A Simple and Effective Pruning Approach for Large Language Models
논문 정보
- Date: 2024-03-12
- Reviewer: hyowon Cho
- Property: Pruning
Introduction
어제 나눈 우리의 짧은 담론과 같이, 거대 언어모델에는 수많은 지식들이 저장되어있기 때문에 대부분의 파라미터는 우리가 타겟으로 하는 정보와 관련이 없습니다. 오늘은 네트워크를 어떻게 지식을 고려하면서 간단하지만 효과적으로 pruning할 수 있는지, 관련 연구를 살펴봅니다.
선행 network pruning 연구에서 가장 문제가 되는 것은 무엇일까요?
-
대부분의 기법들은 retraining을 요구함 — 작기때문에 가능
-
LLM을 retraining하는 것은 말이 되지 않기 때문에 retrain을 하지는 않지만, 여전히 내부적으로 여러번 iteration을 반복해 weight를 update함.
-
retrain&weight update를 하지 않는 방법으로 magnitude pruning (model merging에서 봤던!) 또한 LLM에서 완벽하게 작동하지는 않음.
오늘 소개하는 연구의 핵심 아이디어는 “model의 output을 만드는데는 model weight와 input이 함께 고려되는데, magnitude만 이용하는 pruning은 말이 되지 않는다. input도 함께 고려해야 된다.”입니다.
즉, 3번의 standard weight magnitude pruning metric에 Input activation을 고려하면 더 효과적인 pruning이 가능하다는 것이지요. 이를 통해서 1과 2번과 같이 retraining, 그리고 weight update 없이도 light하게 좋은 pruning 성능을 유지한다고 주장합니다.
PRELIMINARIES
-
Magnitude Pruning
- magnitude를 기준으로 (abs value) 모델의 weight를 삭제하는 방법론. globally하게도 할 수 있지만 each layer에 대해 locally하게 적용하는 것이 일반적이다.
-
Emergent Large Magnitude Features
- Dettmers et al. (2022)에 따르면 LLM이 6B 이상의 크기를 가질 때, 아주 적은 hidden state feature들이 다른 것들보다 magnitude가 ‘훨씬’ 커진다는 것을 관측했다. (100배 이상). 이들을 zeroing하면 성능에 아주 큰 결함이 생긴다.
WANDA: PRUNING BY WEIGHTS AND ACTIVATIONS
| Consider a neuron with two inputs and corresponding weights: y = w_1x_1 + w_2x_2, where | w_1 | ≤ | w_2 | . 우리의 목표는 최종 output에 영향을 가장 덜 주는 weight를 삭제하는 것이다. 이때, x의 크기가 같거나 거의 차이가 없다면 더 작은 Magnitude를 가지는 w_1을 삭제하는 것이 당연하겠지만, 아쉽게도 input들끼리도 scale이 굉장히 다르다. 즉, | x_1 | ≫ | x_2 | , and as a result, | w_1x_1 | ≫ | w_2x_2 | . 이 경우에는 w_2를 삭제하는 것이 output에 가장 적은 차이를 가져온다. |
저자들의 일관된 주장은: magnitude만이 아닌 input activation을 함께 사용해야한다는 것이다.
Pruning Metric
-
a linear layer with weight W of shape
(C_out, C_in) -
input activations X with a shape of
(N × L, C_in)
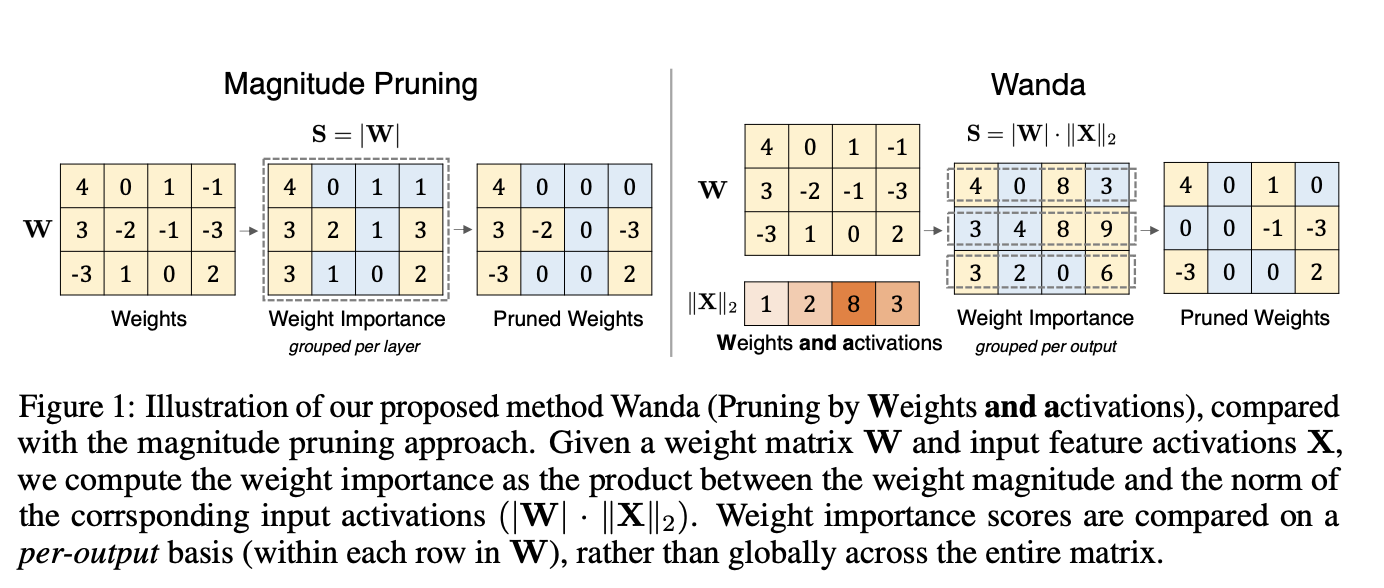
X는 소수의 calibrated input을 통해 만들어내고, 각 layer에 X의 l2 norm을 곱해준다. (다른 norm들보다 좋은 성능)
이러한 방식을 통해서 input activation과 weight magnitude를 고루 고려한 importance matrix를 만들 수 있다.
Comparison Group
기존의 pruning 방법론에서는 layer-wise locally 혹은 gloablly하게 어떤 weight가 더 작은지 판단한다. 하지만 저자들은 이보다 더 작은 단위로 group을 구성했을 때 더 효과적이었다고 주장한다.
즉, 위의 figure와 같이 row별로 pruning을 진행한다 (per-output). drop되는 비율은 pre-defined.
이러한 방법이 layer-wise보다 consisitently better. 그리고 wanda에서 뿐만이 아니라 일반적인 magnitude pruning에서도 더 좋은 성능을 보였다고 한다.
이러한 양상이 general한지를 평가하기 위해, image classifier에 적용을 해본다. 하지만, image에서는 이러한 양상이 발견되지 않았다. 즉, LLM에서만 발견되는 것이다.
Procedure
한 번의 forward로 완료가 된다는 점이 장점.
-
calibration data를 통해 X가 만들어짐
-
각 레이어에 도달했을 때, pruning을 하고 forward.
Structured N:M Sparsity.
Structured N:M Sparsity란 N개의 contiguous weights 중 M개가 non-zero인 구조를 의미한다. 비록 wanda가 이렇게 개수를 정해놓고 하는 방법론은 아니지만, 근본적으로는 같다고 볼 수 있고, 또한 이러한 구조를 이용하면 NVDIA의 sparse tensor core를 이용해 행렬연산의 속도를 끌어올릴 수 있다. 따라서, 실험에서 사용해 보았다고!
Remarks

이때, 각 layer의 hessian (X^TX + λI)에서 hessian dampening factor가 사라질 때, wanda의 input activation과 거의 유사하다고 주장한다.
지금까지의 정리를 하자면 다음과 같다:
-
It maintains the simplicity of magnitude pruning in the pre-LLM era, requiring no gradient computation via back-propagation or any second-order Hessian inverses, but is also_ highly effective _in discovering sparse networks in pretrained LLMs.
-
Wanda can be done with a single forward pass of the LLM. At each layer, the pruned weights can be decided in one shot without an iterative procedure. In practice, computing the pruning metric of Wanda can be 300 times faster in pruning LLMs compared with SparseGPT.
-
Unlike SparseGPT, our approach entails no weight update _**on pruned networks, suggesting that **_LLMs have effective sparse sub-networks that are exact, instead of them merely existing in the neighborhood of the original weights.
EXPERIMENTS
-
model
-
LLaMA 7B/13B/30B/65B
-
LLaMA-2 7B/13B/70B
-
OPT-13B/BLOOM family/Pythia-12B
-
-
Eval:
-
ppl
- WikiText
-
zero-shot
- seven tasks from EleutherAI LM Harness
-
-
Baselines
-
Magnitude pruning
-
SparseGPT
- 엄밀한 비교를 위해 calibration data는 여기서 사용했던 128개의 text data from C4
-
-
Sparsity
- skip the first embedding layer and the final classification head
ZERO-SHOT TASKS
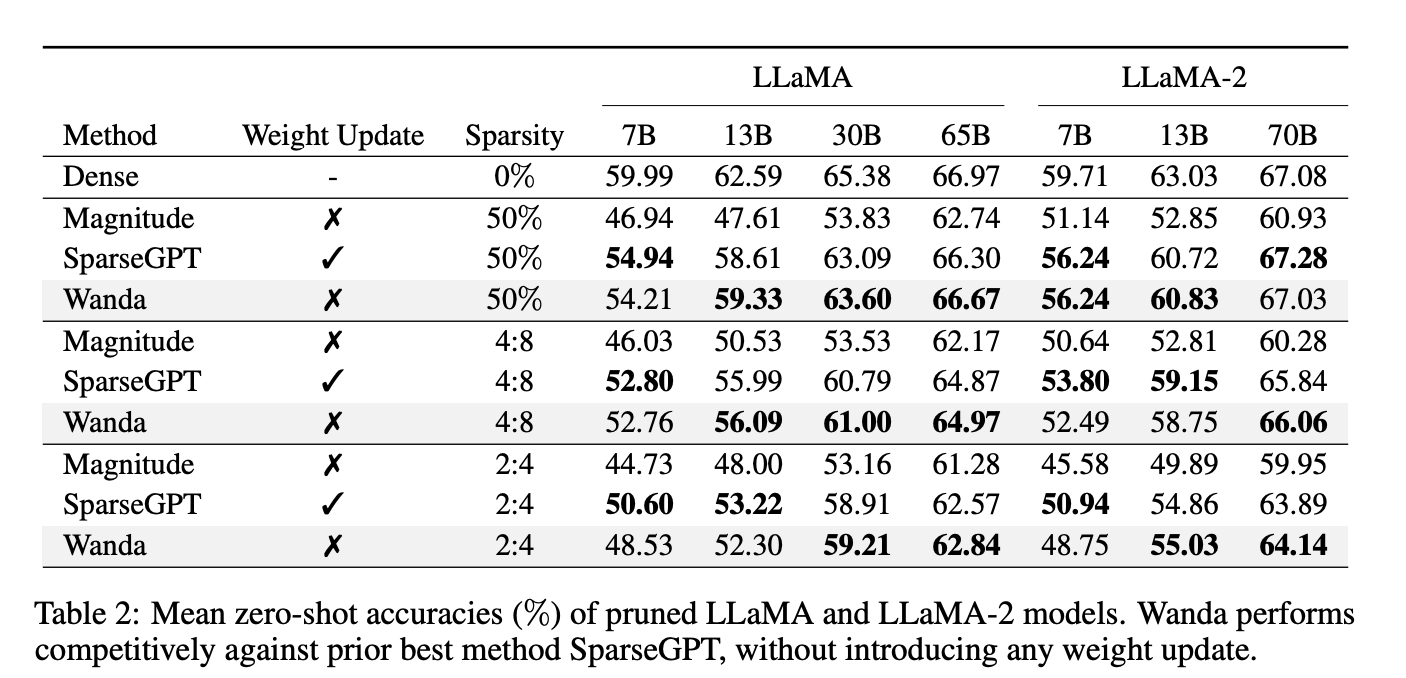
모델 크기가 작을 때는, pruned LLM과 original dense LLM의 gap 차이가 크지만, model size가 카질수록 이 acc gap이 줄어들었다. 실제로, unstructured 50% sparse LLaMA-65B and LLaMA-2-70B의 성능은 Pruining 전과 거의 유사하다.
-
Large Sparse vs. Small Dense.
- sparsity 타입에 따라 다른 양상
-
unstructured sparsity: large sparse LLMs > small dense LLMs
-
reverse
LANGUAGE MODELING
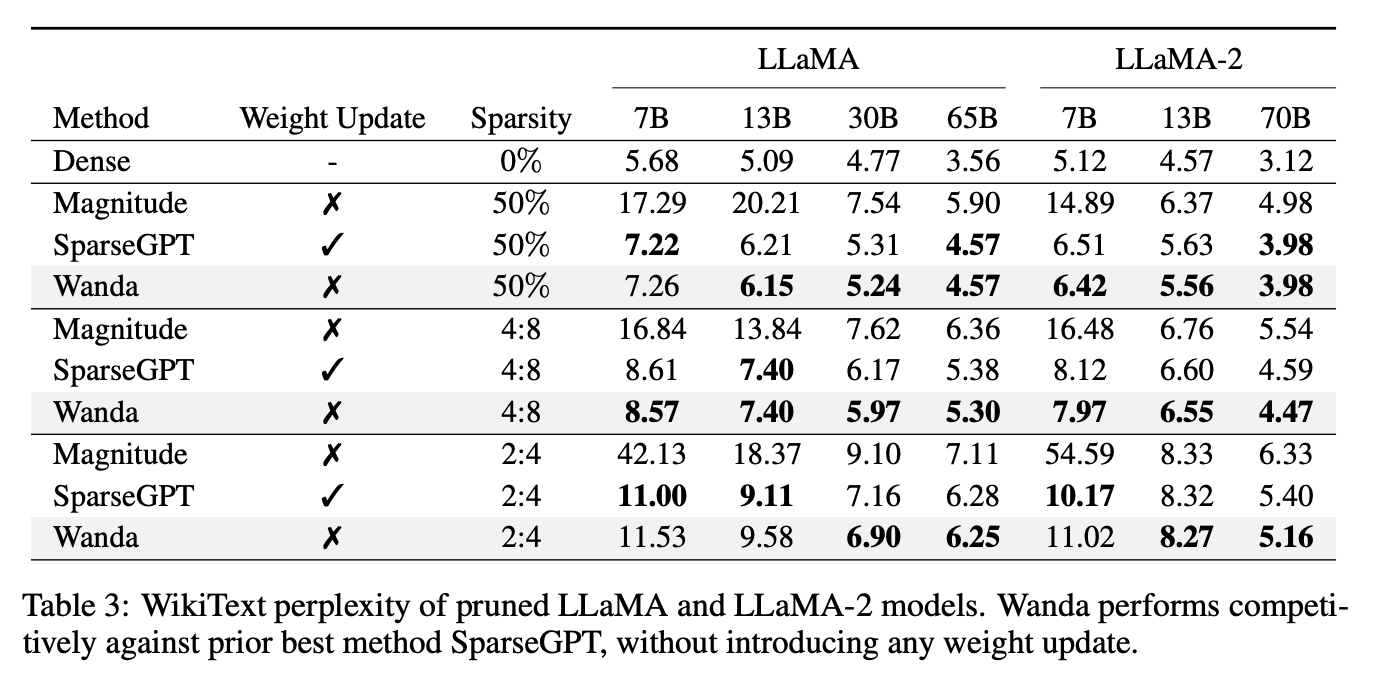
For unstructured 50% sparsity, Wanda의 성능은 SparseGPT과 유사하다.
그러나, appendix에 실은 것도 확인하면 sparsegpt의 성능에는 따라가지 못하는 듯하다.
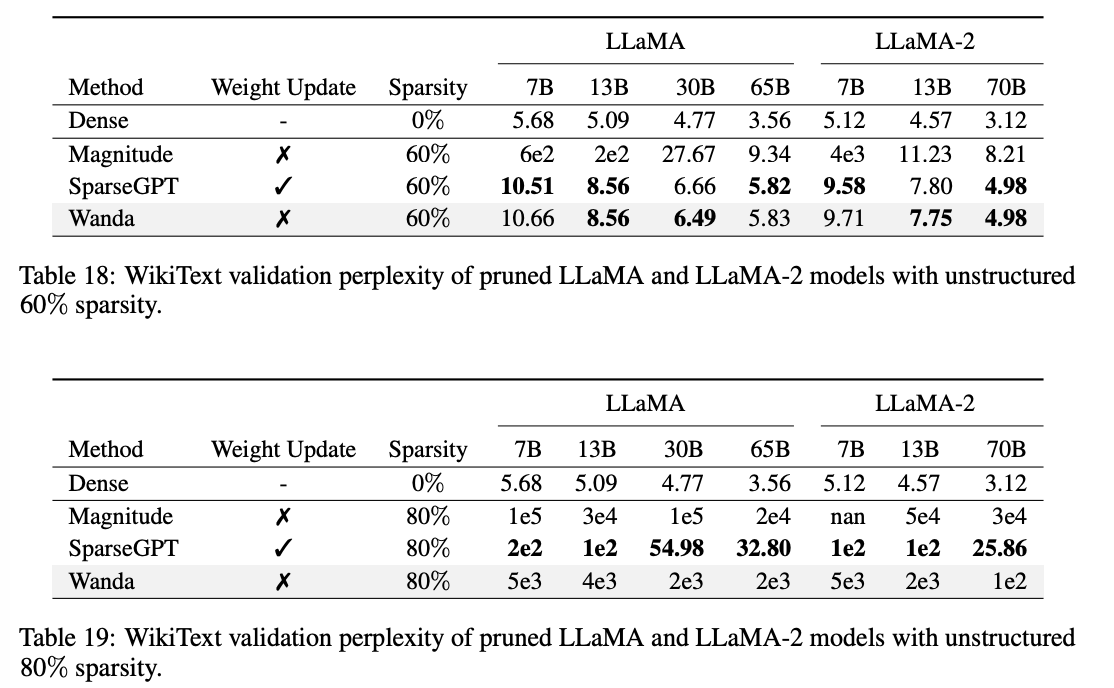
SPEEDUP
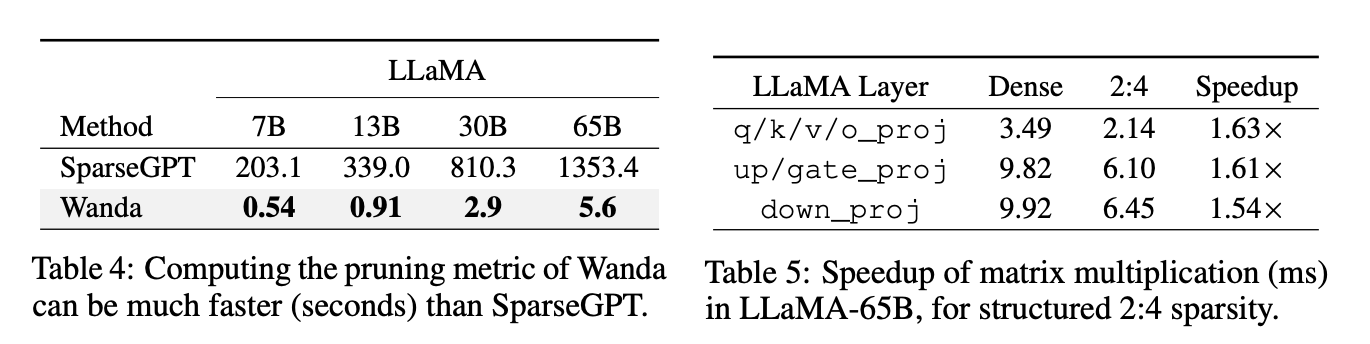
성능에는 따라가지 못하더라도 너무나도 확실한 pruning 속도 개선!
inference speedup은 각 레이어의 Multiplication latency를 측정했다.
ANALYSIS
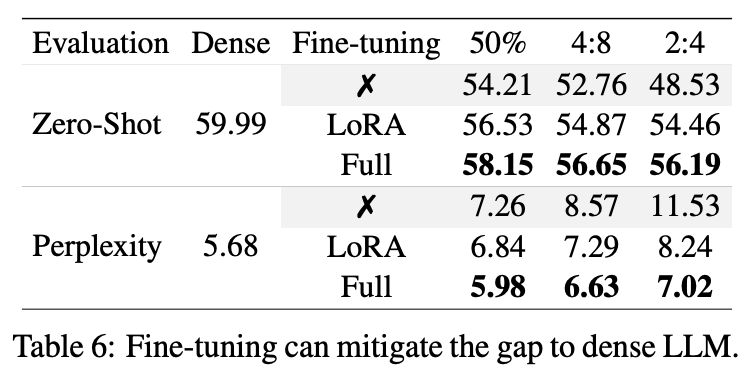
1. Fine-tuning
finetuning이 pruned LLM의 performance drop을 recover할 수 있는가?
-
전략: lora, full finetining
-
데이터: C4
Lora의 경우, additional param이 있지만, 0.06% 밖에. Full fietuning의 경우, mask를 계속 적용함.
2. Robustness to Calibration Samples
calibration sample을 1~256개로 다양하게 주어보았다.
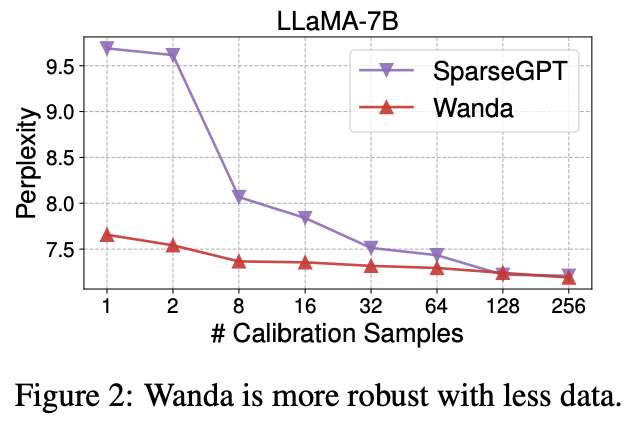
sparseGPT에 비해, wanda는 굉장히 강건한 것을 확인할 수 있는데, 이는 아마 input norm이 full inevrse hessian보다 훨씬 측정하기 쉽기 때문일 것으로 추정된다.
3. Weight Update.
해당 분석에서는 sparseGPT의 weight update가 얼마나 다른 방법론들에서도 도움이 되는지 확인한다.
weight update의 선택지는 다음과 같다
- sequential
- 각 레이어에 대해 prune mask가 먼저 연산이 되고, 그 이후 남아있는 weigth들에 대해 update가 일어난다.
- iterative
- pruning과 weight update가 한 레이어에 대해 반복적으로 일어난다.
sparesGPT의 경우, 128개의 input channel에 대해 iterative하게 update을 진행한다.
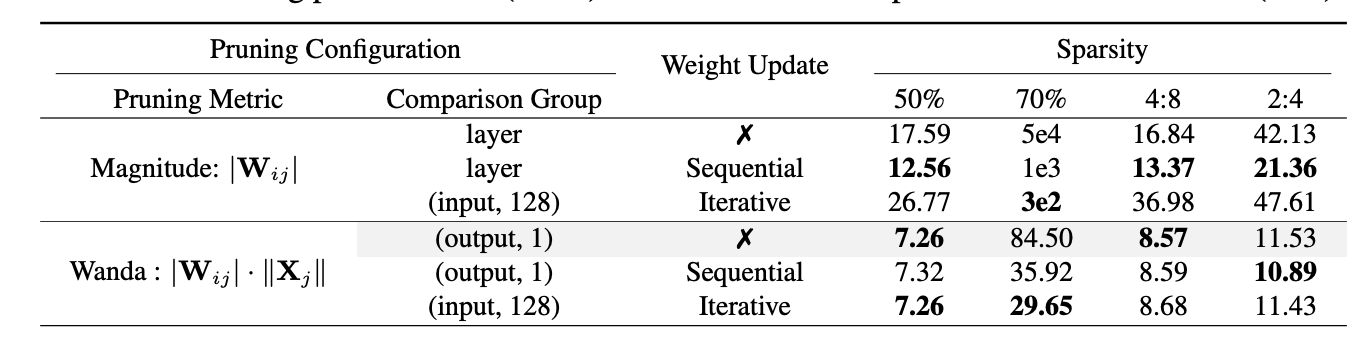
-
weight update는 magnitude pruning의 성능을 크게 증가시킨다.
-
wanda의 경우, pruning이 강하게 들어간 경우에는 도움이 되었지만, 그 외의 경우에는 큰 도움이 되지 않았다.
Conclusion
간단하고, 빠르고, 직관적으로 model pruning을 성공적으로 해낸 연구.
model merging쪽에 관심있는 본인으로서는 task vector에 대해 wanda를 살짝 변형해서 적용했더니 훨씬 robust하고 좋은 성능!
4~5월에는 이거 적용한 제 연구도 가져오겠슴미당 :)