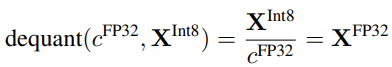
→ outlier 값을 다루기 위해 chunck 단위로 나누어 quantize 진행
- Low-rank Adapters
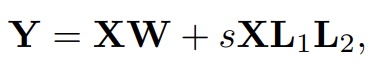
-
Memory Requirement of Parameter-Efficeint Finetuning
-
LoRA가 PEFT로 소개가 (small memory footprint) 되긴 했지만, LLM을 finetuning할 때 발생되는 대부분의 memroy footprint는 LoRA params가 아닌 *Activation Gradients*** **이다.
-
LLaMA-7B
-
LoRA input graidients: 567MB
-
LoRA params: 26MB
-
-
Gradient checkpointing(GC)을 사용하면, input gradients는 18 MB로 줄어들 수 있다.
-
**Gradient checkpointing (GC)**
-
classic backpropagation: 당장 사용하지 않는 node의 값이라도 다 저장함. 연산 속도가 빠르다는 장점이 있지만, 저장해야할 weight가 늘어나 memory 사용량이 늘어나는 단점 존재
-
weight를 저장하지 않는 backpropagation: 연산 속도를 생각하지 않으면, node의 weight를 저장할 필요 없음. 하지만 forward process가 2번씩 일어나서 O(N^2) 시간 복잡도 발생하는 단점 존재.
-
GC: classic backpropagtaaion과 weight를 저장하지 않는 방식의 절충안. 일부 node만 선택하고 그 node의 gradient만 저장하는 방식. checkpoint 이후의 node까지 forward process를 빠르게 할 수 있음 O(N^{1/2})
-
-
-
-
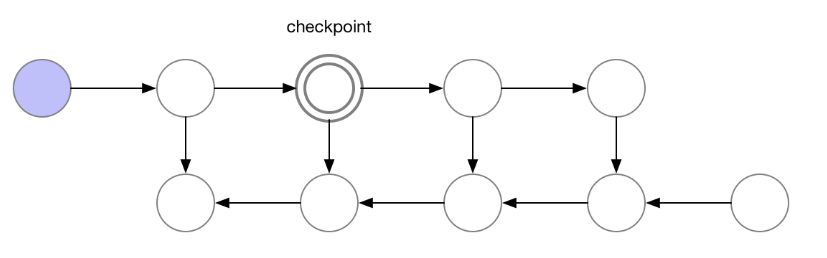
- LoRA 자체의 parameter를 줄이는 것은 중요하지 않으며, GC를 통해 더 많은 LoRA 사용가능 without increasing training memory footprint
QLoRA Finetuning
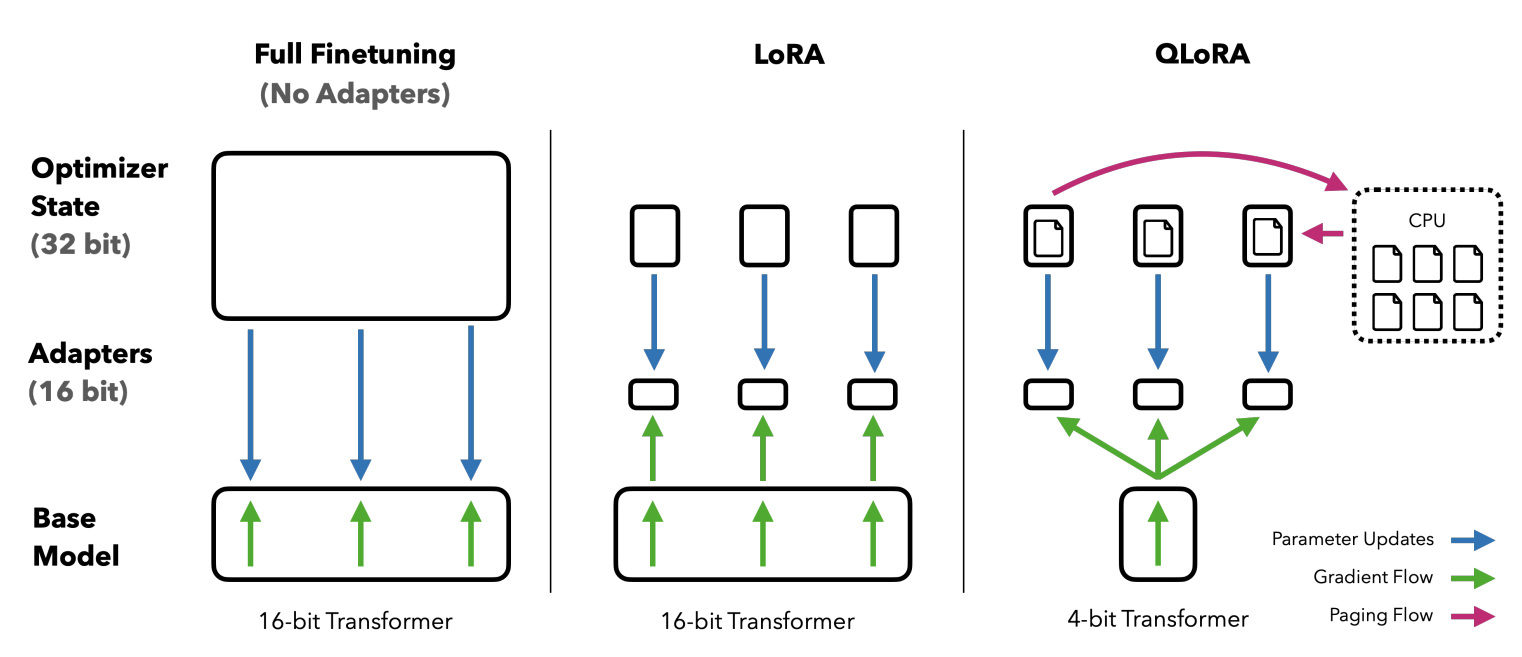
- QLoRA의 storage data type은 4-bit / computation data type은 BFloat16
→ QLoRA weight가 사용될 때, BFloat16으로 dequantize를 하고 16-bit에서 행렬 연산 진행
-
4-bit NormalFloat(NF) Quantization
-
NF data type은 이론적으로 가장 이상적인 data type이며 Quantile Quantization 기법에 사용
- Quantile Quantization: data를 동일한 크기의 quantile로 분류하는 방법. Empirical cumulative distribution function을 통해 tensor의 quantile을 추정하는 식으로 작동.
-
(각 quantization bin에는 동일한 input tensor의 개수가 존재)
- Limitation: quantile 추정이 expensive → 빠른 추정을 하기위해 SRAM quantile같은 approximation을 통해 추정하는 방법이 제안 되었지만, outliers에 대해 large quantization error가 존재해서 불안정
- Input tensor들이 고정된 quantization constant의 분포로부터 나오면 앞선 문제들 해결 가능 → input tensors have the same quantiles (동일한 분포를 갖는다)
-
Pretrained neural network weights follow zero-centered normal distribtuion with standard deivation \sigma
- \sigma scaling을 통해 모든 weight를 single fixed distribution으로 변형 가능 → data type과 weights에 대응하는 quantiles들이 동일한 range [-1,1] 갖게끔 정규화 적용
-
zero-mean normal-dist를 위한 data type을 구하는 Process
-
estimate 2^k+1 quantiles of a N(0,1) distribtuion to obtain a k-bit quantile quantization data type for norm-dist
-
Take this data type and normalize its values into [-1,1] range
-
quantize an input weight tensor by normalizing it into [-1,1] through absolute maximum rescaling
-
-
weight range와 data type range를 맞춘후, data type의 q_i 값들에 대한 quantize 진행 (2^k)
- 위에 (3) 과정이 ‘\sigma scaling을 통해 모든 weight를 single fixed distribution으로 변형’하는 역할 수행
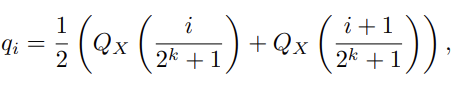
-
Double Quantization
- 추가적인 memory 사용량을 아끼기 위해 소개된 Quantization constant를 quantizing하는 방법
-
Paged Optimzier
- CPU와 GPU간의 연동을 통해 GPU memory가 고갈되면, CPU RAM과 disk에서 memory paging하는 것과 비슷하게 동작. 자동으로 CPU RAM으로 backup해서 process가 끊임 없이 연산을 계속할 수 있게 함. (optimzier update step이 필요할 때, CPU → GPU 이동)
-
QLoRA
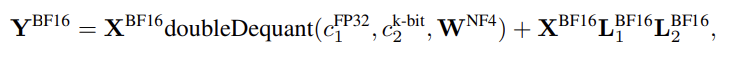
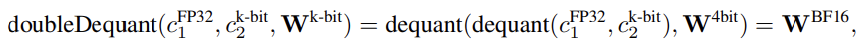
-
One storage data type (4-bit NF)
-
One computation data type (16-bit BF)
- forward/backward process를 진행할 때, data type에 대해 dequantize를 수행
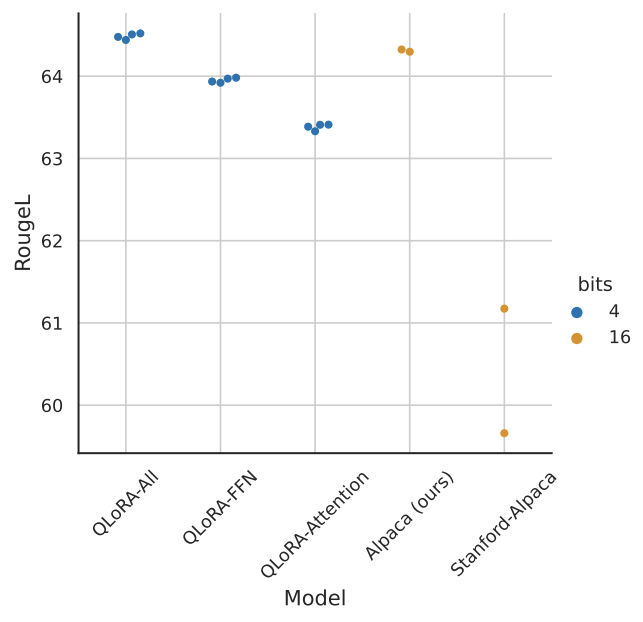
QLoRA vs Standard Finetuning
-
Default LoRA hyperparameters do not match 16-bit performance
-
Alpaca (ours): full-finetuning → QLoRA-All과 비슷한 성능 보임
- Standford-Alpaca역시 full-finetuning인데 hyperparameters 조합에 대해 undertuned 되어 있음을 발견.
-
Hyperparameters 중에 adapter의 개수만 성능에 영향을 미치고, LoRA의 projection dimension과 같은 다른 hyperparameter는 중요하지 않음
-
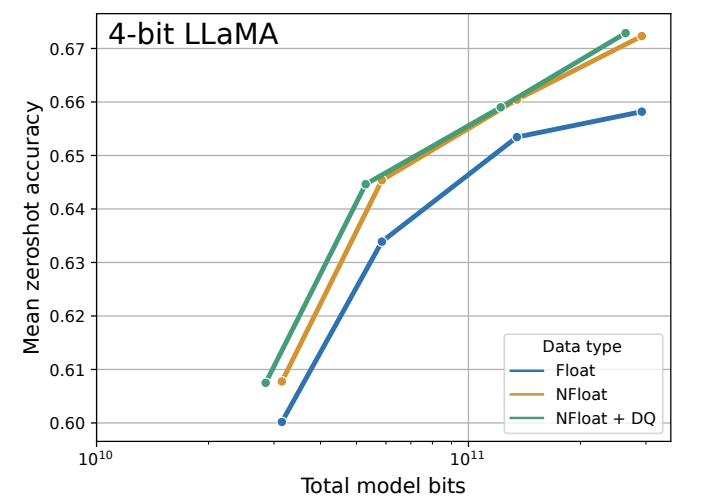
-
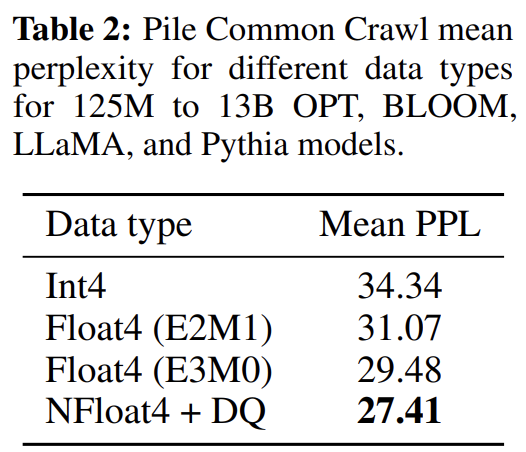
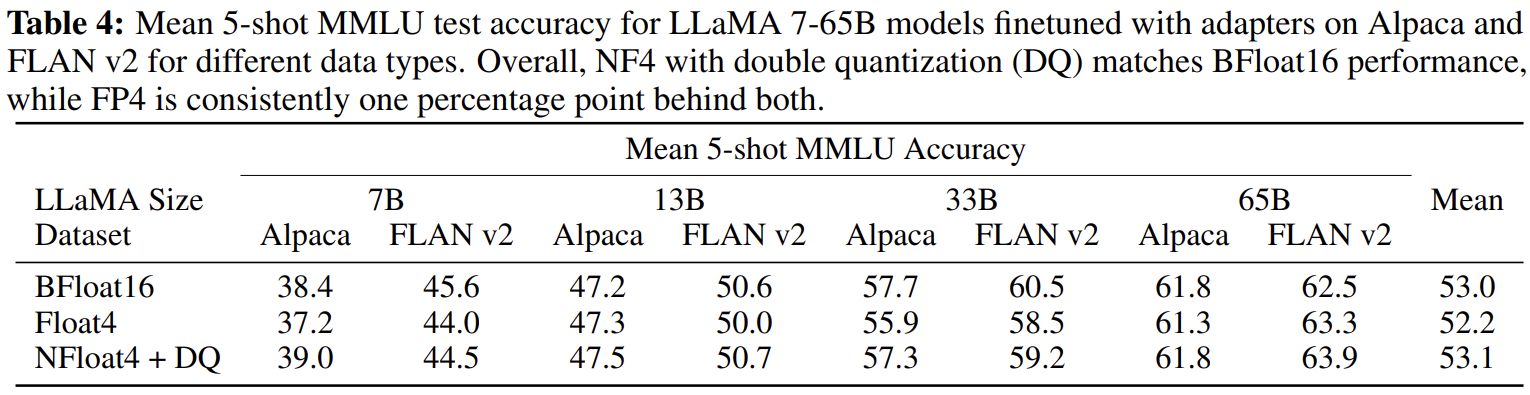
4-bit NormalFloat yields better performance than 4-bit Floating Point
-
NF4가 FP4와 Int4 대비 높은 성능을 보임
- NF4 + Double Quantization (DQ)는 성능 하락 없이 memory 사용량을 줄여줌
-
-
k-bit QLoRA matches 16-bit full finetuning and 16-bit LoRA performance
- 최근까지 4-bit quantization에 대한 연구에서는, inference는* *가능 하지만 16-bit에 비해 performance degradation이 있다는 결과가 있음
→ 그러면 4-bit adatper finetuning을 하면 Loss performance를 되찾을 수 있나?
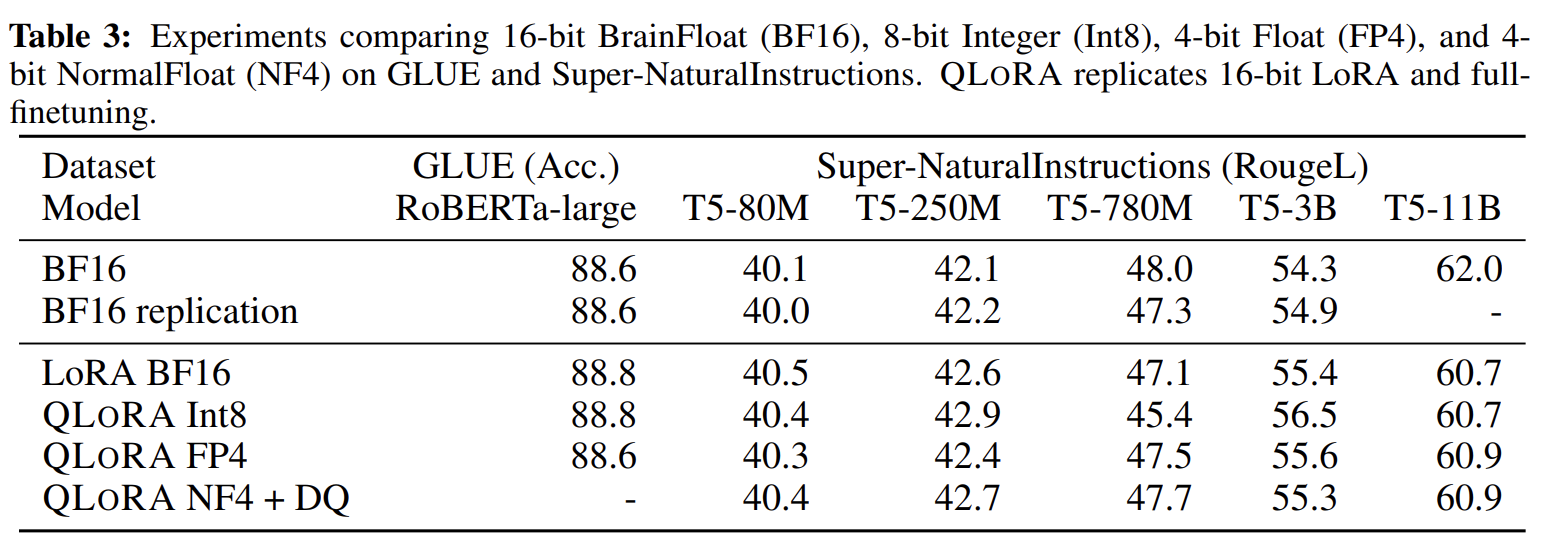
1. **Small Models**
- 16-bit, 8-bit, 4-bit adapter methods replicate the performance of fully finetuned 16-bit baseliens
- BF16: fully finetuned
- BF16 replication: LoRA training
1. **Large Models**
- FP4는 16-bit LoRA baselines의 성능을 재현하지 못함.
- NF4 + DQ는 16-bit LoRA finetuning 성능 재현 성공
- NF4가 FP4보다 quantization precision 관점에서 더 적합함을 보임
-
Summary
-
4-bit (NF) QLoRA는 16-bit full finetuning과 16-bit LoRA finetuning과 꾸준히 비슷한 성능 보임
-
NF4가 FP4보다 더 효과적이고 DQ는 성능 저하가 없음
-
Pushing the Chatbot State-of-the-art with QLoRA
-
Experiment settings
-
Data
-
instruction-following datasets에 대한 comprehensive sutdy가 없어 다음 8개 사용
-
crwod-sourcing: OASST1, HH-RLHF
-
distillation from instruction-tuned models: Alpaca, self-instruct, unnatural instructions
-
corpora aggregations: FLAN v2, Chip2, Longform
-
-
-
Training setup
-
QLoRA finetuning with CE loss (supervised) without RL (different resonse에 대한 human judgement가 있는 것도 RL 활용 x)
-
NF4 QLoRA with DQ + Paged optimizers 적용
-
-
Baselines
-
Research models: Vicuna (LLaMA 13B finetuend), Open Assistant (LLaMA 33B finetuned with RLHF)
-
Commercial models: GPT-4, GPT-3.5-turbo, BARD
-
-
Evaluation
-
NLU task: MMLU (5-shot test accuracy)
-
NLG task
-
Benchmark data
-
Vicuna prompts: 80 prompts from a diverse set of categories
-
OASST1 validation: multilingual collection of crow-sourced multiturn dialogs between a user and an assitant (953 unqiue user queries)
-
-
Evaluation
- use GPT-4 to rate the performance of different systems against ChatGPT on Vicuna benchmark (model과 ChatGPT 비교)
-
-
-
→ query가 주어지면, ChatGPT의 response와 model의 response 각각을 생성하고, GPT-4가 각 response에 대해 점수 (10점 만점)를 매기고 explanation 생성
- model의 performance는 ChatGPT대비 얼만큼 나왔는지 percentage
- GPT-4의 ordering effect가 존재: prompt 초반에 있는 response에게 더 높은 점수를 부여하는 경향이 있음 → 모든 orders를 고려해서 평균
- Direct comparisons between system outputs: win / tie / lose 를 GPT-4가 정하게 시킴
- Human evaluation
- GPT-4의 reliability 수준은 human judgement와 아직 까지는 correlate하지 않기 때문에, 별도의 human evaluation 진행
- Elo Rating
- human과 automated pairwise comparison을 토대로 Elo rating 진행
-
Results
-
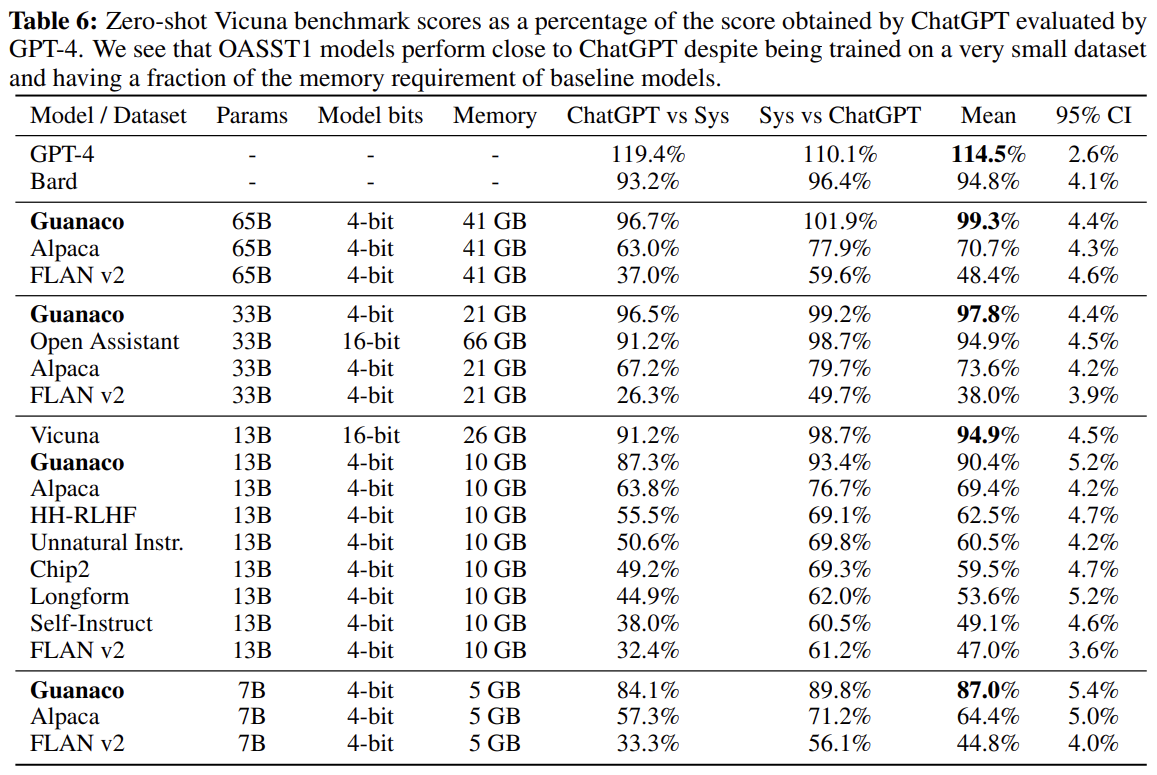
GPT-4 다음으로 Guannaco-65B이 높은 성능을 보임
-
Guannaco-7B는 ALpaca 13B보다 20%p 높음 (5GB 용량으로 핸드폰에 들어갈 크기)
-
Confidence Interval is wide: model 성능이 서로 overlapping하는 경우가 많음
-
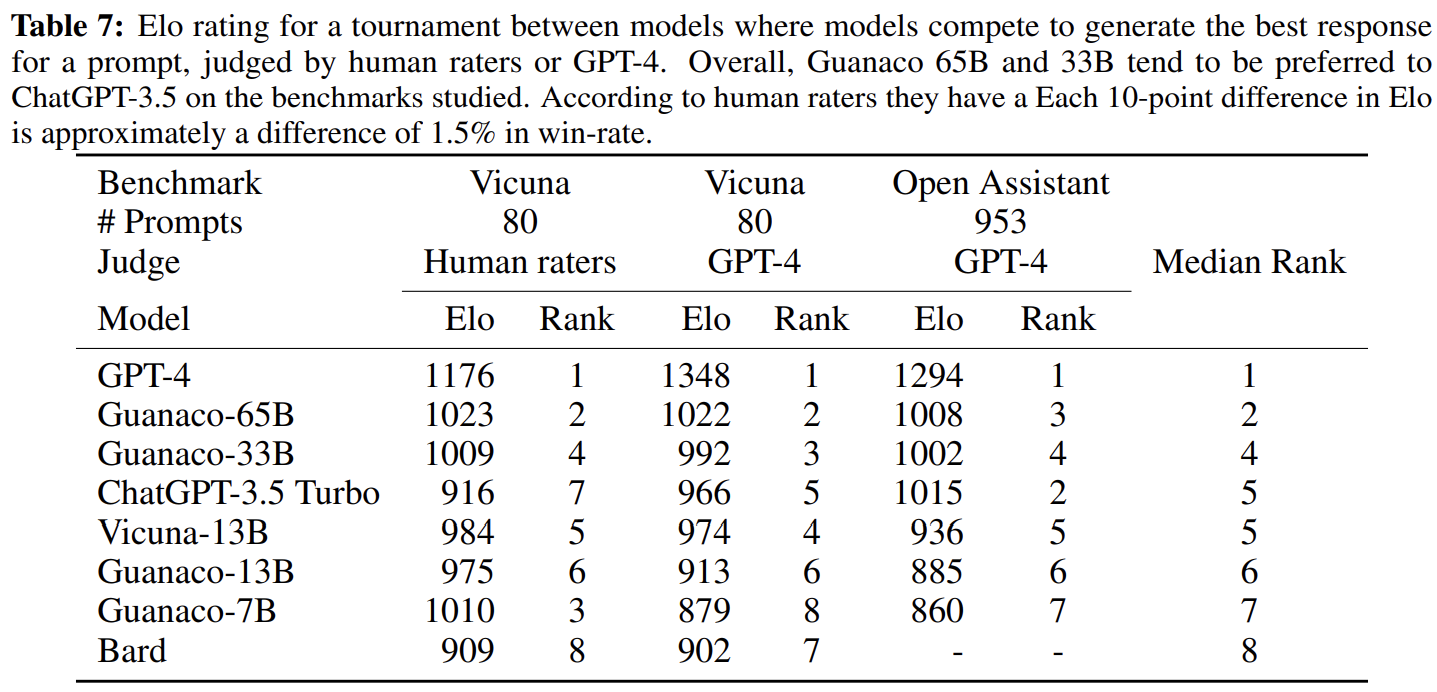
→ Elo 기반으로 평가 진행
- Guannaco-33B,65B는 GPT-4 다음으로 높음
Qualitative Analysis
-
다른 LLMs과 비슷한 양상의 실수들이 존재하기 때문에 생략
-
Factual Recall
- 쉬운 질문은 잘 답하지만, 질문이 어려워지면 답변을 잘 못함 (with confident)
-
Suggestibility
- 말도 안되는 질문에 답변 회피. (e.g. ‘언제부터 지구는 평평해? → ‘그런적 없음’)
-
Math
- math 종류의 reasoning task는 매우 못함
-
etc.
-
Limitations and Discussion
-
QLoRA를 통해 4-bit base model로 16-bit full finetuning 성능을 재현할 수는 있었지만, model의 scale이 33B 혹은 65B까지 가면 그렇지 못했다. → resource 부족으로 원인 발견 x
-
Evaluation of instruction finetuning models
-
BigBench, RAFT, HELM과 같은 benchmark에 대해서 평가를 진행하지 않아, 앞에서 진행한 실험들이 generalize될지 모름
-
finetuning data와 benchmark dataset이 similar한 정도에 성능이 dependent
-
-
다른 bit-precision (e.g 3-bit) base models 혹은 다른 adapter 방법론에 대한 실험 부재
Implementation
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("facebook/opt-350m", load_in_4bit=True, device_map="auto")
##################
from transformers import BitsAndBytesConfig
nf4_config = BitsAndBytesConfig(
load_in_4bit=True,
bnb_4bit_quant_type="nf4",
bnb_4bit_use_double_quant=True,
bnb_4bit_compute_dtype=torch.bfloat16
)
model_nf4 = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_id, quantization_config=nf4_config)
##########
accelerate library를 사용하기 때문에, 지원하는 models은 모두 사용 가능
- Llama, OPT, GPT-Neo, GPT-NeoX
[
'bigbird_pegasus', 'blip_2', 'bloom', 'bridgetower', 'codegen', 'deit', 'esm',
'gpt2', 'gpt_bigcode', 'gpt_neo', 'gpt_neox', 'gpt_neox_japanese', 'gptj', 'gptsan_japanese',
'lilt', 'llama', 'longformer', 'longt5', 'luke', 'm2m_100', 'mbart', 'mega', 'mt5', 'nllb_moe',
'open_llama', 'opt', 'owlvit', 'plbart', 'roberta', 'roberta_prelayernorm', 'rwkv', 'switch_transformers',
't5', 'vilt', 'vit', 'vit_hybrid', 'whisper', 'xglm', 'xlm_roberta'
]