QCRD: Quality-guided Contrastive Rationale Distillation for Large Lanauge Models
논문 정보
- Date: 2024-10-03
- Reviewer: 전민진
- Property: Knowledge Distillation
Abstract
-
LLM은 좋은 성능을 갖고 있으나 resource 제한, inference 효율성 등으로 다양한 application에서 사용되기엔 한계가 존재
-
최근 LLM을 기반으로 한 knowledge distillatinon으로 smaller, task-specific한 모델을 학습하는 여러 방법론이 제안 됨
-
하지만 기존 연구들은 knowledge의 disversity와 quality에 크게 집중하지 않음.
- 특히, negative knowledge을 distillation에 사용하지 않음
-
본 논문에서는 constrative knowledge learning을 통한 reasoning capability 향상을 목표로 하는 quality-guided contrstive rationale distillation(QCRD)을 제안
-
특히 small lm의 이전 iteration모델에서 rationale을 sampling, negative로 사용
-
discriminator를 같이 학습하여 rationale의 pos, neg를 판별, quality score를 계산해 이를 학습에 반영
-
-
실험 결과, 기존의 distillation method보다 뛰어난 성능을 보임
Introduction
-
LLM의 모델 크기가 커지면서 reasoning ability가 발생 → 이를 이용해 작은 모델을 학습하자
- 하지만 아직도 LLM과 distilled small model간의 성능 차이가 심한 task가 reasoning task
-
이를 해소하기 위한 다양한 방법이 제안
-
LLM이 생성한 rationale을 생성하도록 small LM을 학습하는 방법(distill step-by-step )
-
L = L{prediction}+\lambda L{generation}
-
이 방법의 경우 postivie knowledge만 사용, knowledge가 한정적이고 noisy가 있을 수 있음
-
-
LLM이 생성한 rationale을 golden answer로 보고 작은 모델이 생성한 rationale과 정답의 차이를 줄이도록 하는 연구도 존재
- 대부분 LLM의 zero-shot/few-shot 결과를 그대로 사용, reaosning step에서 오류가 발생할 확률이 높음
-
⇒ 하지만 이러한 방법들 모두 negative rationale을 생성해서 학습에 사용하진 않음
-
본 논문에서는, Quality-guided Contrastive Rationale Disilltation(QCRD)을 제안
-
positive example : LLM이 생성한 rationale 중 self-consisteny O
-
negative example : LLM이 생성한 rationale중 self-consistency X + previous iteration student model이 생성한 rationale (with high temp)
-
discriminator가 rationale의 quality를 계산, 이를 학습에 반영
-
- QCRD의 우수성을 입증하기 위해서, T5-base(220M), small(60M)을 student로 사용해 실험 진행, 여러 벤치마크 데이터셋에서 우수한 성능을 보임
Related Work
-
Multi-task learning with LLM generated ratioanles
-
기존에 rationale을 바탕으로 하는 여러 KD 방법론이 제안
-
rationale을 학습에 활용하는 것이 효과가 있다는 것이 밝혀져 있음
-
이전에는 multi-task learning framework방식으로, prefix를 기반으로 모델이 label을 예측하면서 동시에 rationale도 생성할 수 있도록 학습, 내재적으로 rationale에 있는 knowledge를 학습하도록 함
-
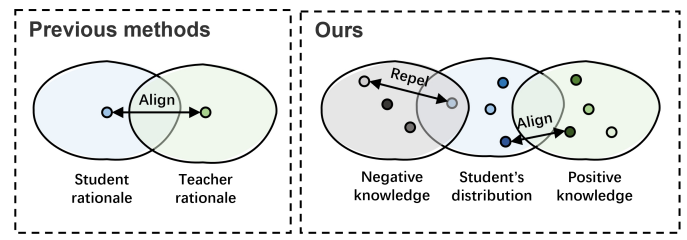
하지만 smalle model의 rationale과 LLM의 rationale이 align 되도록 하나의 loss form에만 집중
-
-
Contrastive learning for LLMs
- LLM에 contrastive leraning을 하는 방법론이 기존에 많이 제안되었으나, CoT distillation쪽에선 한번도 차용되지 않음
Methodology
-
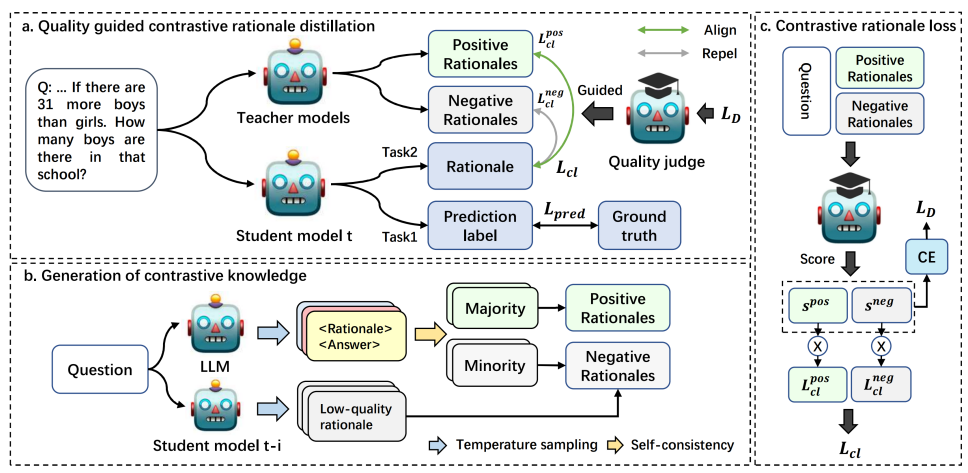
QCRD는 3가지 파트로 구성이 되어 있음
-
multi-task learning framework : L = prediction_loss + CL_loss
-
generate contrastive knowledge from LLM and student model
-
quality-guided contrastive learning strategy
- positive와 negative를 구별하는 online-updated discriminator의 guidance를 사용
-
Multi-task learning framework for the student model
-
이전 연구와 유사하게 prefix를 활용해서 small model이 다양한 형태의 output을 생성할 수 있도록 학습
-
for prediction label task,
-
for rationale generatrion task,
-
Generation of contrastive knowledge
-
Positive sample
- CoT prompting with sampling using LLM
-
각 data마다 K개의 rationale을 생성, self-consisteny를 만족하는 rationale을 positive로 사용
-
Negative sample
-
위에서 self-consistency를 만족하지 못한 rationale을 negative rationale로 봄
-
self-consistency방법론 특성상 negative가 positive에 비해 적음
-
LLM이 생성한 negative는 student가 봤을 땐, positive처럼 보일 수 있음 → 학습 효과가 떨어짐
-
-
이전 iteration의 student model에 high temperature를 사용해서 rationale을 sampling
-
→ low quality rationale이라 판단, negative로 사용
- \mathbf{x} = [x_1, x_2,..,x_n], S{pos}={r_1^{pos},…,r_m^{pos}}, S{neg} = {r_1^{neg},..,r_k^{neg}}
Constrastive knowledge distillation
-
Train a discriminator to judge rationales
-
같은 question에 대한 rationale의 quality는 상이, 하지만 학습하면 할수록 student가 생성하는 rationale은 positive rationale과 가까워질 것
- 무작정 student model이 생성했다고 계속 negative로 보는 것은 합리적이지 않을 수 있음
-
그래서 효과적으로 positive와 negative rationale를 판별, quality score를 계산해줄 discriminator가 필요
-
Discriminator에 input으로 question과 rationle을 넣고, score를 계산하도록 함
-
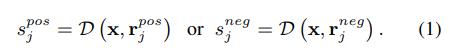
- discriminator로는 encoder architecture를 사용
- T5-base의 encoder를 사용, max pooling layer랑 2개의 linear layer를 추가
- 학습 전에 LLM이 생성한 rationale로 pretrain진행(with 500 max step), pos와 neg의 비율을 맞춰주기 위해 word_mask and replacement로 data augmenatation.
- online-updated during training
- LLM으로 생성한 positive, negative로 D를 pretrain, 학습 동안에는 D를 regular epoch interval로 업데이트
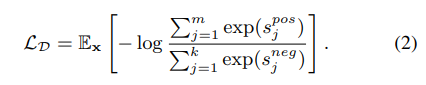
-
Quality-guided contrastive distillation
- 위의 단계로 여러 positive, negative sample을 수집
→ many-to-one contrastive distillation loss를 사용
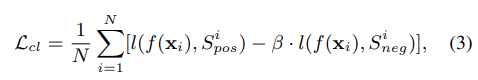
- l(f(\mathbf{x}_i),s_{pos}^i)=min_{r_{j}^{pos,i}\in S^i_{pos}}\{l(f(\mathbf{x}_i),r_j^{pos,i})\}
- 모델이 생성한 rationale과 가장 유사한 postivie rationale과의 Cross entropy loss
- l(f(\mathbf{x}_i),s_{pos}^i)=min_{r_{j}^{neg,i}\in S^i_{neg}}\{l(f(\mathbf{x}_i),r_j^{neg,i})\}
- negative는 가장 차이 많이 나는 것 선택
- l(f(\mathbf{x}),r_j^{neg})=min(l(f(\mathbf{x},r^{neg}_j))-\delta,0)
- 너무 단순한 neg는 거르기 위해 margin사용
- 또한, student model이 생성했다고 해서 무조건 negative로 볼 경우, 학습이 진행되면서 local optima에 빠질 수 있기 때문에 discriminator를 사용하는 quality-guided distillation을 사용
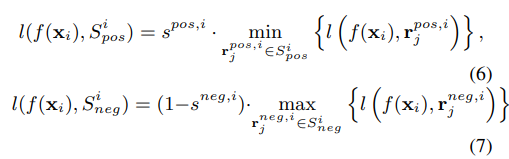
- Discriminator로 quality score s를 계산, pos의 경우 quality가 높으면 더 학습에 반영되도록, neg의 경우 quality가 높으면 학습에 덜 반영되도록 함
- Training loss
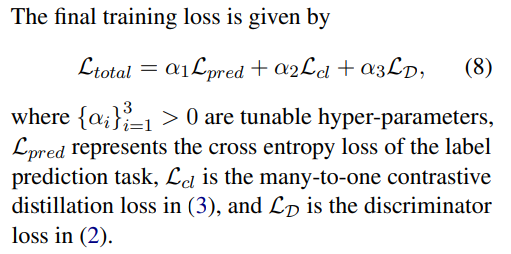
- 이 total loss를 보면 최종적으론 student model의 encoder를 똑 떼서 discriminator로 학습한다는 느낌같은데.. 확실히 맞는지 모르겠음
Experiments
Datasets
-
SVAMP : arithmetic word problem solving
-
CQA : commonsense QA
-
e-SNLI, ANLI : NLI
-
rationale을 GPT-3.5-turbo로 생성
Implementation details
-
T5-base(220M),T-small(60M)사용
-
\alpha_1,\alpha_2,\alpha_3은 실험적으로 0.5으로 세팅 \alpha_3은 매 iteration마다 0.9를 곱함
-
\beta=0.2,\delta=3
-
LLM temp 0.7로 5번 샘플링, small model은 5-iteration-before model에서 temp 1.5로 1개 샘플링
Baselines
-
Fintuning
-
Single-supervision : teacher model이 예측한 label을 맞추도록 학습
-
DSS : multi task learning with label prediction and rationale generation
-
MI : DSS기반에 prediction label과 rationale사이의 mutual information이 최대화하도록 task 추가
Experimental result
- Experiments across four benchmarks
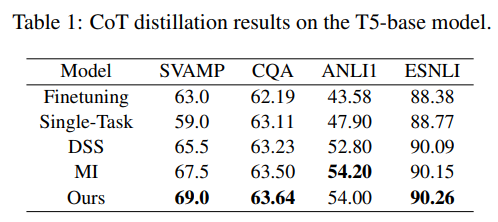
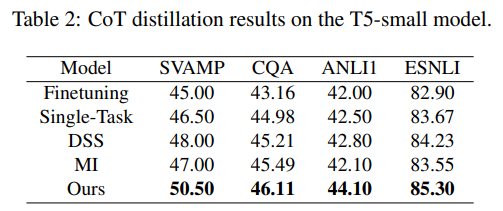
-
다른 유사한 CoT distillation 방법론과 비교해도 높은 성능을 보임
-
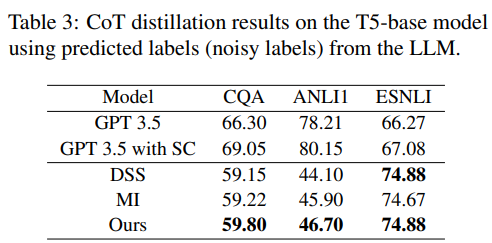
Distillation with LLM labels
-
ground truth를 사용하지 않고, LLM이 생성한 label로 학습했을 때의 실험
-
temperature sampling, self-consistency의 효과로 noisy label을 사용해도 비교적 높은 성능을 보임
- 이전에 SC로 rationale을 pos랑 neg로 분류했다더니.. 아니었나..?
-
-
- Distillation with smaller datasets
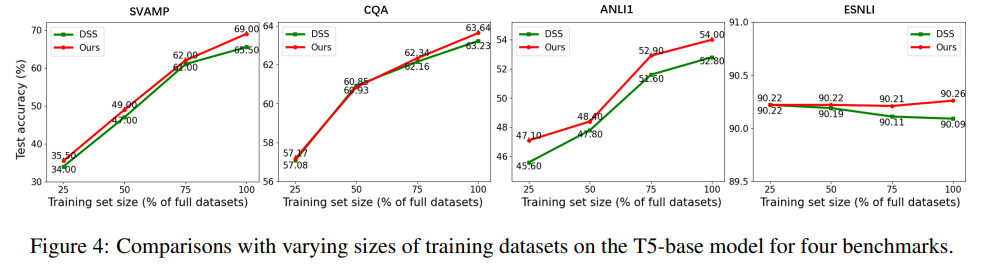
-
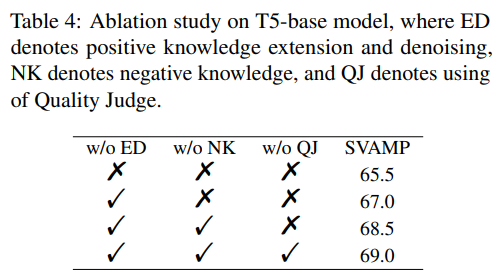
Ablation study on QCRD
-
ED : sample the outputs of the LLM and leverage the self-consistency to denoise rationales
-
NK : generator low-quality rationaels as negative rationales
-
QJ : use of discriminator
-
Discussion
-
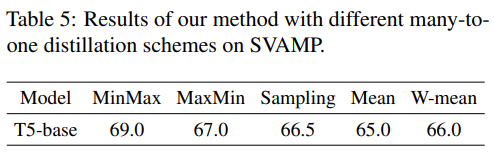
Different contrastive distillation schemes
- min-max방식이 가장 좋더라!
-
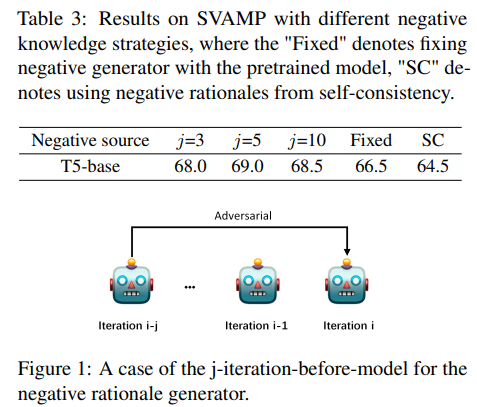
influence of negative sample
-
5번 전 iteration의 모델로 negative를 만들때가 가장 효과적
-
Fixed의 경우 DSS로 학습된 모델이 생성한 rationle을 negative로 썼을 때
-
-
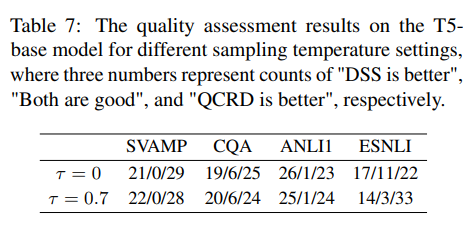
Assessment for generated rationales
-
GPT-3.5로 DSS와 QCRD로 만든 rationale중 무엇이 더 좋은지 평가
-
DSS win / tie / QCRD win
-
QCRD가 더 좋은 rationale을 생성한다!
-
-
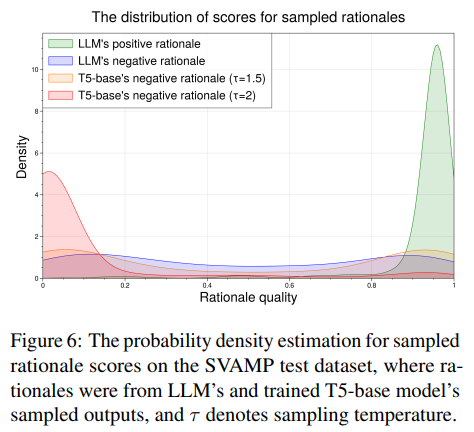
Distribution of rationale quality scores
- 확실히 좋은 rationale과 나쁜 rationale은 잘 scoring하는 것을 볼 수 있음
Conclusion
- Contrastive learning을 CoT distillation에 접목한 최초의 논문!