ORPO: Monolithic Preference Optimization without Reference Model
논문 정보
- Date: 2024-04-23
- Reviewer: 건우 김
- Property: Alignment
Abstract
최근에 LM에 preference alignment에 supervised fine-tuning (SFT)가 많이 활용되고 있음. 본 연구에서 minor한 disfavored generations style로 SFT 중에 penalty를 주는 것이 preference-alignment에 다다르기에 충분하다는 것을 보여줌.
-
ORPO algorithm은 기존 방법론과 달리 preference alignment tuning 단계 및 reference model이 별도로 필요하지 않음
-
Odds ratio가 125M~7B 크기 model의 SFT에서 favored / disfavored style을 구분 짓는데 적절하다는 것을 실험 및 이론적으로 증명함.
Introduction
Large corpus로 학습한 PLMs이 general-domain applications에 사용되기 위해서는 instruction tuning 혹은 preference alignment 과정이 필요함.
- Instruction tuning: 자연어로 되어 있는 task description을 이해하며 unseen task도 수행할 수 있게 학습시키는 방법
→ instruction을 잘 따르긴 하지만, harmful / unethical outputs을 생성하는 문제가 존재함
- Preference alignment: human values와 model 간의 align을 형성시켜주는 학습 방법
→ pairwise preference data가 있으면 RLHF / DPO로 학습 가능 (multi-stage train, reference model 필요)
본 연구에서 pairwise preference dataset이 model alignment에 있어 SFT에 어떤 영향을 주는지 확인하고, 새로운 효과적인 preference alignment algorithm을 제안함.
- ORPO (odds ratio preference optimization): SFT에서 model로 하여금 undesired generation style을 학습하는데 있어 penalty를 줌
→ monolithic alignment method (multi-stage training 필요 x)
→ Reference model 필요 X
Related Works
Alignment with Reinforcement Learning (RLHF)
- SFT Training
→ PLM이 어느 정도 보장된 quality의 response를 생성할 수 있게 fine-tuning
- Reward model Training
Bradley-Terry model을 적용한 RLHF는 두개의 독립적인 instances (y1, y2)에 대해 우위에 대한 probability 추정
training dataset 형태는 triplet 구조 (x, y1, y2)
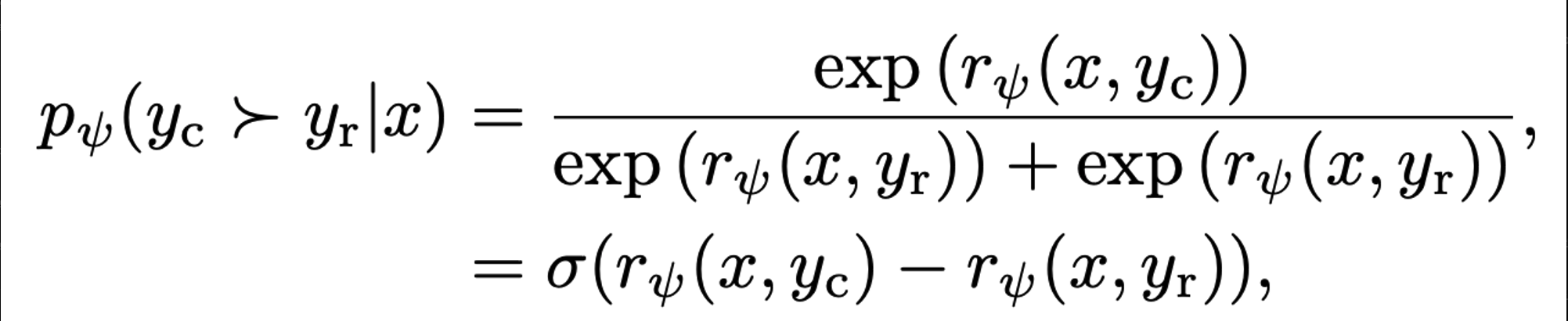
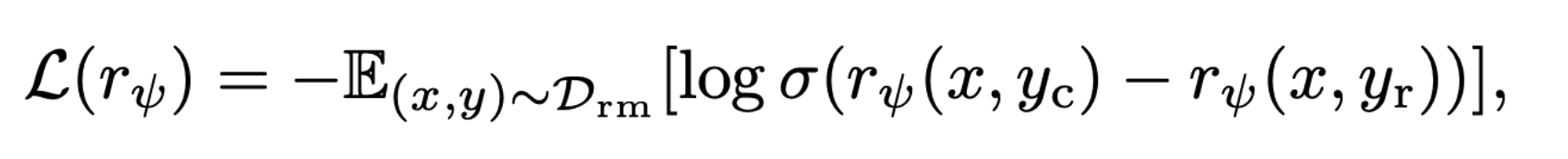
r(y, x): reward model이 주어진 Context에 대한 y의 logit score
→ positive response에 대한 Logit은 크게 / negative response에 대한 Logit은 작게 reward model 학습
- RLHF Training
SFT model이 Context c에 대해 y1~yn candidates 생성을 한 뒤에, 학습한 reward model로 scoring 진행
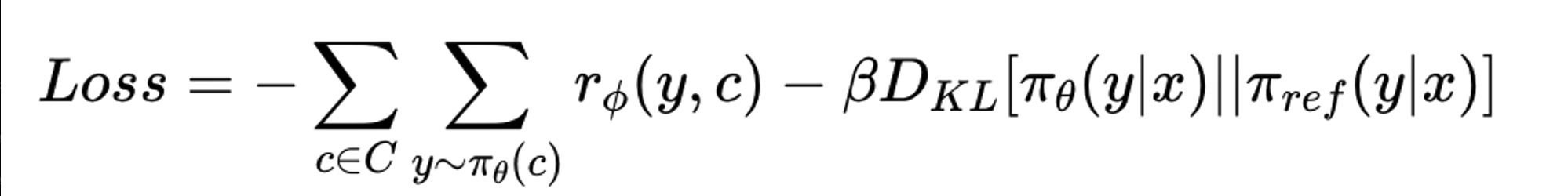
→ chosen response에 대한 reward model의 Score가 커지도록 PPO 학습 진행
Alignment without Reward Model (DPO)
Reward modeling 단계를 preference learning에 포함시켜 별도의 reward model이 필요없이 alignment 학습 가능
-
SFT Training (위와 동일)
-
DPO Training
Reward model이 학습에 사용한 preference dataset을 직접 학습에 사용.
Chosen response에 대한 SFT model과 학습 하고자 하는 model의 ratio가 unchosen case의 ratio보다 커지게 학습
→ 즉, 별도의 reward model이 필요없긴 하지만 학습 중에는 reference model (SFT)이 필요함
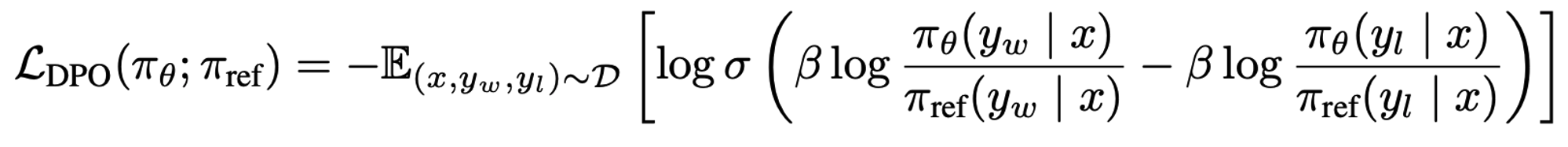
Alignment with Supervised Fine-Tuning
LIMA (2023)와 같이 Human-aligned model을 소량의 high quality dataset (filtered dataset)만 가지고 SFT로 만들 수 있다는 연구들도 등장함
→ SFT의 effectiveness를 보여주긴 했지만, 아직까지 preference alignment를 SFT에 통합 시키는 것에 대한 theoretical background가 부족
The Role of Supervised Fine-tuning
Preference alignment에서 Initial stage로 사용되는 SFT의 loss function과 preference comprehension ability에 대한 분석
-
Cross-Entropy Loss
- CE Loss는 일반적으로 reference에 대한 predicted logits이 낮을 경우에 penalty를 주게끔 objective function이 설계됨
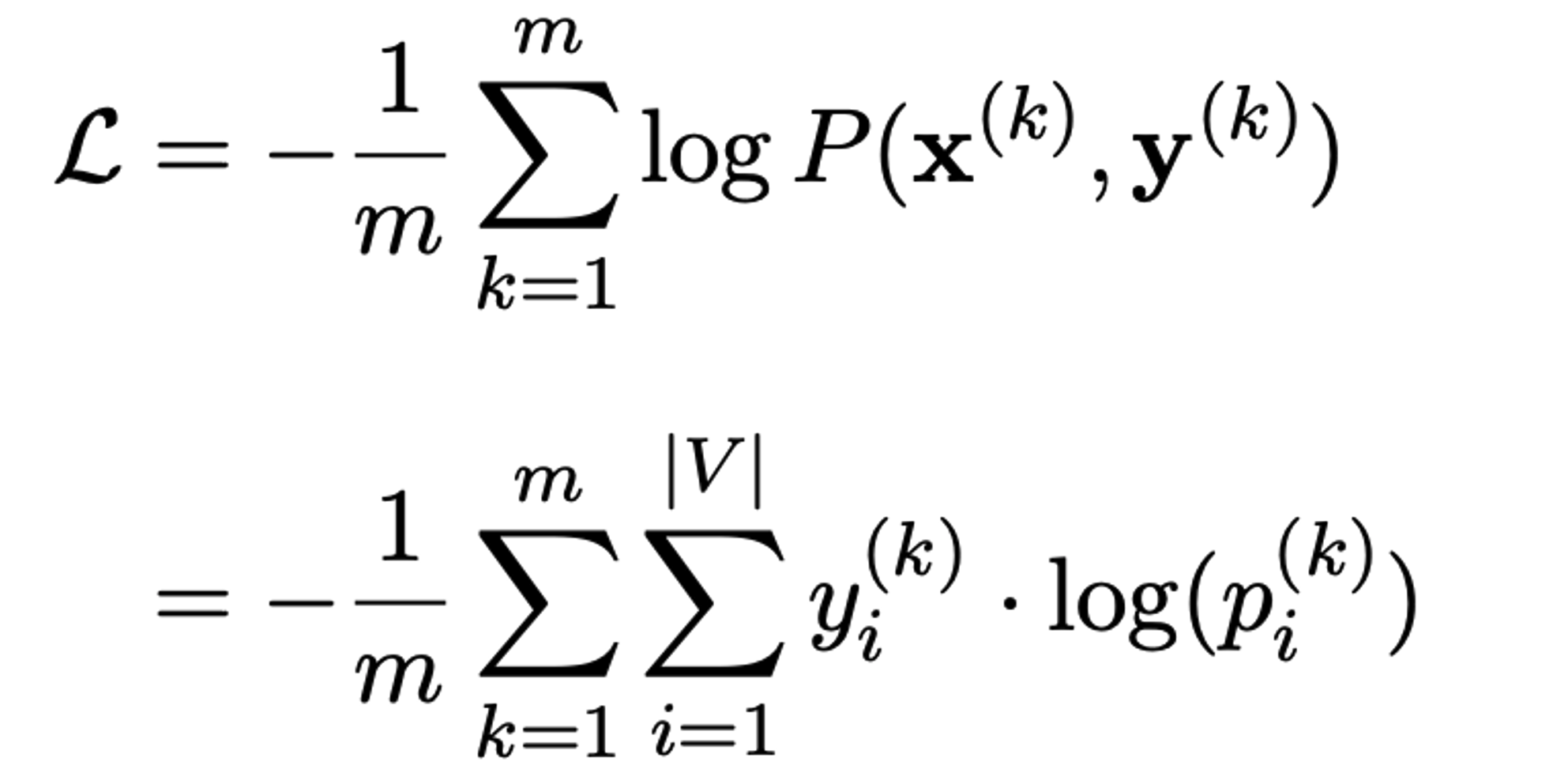
→ 이는 non-answer token에 대한 penalty가 별도로 존재하지 않기 때문에, rejected response에 대한 token의 log prob 값도 커지게 되어 있음. (preference alignment에 있어 치명적인 문제)
SFT는 PLM을 특정 domain에 맞춰 학습 시킬때 주요 역할을 담당하는데, 이는 undesirable style로 token을 생성하는 것에 대한 Likelihood를 높이는 문제가 존재함 (아래 Figure 확인).
- HH-RLHF dataset에서 chosen-response에 대해서만 SFT를 진행하고 chosen 및 rejected response에 대한 log probability
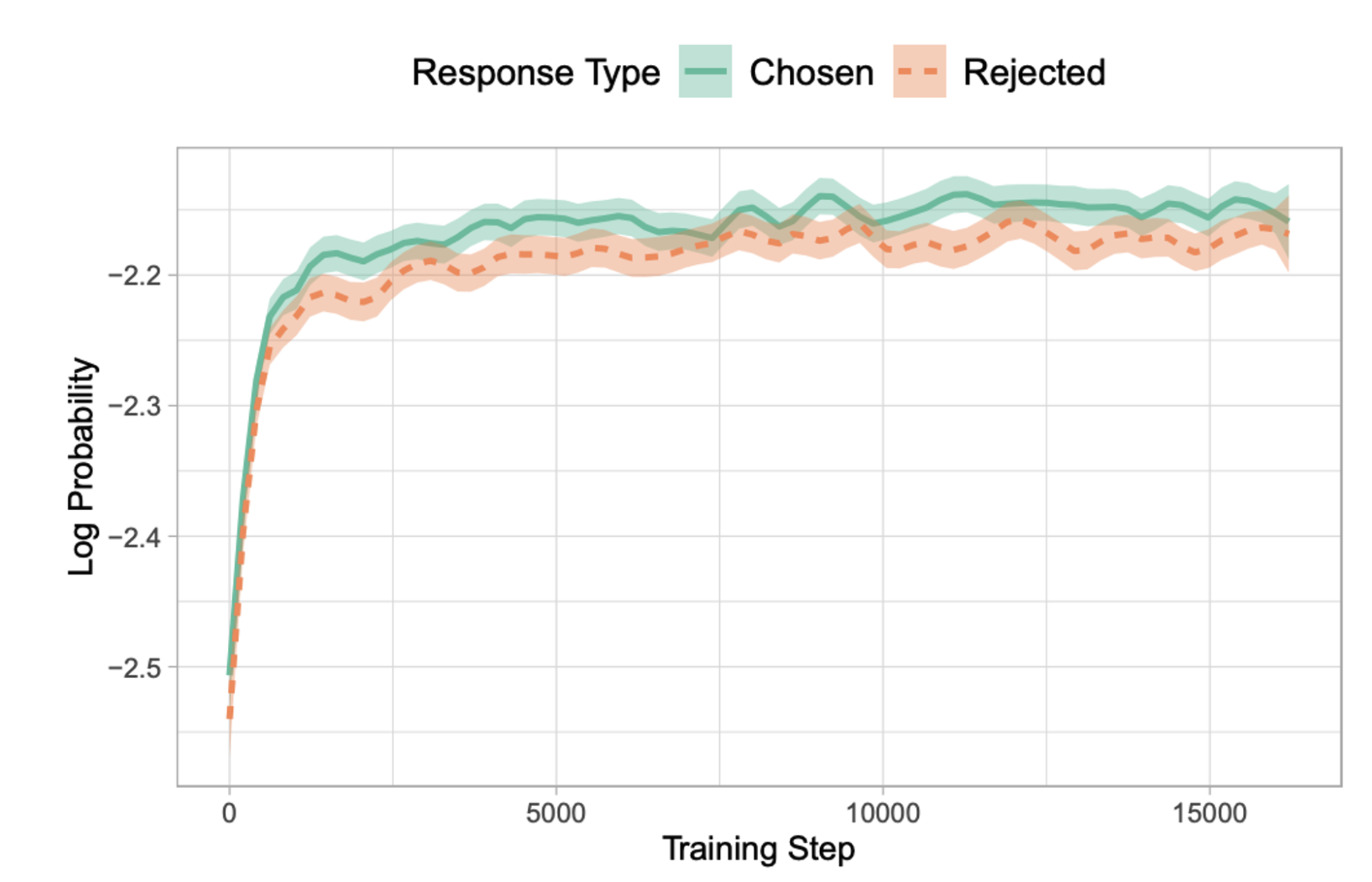
위 figure에서 Rejected response에 대한 log probability 값이 (unwanted generation에 대한 penalty 부재로 인해) 학습할 수록 계속 커지는 것이 관찰됨.
→ 따라서, SFT의 domain adaptaion을 유지하며 unwanted generation styles을 완화시키는 방법이 필요함
-
Penalizing Undesired Generations
- LLM이 유행하기 전에 2019, 2020년도에 unlikelihood penalty를 loss function에 적용하여 unwanted token에 대해 model에게 penalty를 주는 연구도 존재함 (e.g. repetitions issue: previous contexts ‘k’)
→ rejected token에 High probability 주는 것에 영감을 받아 각 query당 disfavored response에 대해 penalty를 주는 monolithic preference alignment method (ORPO) 제안
Odds Ratio Preference Optimization (ORPO)
Odds ratio 기반의 penalty를 기존 CE Loss와 결합하여 Favored response와 disfavored response 간의 style 차이를 구분이 가능
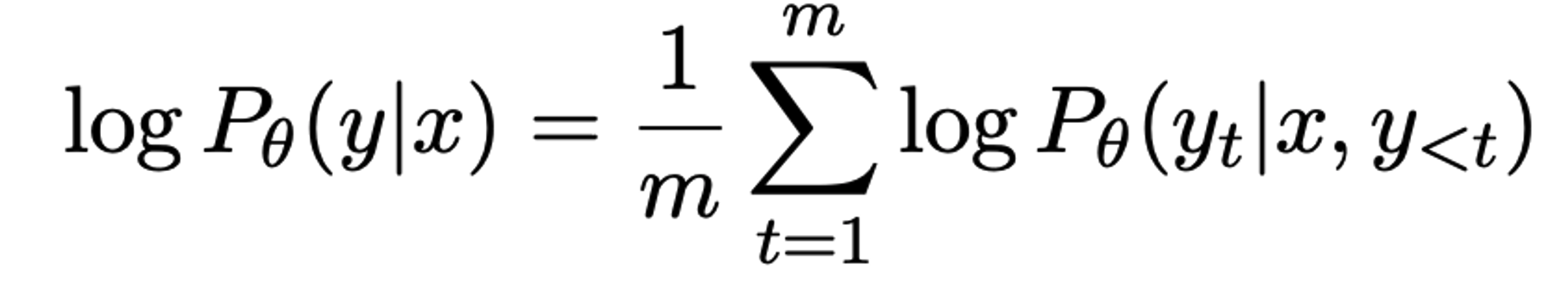
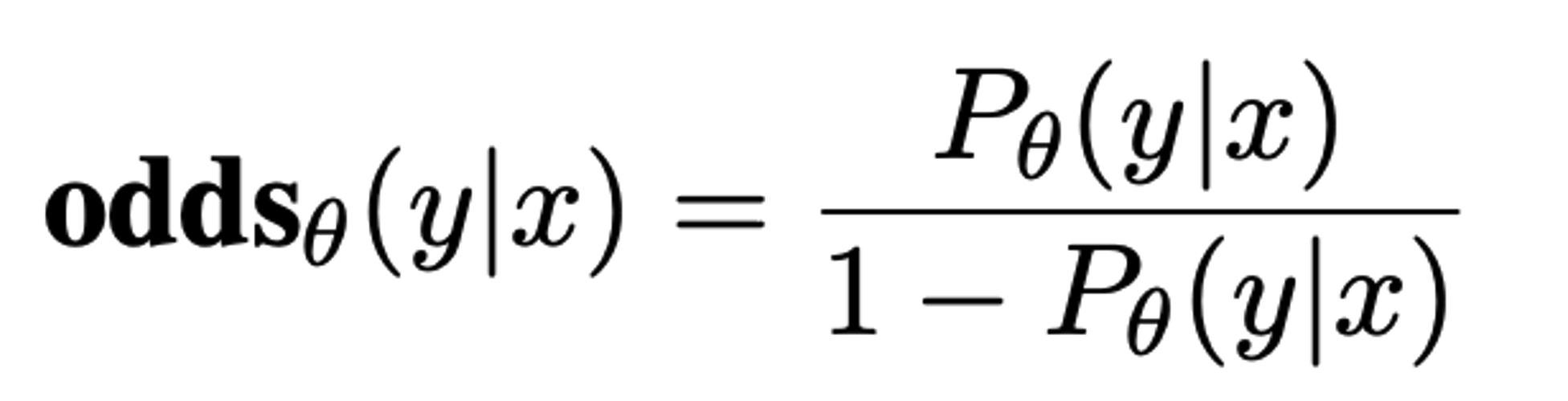
| 직관적으로 odds(y | x)=k 가 의미하는 것은 model이 output sequence y를 생성하는 확률이 그렇지 않은 경우보다 k배 높음을 의미하기에, |
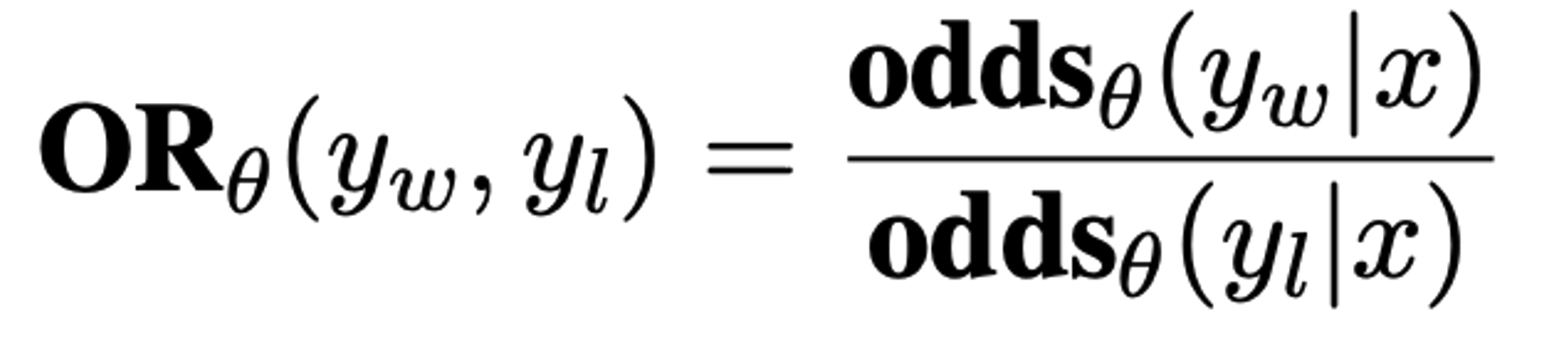
가 의미하는 바를 ‘model이 rejected response보다 chosen response를 얼마만큼 더 잘 생성하는 정도’로 볼 수 있음.
-
ORPO’s objective function
-
SFT loss: causal language modeling (NLL)
-
Relative Ratio loss: likelihood of generating favored response and disfavored response
-
→ OR의 Logit을 Maximize을 해야하기 때문에, log sigmoid 취한 값에 minus를 취해 minimize하도록 치환해줌
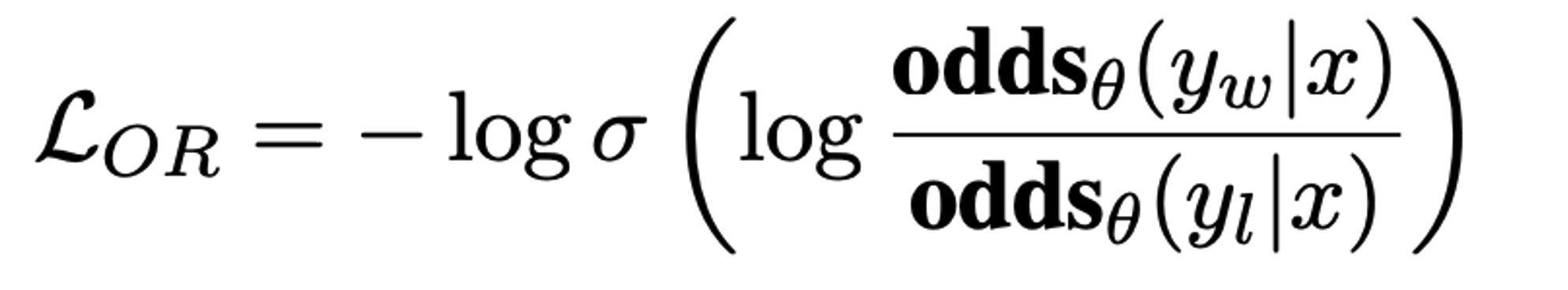
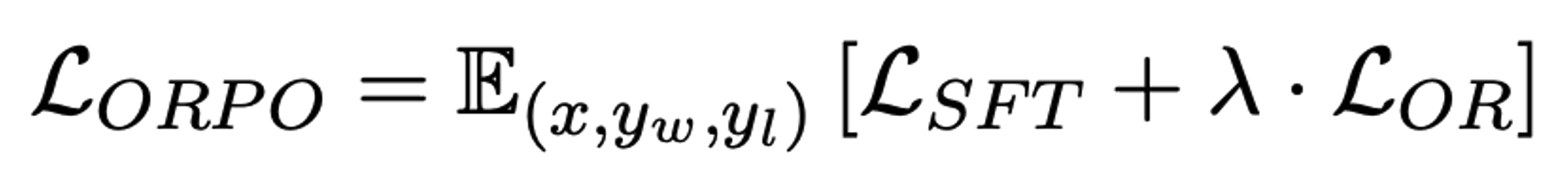
-
Gradient of ORPO
- 유도1

- 유도2

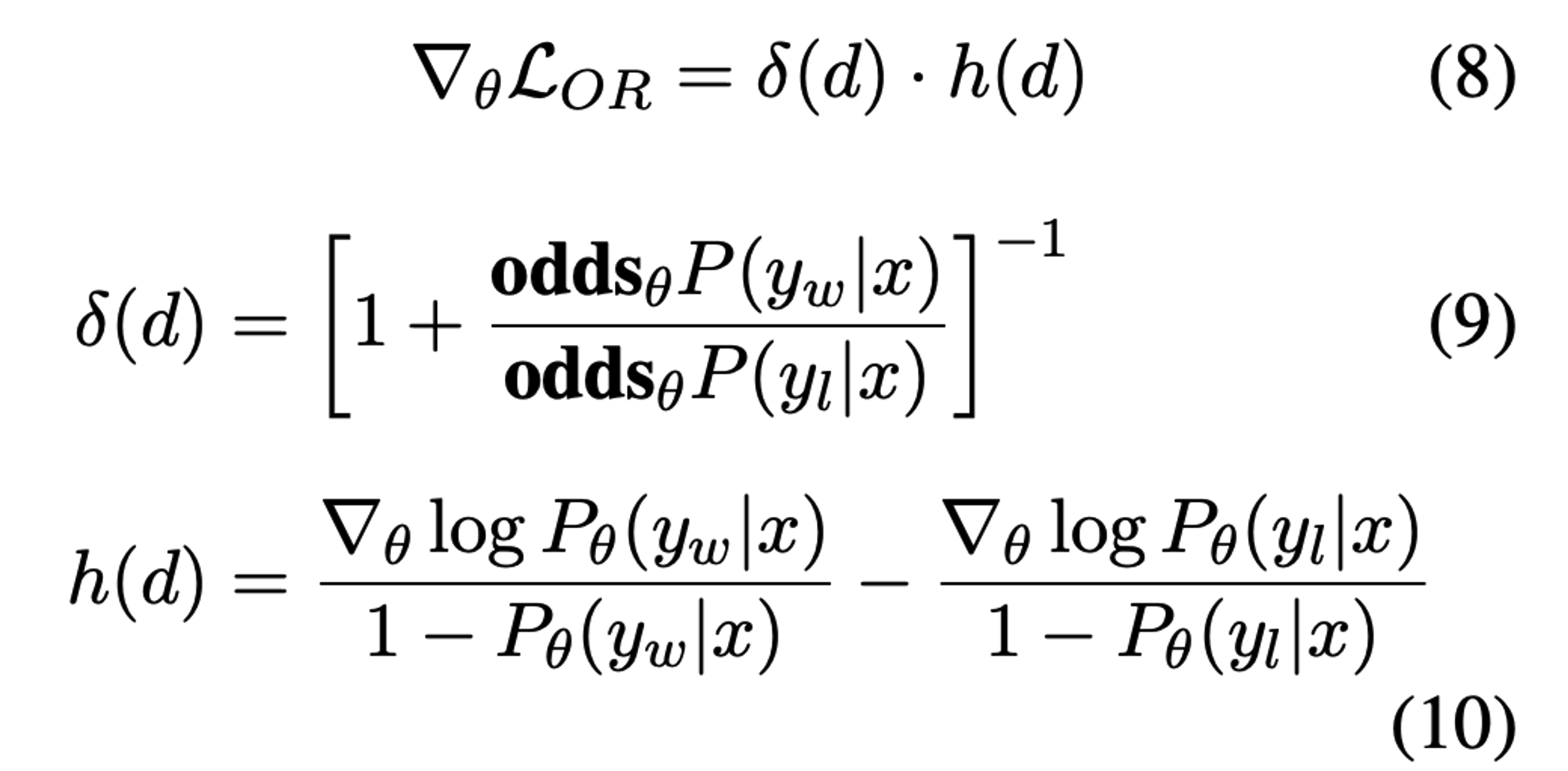
-
Penalize wrong prediction
- eq9: favored response의 odds 값이 상대적으로 disfavored 보다 더 크면 delta(d)는 0으로 수렴
→ delta(d)는 penalty term으로 model이 잘못된 답변을 생성하고자 하면 parameter update를 accelerate함
-
Contrasts between chosen and rejected responses
- eq10
Experimental Settings
-
Model
-
OPT 125M ~ 1.3B (SFT, PPO, DPO, ORPO)
-
Phi-2 (2.7B), Llama2 (7B), Mistral (7B)
- PPO, DPO는 chosen response에 대해 학습한 SFT model위에 학습
-
-
Training dataset
-
Antrophic’s HH-RLHF
-
Binarized UltraFeedback
-
-
Reward Models
- OPT-350M, 1.3B (1 epoch train)
-
Leaderboard evaluation
- AlpacaEval1.0, AlpacaEval2.0
Results and Analysis
- **Single-turn instruction following **
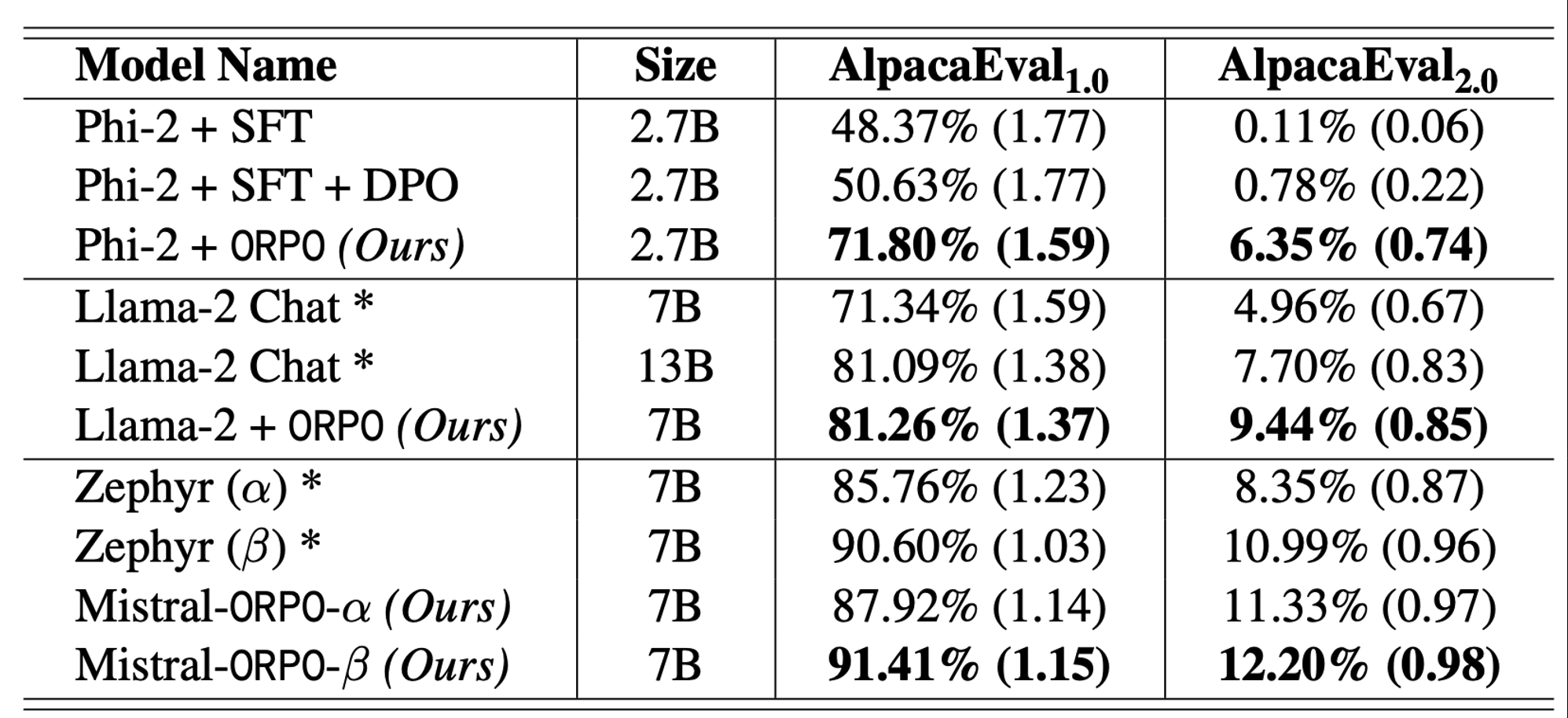
-
Mistral-alpha: orig version
-
Mistral-beta: cleaned version in UltraFeedback
→ model type과 크기에 관계 없이 ORPO를 적용한 것이 다른 alignment preference method 대비 우수한 것을 볼 수 있으며, data quality를 높이면 성능이 개선되는 것을 확인함.
-
Multi-turn instruction following
- MT-Bench results of Mistral-alpha/beta
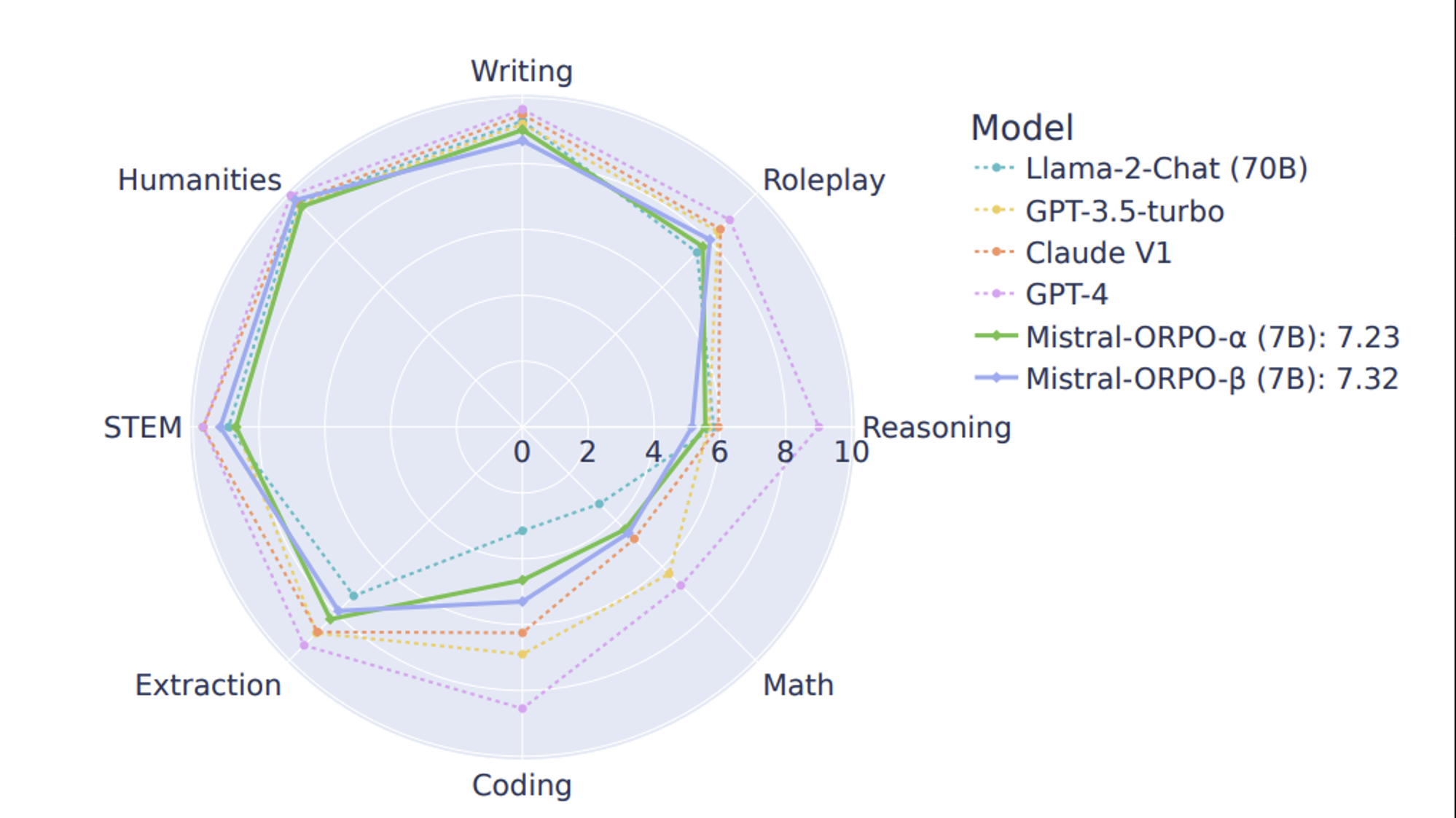
→ reasoning을 요구하는 task를 제외한 나머지에서 Larger size model과 비슷한 성능을 보여줌
-
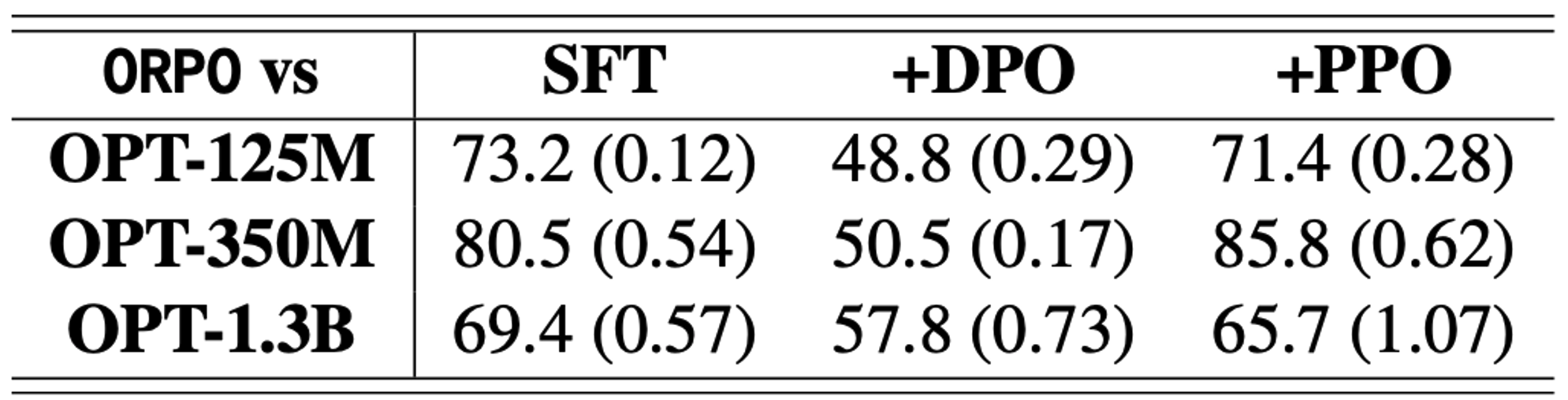
Reward win-rate
- HH-RLHF
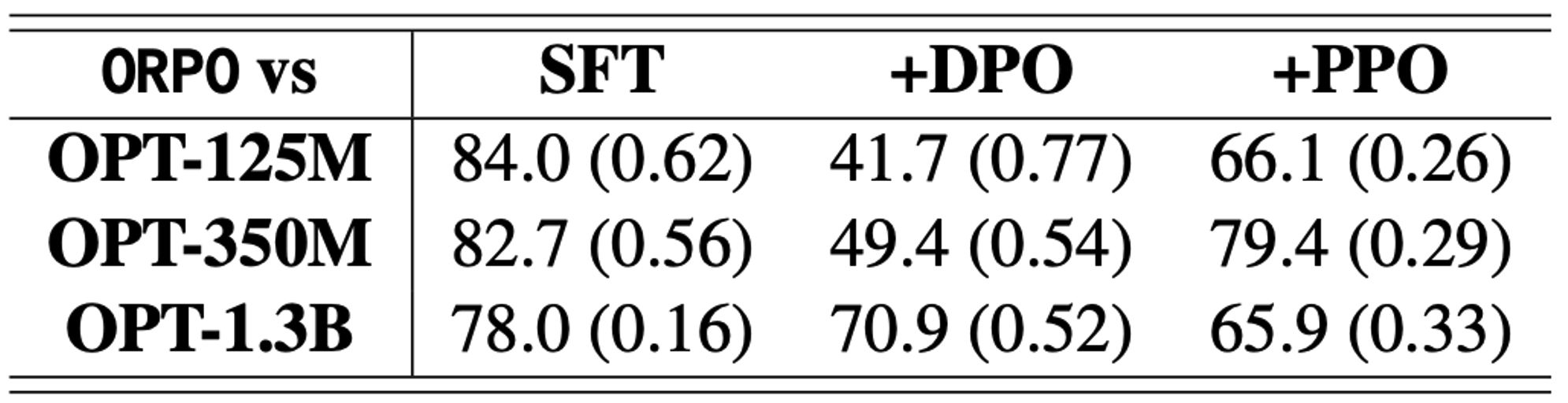
- UltraFeedback
- Reward Distribution
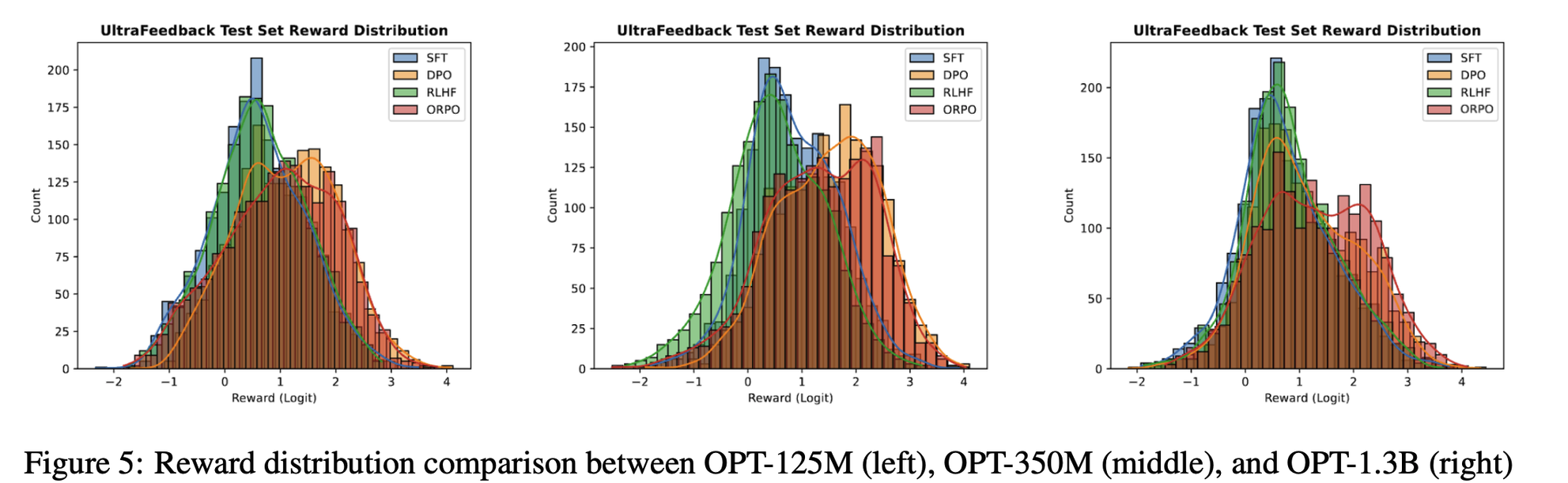
→ 동일한 Input에 대한 response들을 reward model로 scoring을 진행했을 때, reward model size에 상관 없이 ORPO가 모두 더 높은 점수의 분포를 보임
Discussion
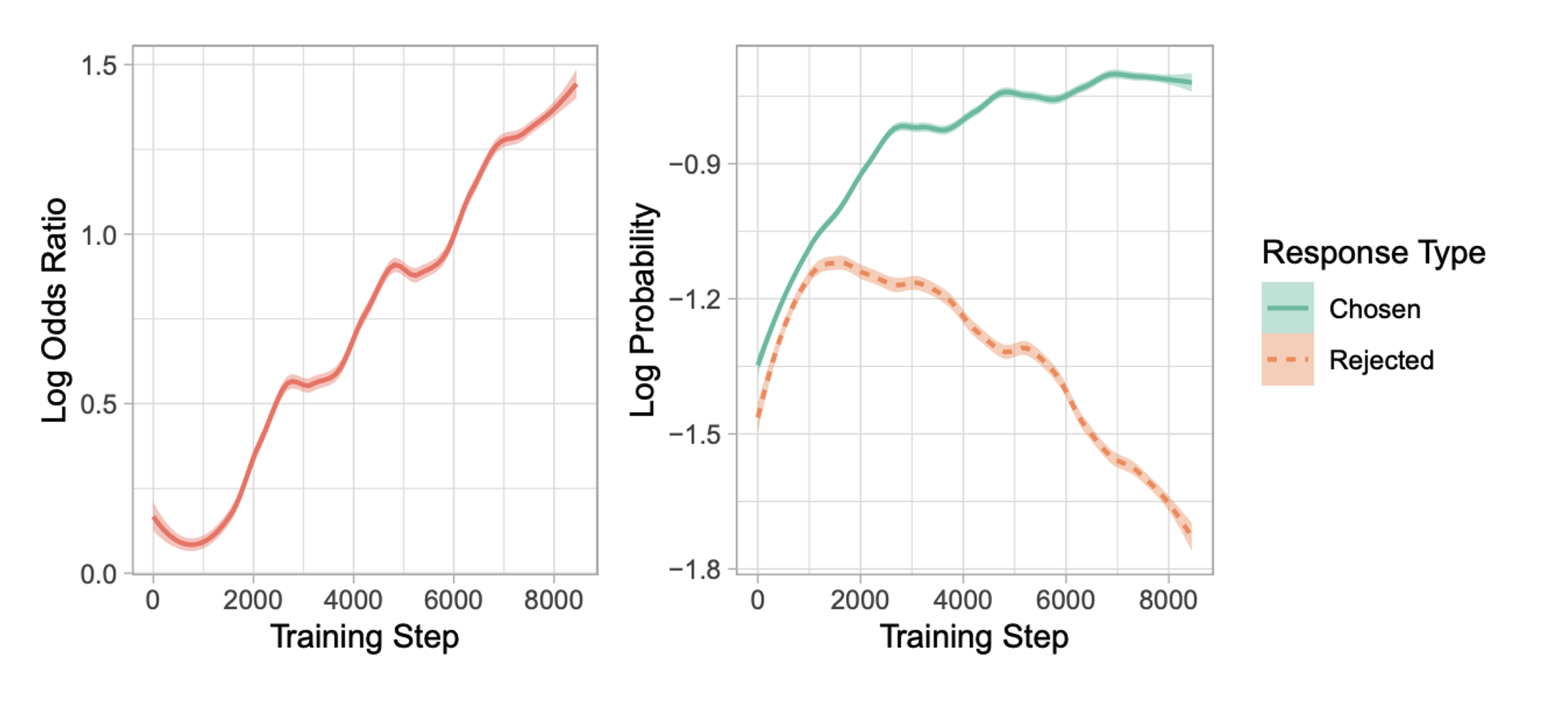
-
ORPO는 SFT의 domain adpaptaion을 잘 유지하며 OR이 unwanted generation token에 대한 Penalty를 잘 주고 있는 것을 볼 수 있음.
-
학습이 진행됨에 따라 odds ratio 값도 점점 커짐 → penalty를 잘 줌
Conclusion
-
Reference-free monolithic preference alignment method인 ORPO을 제안
-
RLHF, DPO 대비 비교적 간단하고 효과적인 방법으로 preference alignment 학습이 가능