Lion: Adversarial Distillation of Proprietary Large Language Models
논문 정보
- Date: 2024-01-30
- Reviewer: 전민진
- Property: Knowledge Distillation
Abstract
-
지금까지 제안된 knowledge distillation 방법론은 student model의 답변과 teacher model의 답변 align되도록하는, unidirectional knowledge(teacher → student)에 초점을 둠
-
본 논문에서는 이러한 방법론들이 “feedback”을 학습 과정에 포함시킬 가능성을 간과했다고 지적
-
feedback이란 student model의 성능을 저하시키는 어려운 데이터(instruction)을 식별하는 것을 의미
-
feadback을 바탕으로 반복적으로 학습한다면 student model의 성능을 끌어올릴 수 있을거라 봄
-
-
본 논문에서는 3단계(imitation, discrimination, generation)로 구성된 novel한 adversarial distillation framework를 제안
-
teacher model이 prompt를 통해 “hard” instruction을 식별하고 새로운 “hard” instruction을 생성하도록 하도록 함
-
생성한 instruction을 바탕으로 다시 student model 학습, 이를 반복
-
해당 프레임워크를 통해, ChatGPT로부터 knowledge를 transfer, 70k training data만을 사용
-
-
실험 결과, open-ended generation 능력이 ChatGPT에 상응할 뿐만 아니라, BIG-Bench Hard, AGIEval에서 기존의 instruction-tuned model를 능가하는 성능을 보여줌
Introduction
-
최근, LLM이 새로운 task에 대한 zero-shot 성능을 보였지만, 대부분의 모델이 소유권이 있음
-
proprietary “teacher” LLM으로부터 knowledge distillation을 하기 위해 teacher model의 답변과 student model의 답변을 aligning하는 방식을 사용
- 이 때 사용되는 instruction은 manully or automatically generated
-
그러나 지금까지는 학습 과정에 “feedback”을 활용하려는 시도가 없었음
-
학교 수업을 생각해보면, 학생의 성적을 저하시키는 포인트를 짚어서 feedback을 해줌
-
즉, feedback은 학생 개개인에 적합한 맞춤형 학습을 제공
-
-
adversarial knowledge distillation(AKD)에 영감을 얻어, proprietary LLM을 compact student model로 distilling하는 adversarial framework를 제안
- AKD는 반복적으로 generated hard sample로 학습해서 student model의 성능을 끌어올리는 방법론
-
하지만, 바로 AKD방법론은 teacher model의 weight나 gradient가 필요하기 때문에 현상황에 바로 적용할 순 없음
-
이러한 문제를 우회하기 위해, unparalleled role adaptability를 극대화
- teacher model이 referee(to discriminate hard instructions), generator(to produce new instructions)역할도 같이 함
-
-
해당 프레임워크는 다음과 같은 단계로 구성
-
imitation stage : to align the student’s response with the teacher’s repponse
-
discrimination stage : to identify hard instructions
-
Generation stage : to produce new hard insturctions for escalating the challenges presented to the student model
-
Alpaca’s training data(175개의 사람이 작성한 seed instruction으로 생성된 데이터셋)으로 기반으로 해당 프레임워크를 3번 반복, 총 70K data로 student model을 학습(iteration한번에 6K data얻음)
-
실험 결과, instruction-tuned baseline model보다 뛰어난 성능 보임
- Vicuna보다 더!
-
본 논문의 핵심 contribution은 다음과 같음
-
LLM에 adversarial knowledge distillation을 적용한 첫번째 논문
-
human annotation이 없이 70k의 data로 instruction tuning한 Lion-13B 모델이 ChatGPT의 open-ended generation 성능에 필적함
- 다른 SOTA모델(Vicuna—13B)보다 reasoing tasks에서 뛰어난 성능을 보임
-
범용성이 좋음
- ChatGPT외의 다른 proprietary LLM에도 해당 학습 방법을 적용할 수 있음
-
Related Work
-
Knowledge Distillation
-
KD를 할 때, privacy, legality, security, confidentiality 등으로 인해 학습에 사용할 수 있는 data가 제한적
-
이러한 문제를 해결하기 위해, student model을 teacher model에 align하는 data-free KD method가 제안됨
-
관련 있는 proxy data를 사용
-
learnable generator로 생성된 synthetic data를 사용
-
teacher model inversion
- 학습 데이터의 공통된 특징을 재사용해서 다른 data를 생성(비전논문)
-
-
** 이러한 방법론들은 teacher model의 gradient나 weight가 필요
- 한편으로는, data-free model extraction(or stealing)이라 불리는 연구가 제안
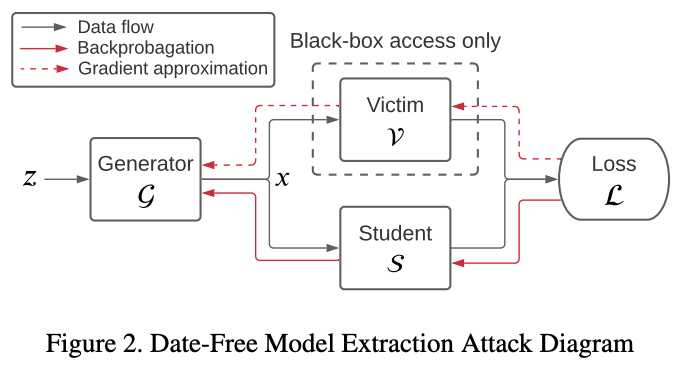
- generator를 update하기 위해 teacher model의 진짜 gradient을 근사하기 위한 zero-order estimation과 같은 방법론을 적용(빨간색 점선 부분)
- 이러한 방법론을 그대로 적용할 경우 크게 2가지 문제가 발생
- **image-based classification task를 위해 설계된 방법론이기 때문에, teacher model에서 continuous softmax vector(activation function에 넣기 전)에 접근 가능하다고 가정**
- 또한, zero-order gradient의 경우, responses가 sequence-oriented이기 때문에 문제가 됨 ⇒ 아마 각각의 단어 벡터를 생성할 때 직전 단어들에게 영향을 받아서 생성되기 때문에, x로 gradient를 흘리려면 이 방향도 고려해야하기 때문?
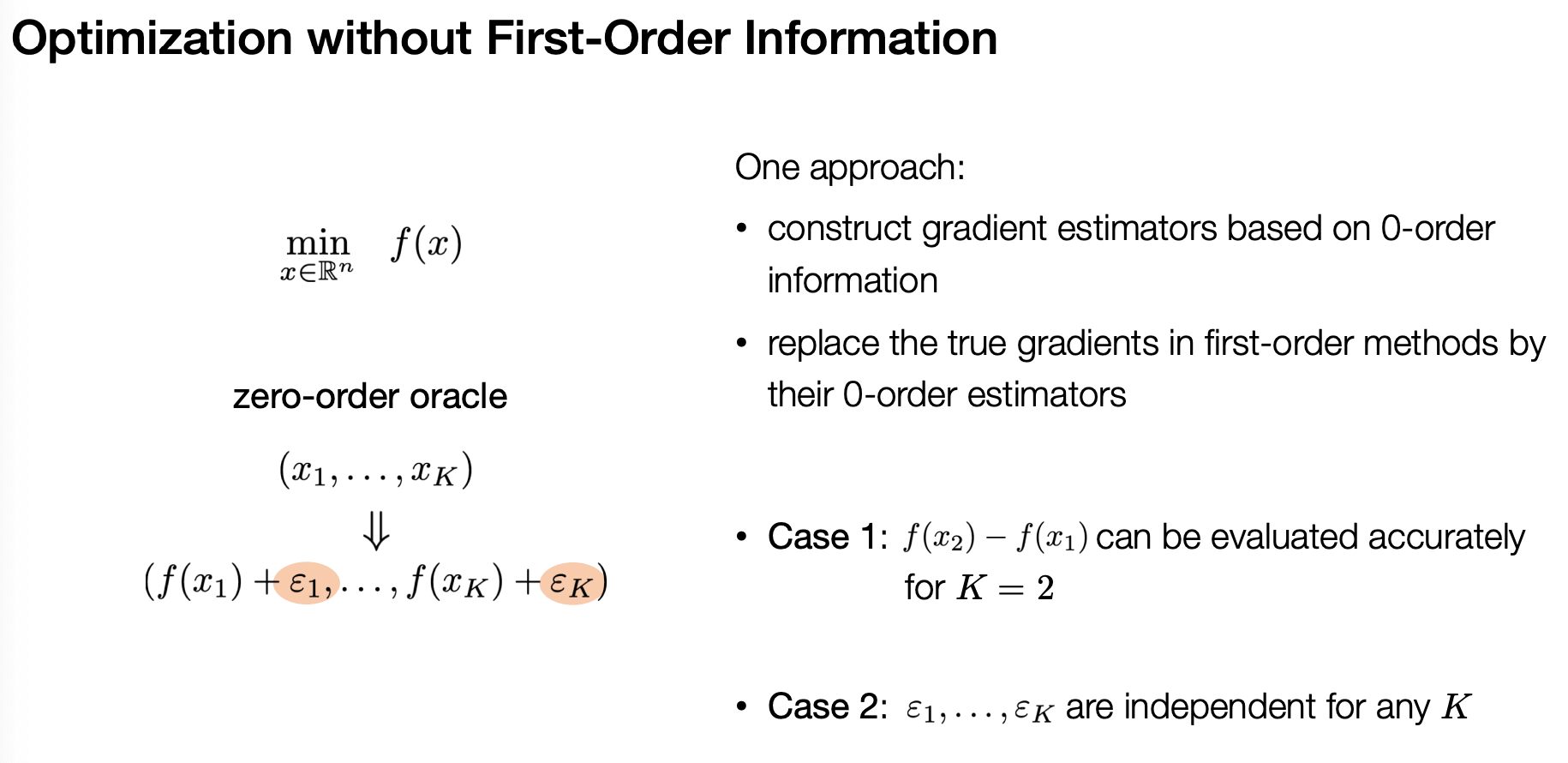
- zero-order gradient
- 0-order 정보로 gradient 근사 / 비전 논문에서는 input x를 기반으로 gradient를 근사한다고 함
- teacher model의 학습 데이터 분포를 모방하는 diverse, high-quality instruction을 생성하는 효과적인 instruction generator를 개발하는 것이 image domain보다 훨씬 어려움
Method
-
문제 정의
-
teacher model T(x;\theta^T)의 학습된 지식을 이용하려고 함
- \theta^T는 inaccessable
-
목표는 student model S(x;\theta^S)에 teacher model의 지식을 넣는 것
- 이상적으로, uniform data distribution에 대해 model discrepancy의 expectation이 최소화될 때, student model이 optimal
-
본 논문의 저자들은 expectation의 upper bound를 낮추고자 함
-
⇒ hard sample에 대한 model discrepancy를 낮추자!
- 단, 학습 과정에서 hard sample를 그대로 student가 마스터(?)할 것이니, 곧 easy sample로 바뀔것
⇒ 지속적으로 hard sample를 생성해서 학습하는 프레임워크 필요
- Initialization
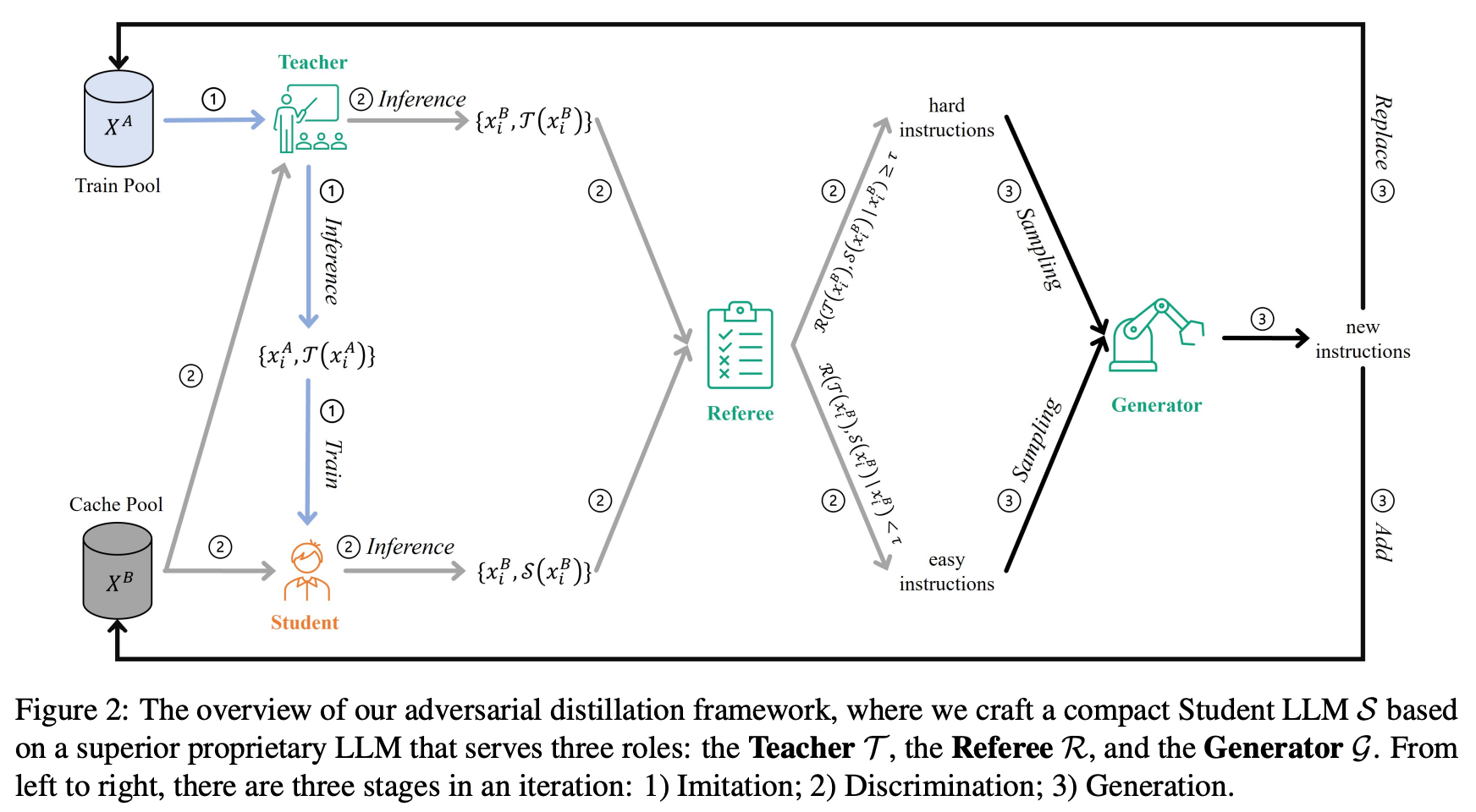
-
4가지 역할과 2가지 data pool이 존재
-
Teacher, Student, Referee, Generator
-
Student로는 LLaMA와 같은 foundation LLM으로 초기화
-
Teacher, Referee, Generator는 proprietary LLM을 사용
- 각각의 역할은 다른 prompt template을 통해 수행 가능
-
-
Train pool, Cache Pool
-
Train Pool X^A = {xi^A}{i\in[1,N^A]}, 여기서 x는 i번째 instruction, N은 train data 수
-
Cache pool X^A = {xi^B}{i\in[1,N^B]}
-
student와 teacher의 성능을 평가하기 위한 instruction으로 구성됨
-
처음엔 train pool과 같지만, 반복할수록 cache pool은 데이터 누적, train pool은 반복마다 다른 데이터셋으로 교체됨
-
-
-
-
Imitation Stage
-
베이직한 knowledge distillation 단계
-
teacher의 knowledge를 student에게 전달하기 위해, Train pool에 있는 instruction을 forward, instruction-response data를 구축
-
finetune시에는 autoregressive language modeling objective를 최적화하는 방법을 사용해 studunt model이 teacher모델의 response를 align하도록 함
-
-
Discrimination Stage
-
student와 teacher의 성능 차이를 유발하는 “hard” instruction을 찾는 단계
-
이번 단계는 Cache Pool를 기반으로 진행
-
처음엔 Train Pool과 Cache Pool이 같지만, 반복할 때 Cache pool는 새로 생성한 데이터를 누적해서 저장, Train Pool은 교체
-
Cache pool의 저장 용량을 늘리면 더 다양한 범위에서 teacher와 student의 performance gap을 평가 가능
-
-
이 단계에서는 proprietary LLM이 “referee”로서 활동, teacher와 student사이의 성능 갭을 정량화
- Cache pool안에 있는 각각의 instruction x_i^B를 student, teacher에 forward, 해당 instruction과 모델의 forward결과를 LLM에 넣어서 둘의 퀄리티 차이를 측정
-
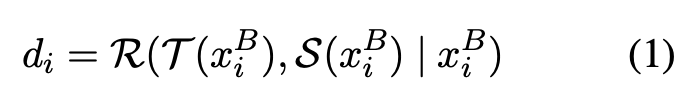
- helpfulness, relevance, accuracy, level of detail을 고려하여 모델 output의 점수를 각각 측정, 둘의 차이가 d_i
- 단 positional bias를 고려하여 순서 바꿔서 2번 실행, 평균값을 최종 점수로 씀

- 이 때, 점수 d_i 가 threshold \tau보다 크면 “hard” instruction으로 분류, 아닐 경우 “easy” instruction으로 분류
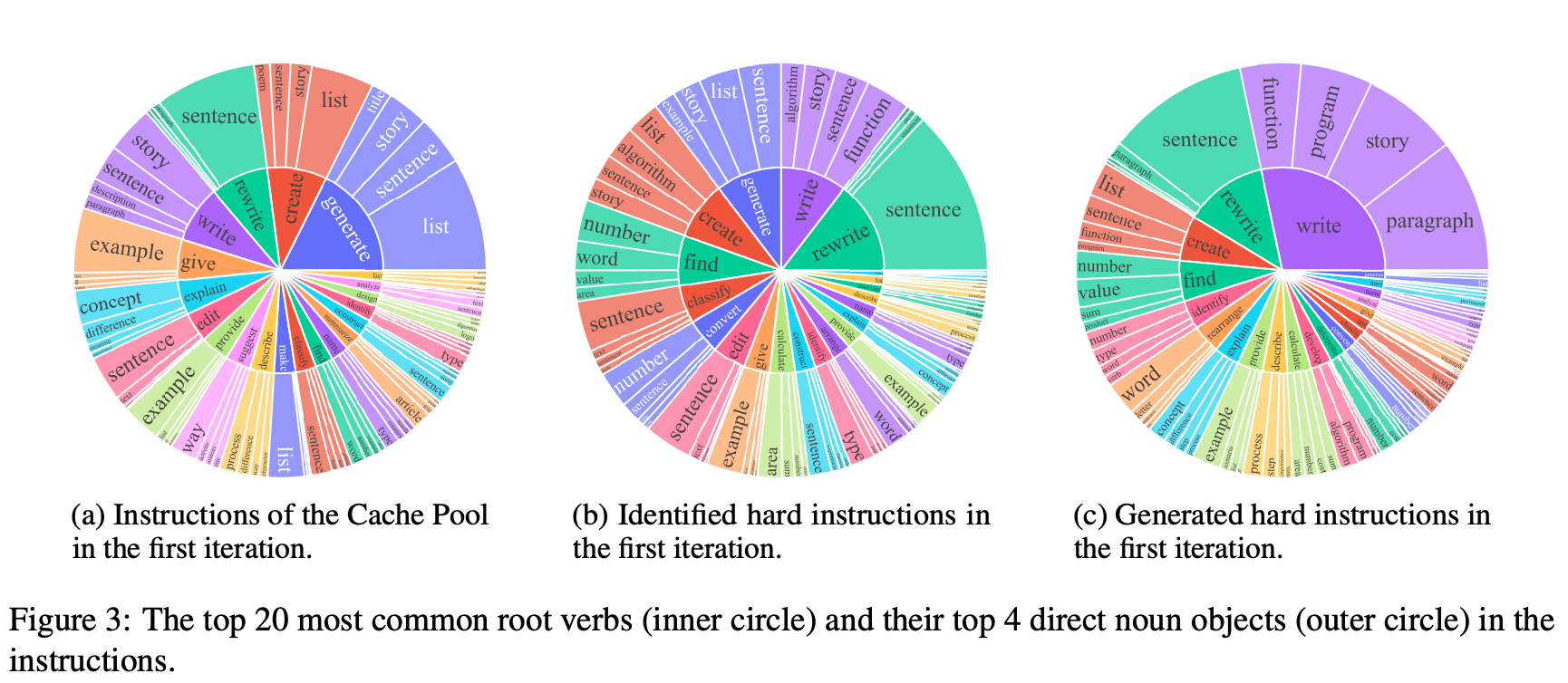
- a와 b를 비교해보면, hard instruction의 pool이 기존 학습데이터셋과 꽤 다르고, 좀 더 복잡한 math, coding과 같은 태스크에 초점을 두고 있다는 것을 알 수 있음
-
Generation Stage
-
hard instruction의 data distribution에 근사해 instruction을 생성하는 단계
-
proprietary LLM을 generator로 사용하여, instruction을 생성
-
hard instruction에서 랜덤하게 instruction을 샘플링, 이를 바탕으로 prompt를 사용해 new instruction 생성
- 새로운 instruction은 샘플링된 instruction과 task type, domain이 같아야함
-
catastrophic forgetting문제를 줄이고 다양성을 높이기 위해서, easy instruction에서도 instruction을 샘플링, 새로운 instruction을 생성
- 동일 도메인에 속하지만, 보다 long-tail distribution을 나타내는 instruction을 생성하도록 유도
-
-

-
각 iteration마다, N개의 새로운 instruction을 생성하고, generated hard instruction과 generated easy instruction의 비율 r을 유지하도록 함
-
여기서 r이 1이면 generated hard instruction만 있는 경우
-
또한, 다양성을 높이기 위해, new instruction이 기존 cache pool에 있는 instruction과 ROUGE-L기준 0.7보다 낮도록 함
-
-
마지막으로, generation stage에서 생성한 데이터로 train pool을 교체하고, cache pool에는 생성한 데이터를 누적해서 추가함
-
Min-Max Game Interpretation
-
본 논문에서 제안하는 adversarial knowledge distillation framework는 dynamic min-max game으로 해석될 수 있음
-
imitation stage에서 student를 finetune, student와 teacher사이의 model discrepancy를 최소화
-
discrimination, generation stage에서 model discrepancy를 최대화하기 위해 hard instruction을 분류, 생성
-
-
이러한 학습 방식은 student model이 커버하지 못하는 hidden knowledge쪽으로 모델이 학습되게 함
-
여러 번의 iteration을 거치면, 시스템이 이상적으로 equilibrium에 도달해야함
- 이 지점이 student가 모든 hard sample을 마스터, 모든 hard instruction에 대해서 student가 낸 답과 teacher가 낸 답을 referee가 구분할 수 없는 지점
-
⇒ 기능적으로 S와 T를 구별할 수 없게 됨
Experiments Settings
-
Datasets
-
Open-ended Generation Datasets
-
Vicunna-Instructions
-
9개의 task category에 대한 80개의 질문으로 구성
-
LLM의 capabilities를 평가하는데 광범위하게 사용됨
-
본 논문에서는 2가지 세팅에서 LLM의 성능 측정
-
Setting 1 : Vicuna와 같이, GPT-4를 사용해서 teacher(ChatGPT)와 student 의responses quality를 측정(1-10점 사이로 평가), student model의 성능은 teacher model 대비 총 점수의 percentage로 계산
- (ChatGPT의 답변이 100일 때 student의 답변은 몇점인지)
-
Setting 2 : GPT-4에 systematic bias가 있다는 최근 연구를 고려. 해당 연구에서 이를 줄이기 위해, Multiple Evidence Calibration과 Balanced Position Calibration을 제안, human judgements와 유사한 alignment를 얻음
- 아마 이 방식으로 response 점수를 계산했다는 것인듯(논문엔 딱 저 말까지만 쓰여있음. 쓰다가 까먹었나보다..)
-
-
-
-
Reasoning Dataset
-
AGIEval
-
대학 입학 시험을 포함해서 법학 적성 시험 등 human-centric standardized exam으로 구성
-
영어 다지 선다 문제를 선택(8 tasks, 2546 sampels)
-
-
BIG-Bench Hard(BBH)
-
LLM의 능력과 한계를 평가하기 위해 설계된 데이터셋
-
다지선다 문제로 바꿀 수 있는 모든 task를 선택(23 tasks, 5511 sampels)
-
-
Setting
-
CoT나 examplar를 사용하지 않고 zero-shot으로 성능 평가
-
답변의 첫번째 대문자만 gold answer로 간주(exact match), accuracy로 성능 리포팅
-
-
-
-
Baseline
-
LLaMA, Alpaca, WizardLM, Vicuna, ChatGPT
-
Vicuna가 현재 open-source LM중에 탑이라, Vicuna중심으로 비교 진행
-
Vicuna는 공개 API를 사용하여 ShareGPT에서 수집한 약 70K의 사용자 대화로 LLaMA을 fine-tuning하여 생성
-
Alpaca 모델은 fine-tuning에 필요한 데이터셋을 얻기 위해 사람이 작성한 instruction-output 쌍으로 구성된 self-instruct seed를 GPT-3(text-davinci-003)의 프롬프트로 입력하여 추가 instruction(52K 예제)을 생성
-
WizardLM
- it uses an Evol-Instruct method to bootstrap the 52k instruction-following examples of Alapca into a larger set of 250k more intricate instructions. Out of this larger set, 70k examples were selected to fine-tune LLaMA
-
-
-
Implementation Details
-
Training Details
-
student model은 pre-trained LLaMA로 initialized
-
Train Pool과 Cache Pool은 Alpaca에서 사용한 52K의 automatically generated instruction으로 초기화
-
iteration은 3으로 설정, 각 iteration마다 6k의 instruction 생성
-
전체 70K의 데이터로 student model 학습
- 다른 모델과 fair한 비교를 위해!
-
-
-
Inference Details
-
Lion, ChatGPT에서 inference할 때 Temperature로 0.7사용
-
최대 생성 길이 1024
-
다른 파라미터는 default setting
-
baseline의 경우 각자 논문에서 소개된 setting대로 사용함
-
GPT-3.5-turbo API를 쓸 때 각 role에 맞게 상이한 hyperparameter사용
-
-
Experimental Results
- Results for Open-ended Generation
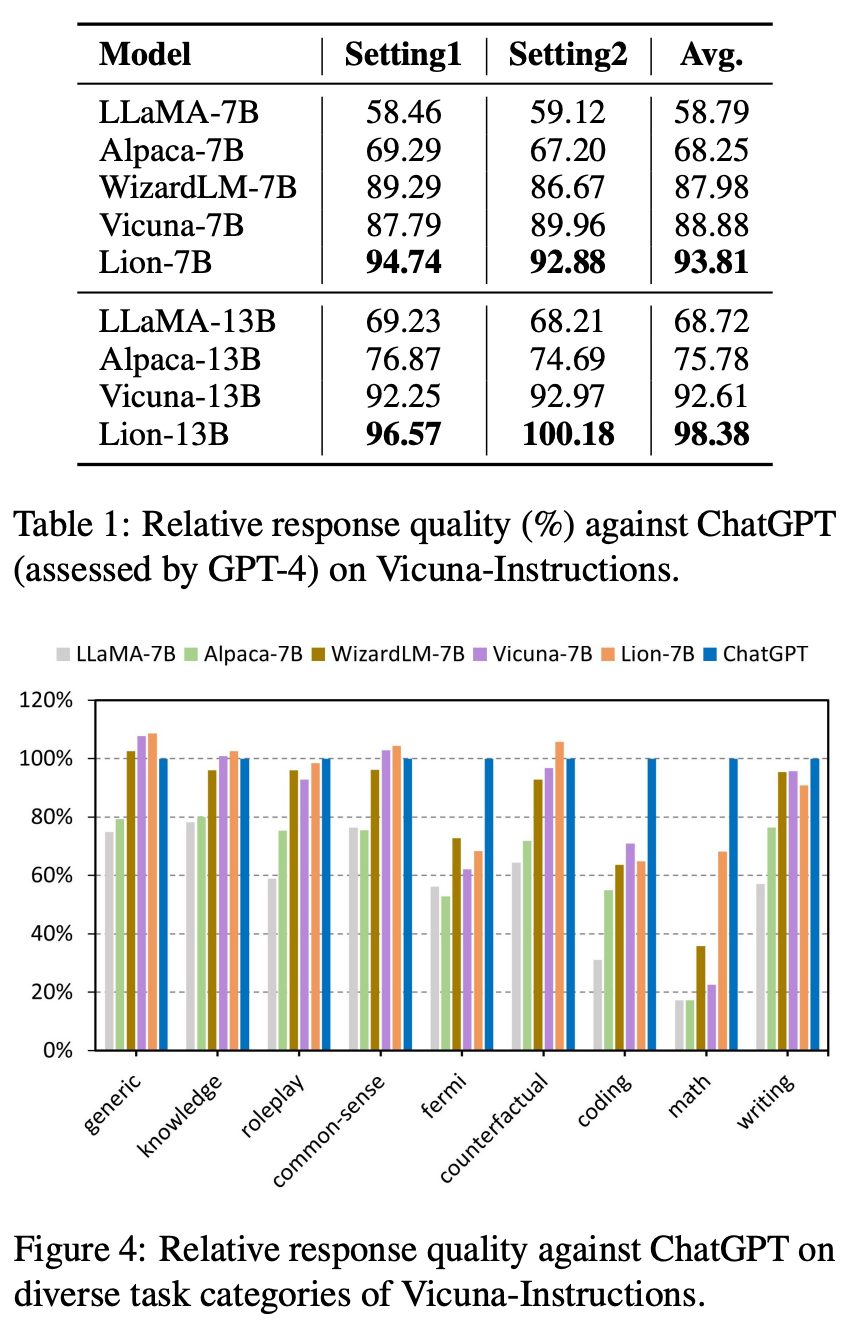
-
ChatGPT를 teacher model로, GPT-4를 referee/rater로 사용
-
baseline에 비해 Lion의 성능이 압도적
-
generic, knowledge, common-sense, counterfactual에 대해선 ChatGPT보다 높은 성능을 보였지만, fermi, coding, math과 같은 task에서는 비교적 낮은 성능을 보임
-
Results for Reasoning
-
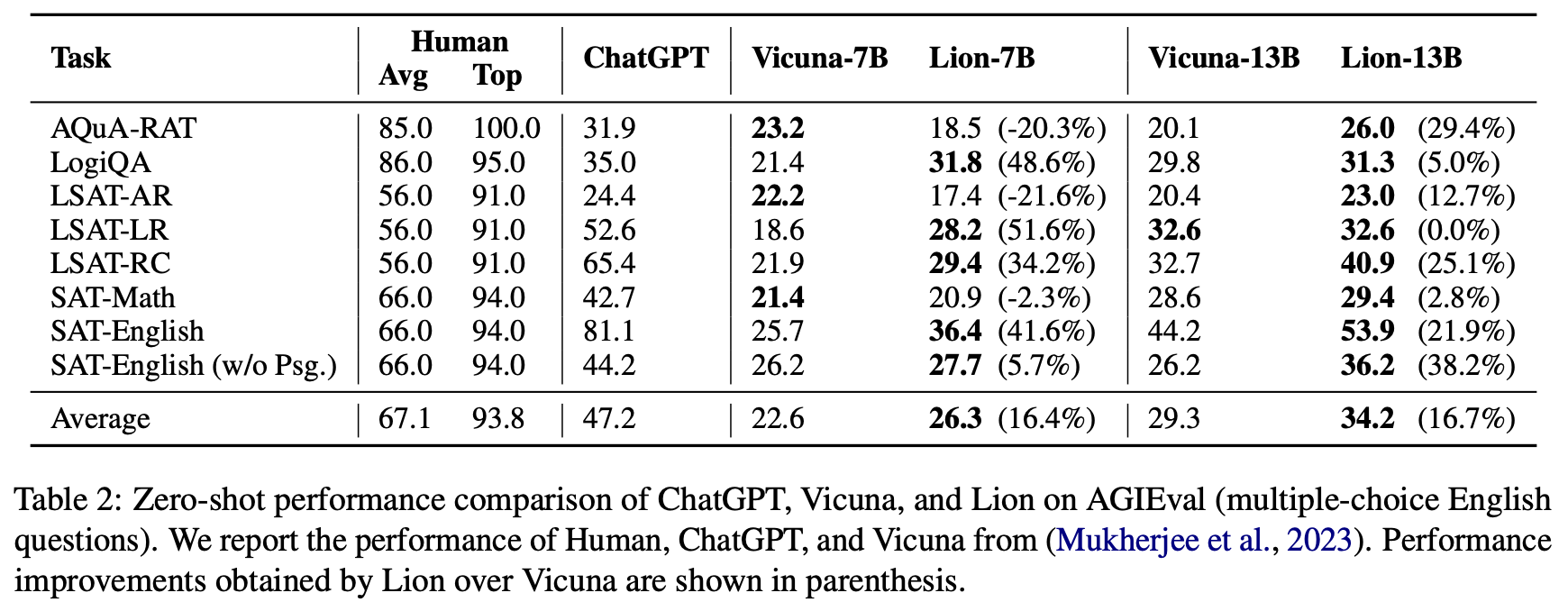
AGIEval
-
다지선다 영어 문제에 대한 AGIEval benchmark의 성능이 나와있음
-
baseline모델 중에선 대체로 뛰어난 성능을 보이지만, ChatGPT보다는 훨씬 낮은 성능을 보임
-
-
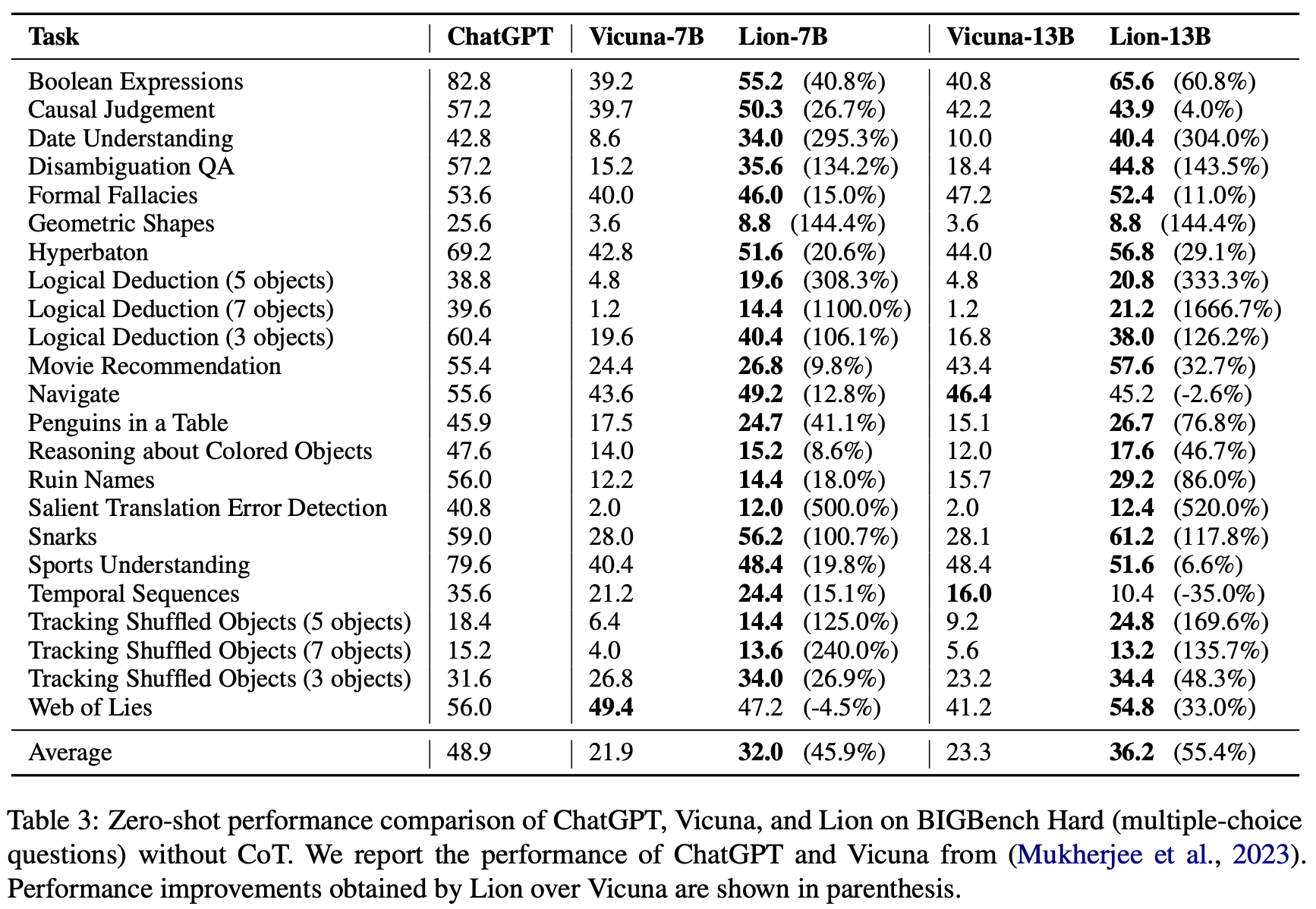
-
BIG-Bench Hard Results
-
standard zero-shot prompting상황에서의 성능이 나와있음
-
Vicuna는 정교한 reasoning task에서는 낮은 성능을 보이지만, Lion은 상대적으로 높은 성능을 보임
-
특히 Movie Recommendation, Snarks(두가지 거의 동일한 문장에서 비꼬는 문장 식별), Tracking Shuffled Objects에서는 Lion-13B가 ChatGPT를 능가함
-
Analyses
-
Ablation study
-
hard와 easy instruction 사이를 가르는 threshold \tau
-
\tau를 0에서 2사이로 두고 실험한 결과, 1.0과 1.5사이가 가장 성능이 좋았음
-
0에서 1로 증가시킬 때는, hard와 easy를 구별하는것이 효과적이어서 성능이 점차 증가헀지만, 1에서 2로 증가시킬 때는 hard instruction의 다양성이 떨어져서 성능이 점차 감소
-
-
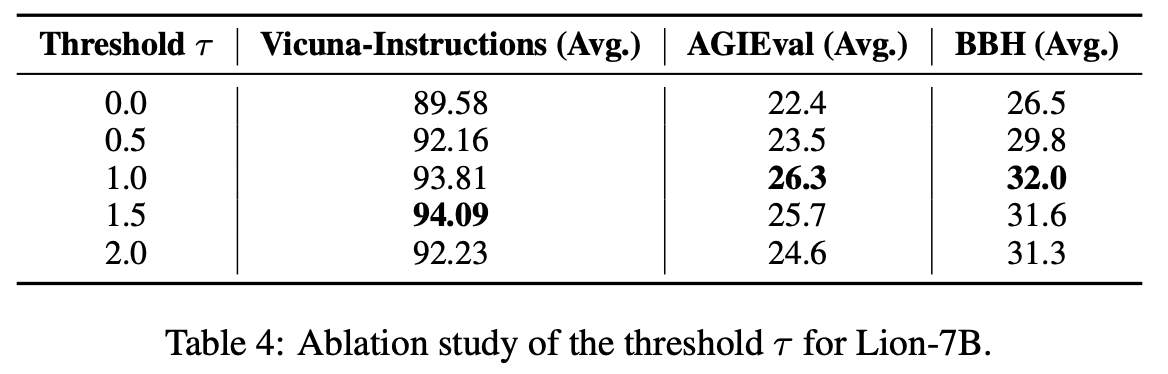
-
generated hard와 easy instruction의 비율 r
-
r이 1이면(1:0) all hard, 0이면(0:1) all easy
-
1:1일때가 성능이 가장 높았음
-
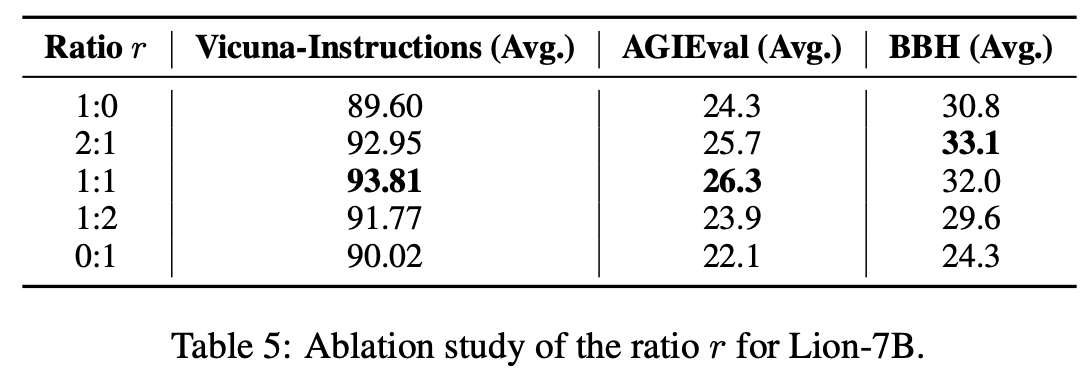
-
The Learning Dynamics of Lion
-
iteration마다 Lion의 성능을 측정
-
본 논문에서 제안하는 방법론의 효과성을 보여주는 장표
- 특히 첫번째 iteration에서 성능이 급격히 향상, challenging example pattern을 식별하는 것이 중요하다는 걸 알 수 있음
-
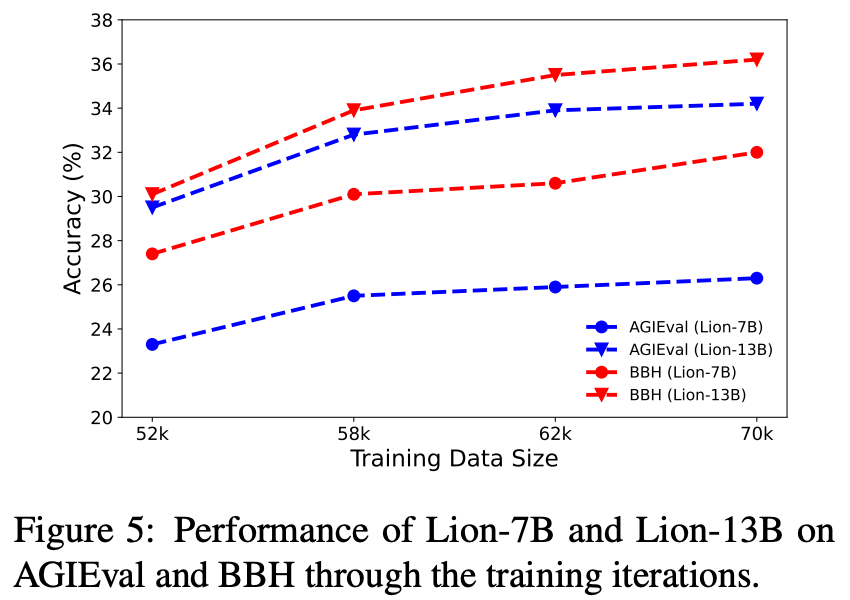
-
Case Studies
-
본 논문에서 제안한 모델과 타모델의 답변을 명확하게 분석하기 위해 만든 장표
-
Vicuna-instruction, BBH, AGIEval에서 9개의 case를 sampling
-
math instuction에선 ChatGPT와 Lion만이 맞는 답변과 풀이과정을 보임
-
conterfactual case에서는 Lion이 더 디테일한 답변을 제시
-
Conclusion
-
본 논문에서는 proprietary LLM을 distill하기 위한 adversarial knowledge distillation framework을 제안
- feedback을 활용하여 데이터를 생성, 이를 학습에 이용하는 프레임워크
-
학습 결과, open-ended generation에선 ChatGPT와 상응하는 성능을, Reasoing task에서는 기존 SOTA모델인 Vicuna와 비슷한 성능을 보임
-
Limitation
-
학습데이터에 dialogues가 포함되지 않아서, Lion의 경우 multi-turn dialogues에는 취약함
-
최대 시퀀스 길이가 1024로 제한됨
-
student model 하나를 학습시키기 위해서 gpt-3.5-turbo API를 450K번 request, 이는 WizardLM의 사용량 624K의 70%에 육박, 비용도 900불 가까이 듦
-
다른 방법론에 비해 iteration이 필요해서 학습 속도가 다소 느림
-
LLM의 성능에 의존해서 학습하는 방법이기 때문에, LLM이 역할이 매우 중대함
-