SELF-RAG: LEARNING TO RETRIEVE, GENERATE, AND CRITIQUE THROUGH SELF-REFLECTION
논문 정보
- Date: 2024-02-27
- Reviewer: 상엽
- Property: Retrieval, Natural Language Generation
Introduction
- LLM의 발전에도 불구하고 Factual error는 발생
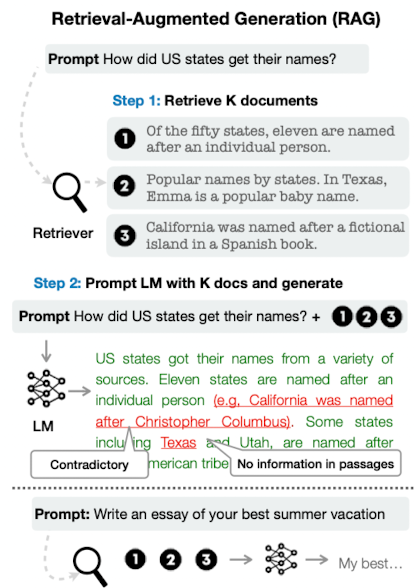
- RAG : 관련 문서 retrieval → Knowledge-intensive task에서 factual error 감소 확인
하지만 여전히 몇 가지 문제점이 있음.
-
RAG 기술은 LLM의 성능에 악영향을 미칠 가능성이 있음.
-
RAG는 factual grounding 여부를 판단할 수 없어 off-topic passage를 제공할 수 있음.
-
결과값과 passage의 내용이 일치한다는 보장 역시 없음.
-
→ Self-Reflective Retrieval-augmented Generation (SELF-RAG)
-
via on-demand retrieval and self-reflection.
-
gnereation quality 증가 시키겠다.
-
factual accuracy도 증가시키겠다.
-
How?
-
generation process에서 task output generation과 retrieval 여부와 결과를 평가하는 reflection token 생성을 동시에 하겠다.
-
Reflection tokens
-
retrieval token : retrieval o/x
-
critique token : generation quality
-
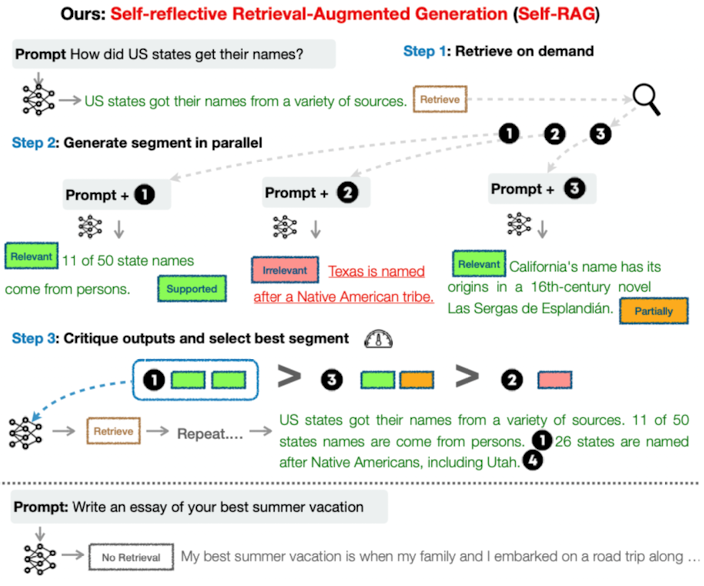
절차
-
input이 주어지면 생성 시작
-
생성 과정 중 Retrieval을 하는 것이 도움이 될지 안될지 판단, 만약 retrieval이 필요하다고 판단된다면 retrieval token을 생성 (on demand)
-
동시에 multiple retrieved passages를 평가 (relevance, support)
-
factuality and overall quality 관점에서 최선의 passage 선정.
차이점
-
항상 고정된 개수의 document를 추출하는 RAG와는 달리 retrieval을 조절할 수 있음.
-
SELF-RAG는 support에 대한 self assesment를 진행하기 때문에 citation을 제공할 수 있음. → fact verification을 쉽게 함.
Related work
RAG (Retrieval Augmented Generation)의 첫 등장 이후 많은 variation들이 생기고 있음.
-
inference 시 retrieval 후 결과값 생성
-
training 시 retrieval 결과 포함하여 학습
-
adaptively retrieve passages for generation on top of a proprietary LLM
Training and generating with critics
-
RLHF (reward 모델과 비교하는 내용을 계속 작성하더라…)
-
Human feedback에 따라 preference 학습 → relevance, support 등 factuality에 큰 영향을 주는 요소들에 대한 모델 결과를 generation 모델에 학습 (SELF-RAG에서 critique의 역할은 일종의 reward 모델로 작용)
-
SELF-RAG는 training cost 절감을 위해 reflection token을 사전에 만든 후 학습 진행
-
-
LLM의 결과를 평가해 수정 및 생성하는 이전 논문들
-
Xie et al. (2023) propose a self-evaluation- guided decoding framework
- 오직 reasoning task에만 집중
-
LLM refinement (Dhuliawala et al., 2023; Madaan et al., 2023; Paul et al., 2023)
-
natural language feedback을 통해 output 수정
-
비용이 비쌈.
-
-
SELF-RAG: LEARNING TO RETRIEVE, GENERATE AND CRITIQUE
Reflection tokens
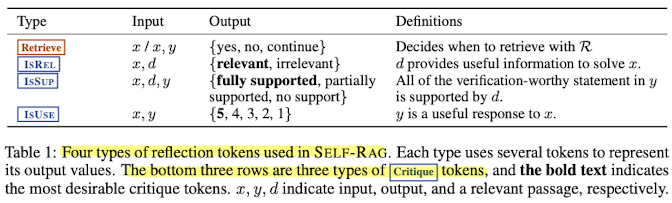
output’s relevance, support, or completeness를 평가
PROBLEM FORMALIZATION AND OVERVIEW
x : given input
\mathcal{M} : language model
y : textual outputs consisting of multiple segments [y_1, …, y_T] (original token + reflection token)
Inference overview
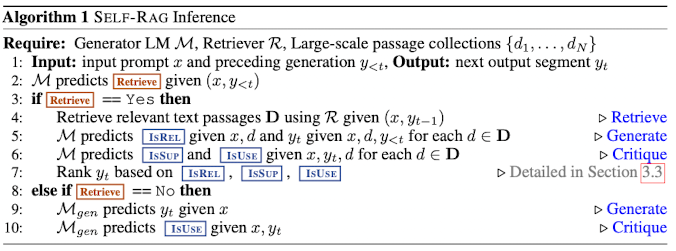
x가 주어졌을 때 모든 generation 과정 y_{<t}에 대해서 모델은 retrieval 여부를 판단
-
retrieval이 필요없을 경우 : standard LM과 똑같이 next output segment prediction 진행
-
retrieval이 필요할 경우
-
retrieval 진행 → critique token을 이용해 retrieved passage의 relevance 평가 (IsRel) → next segment 생성 → retrieved passage에 의해 support 되는지 확인 (IsSup) → next segment에 대해 전반적인 utility 평가 (IsUse)
-
위의 작업을 병렬적으로 진행 후 critique token에 의해 평가된 점수의 가중합으로 최종 output 선정.
-
e.g.) Figure 1 예시, prompt 1 선택
-
Training overview
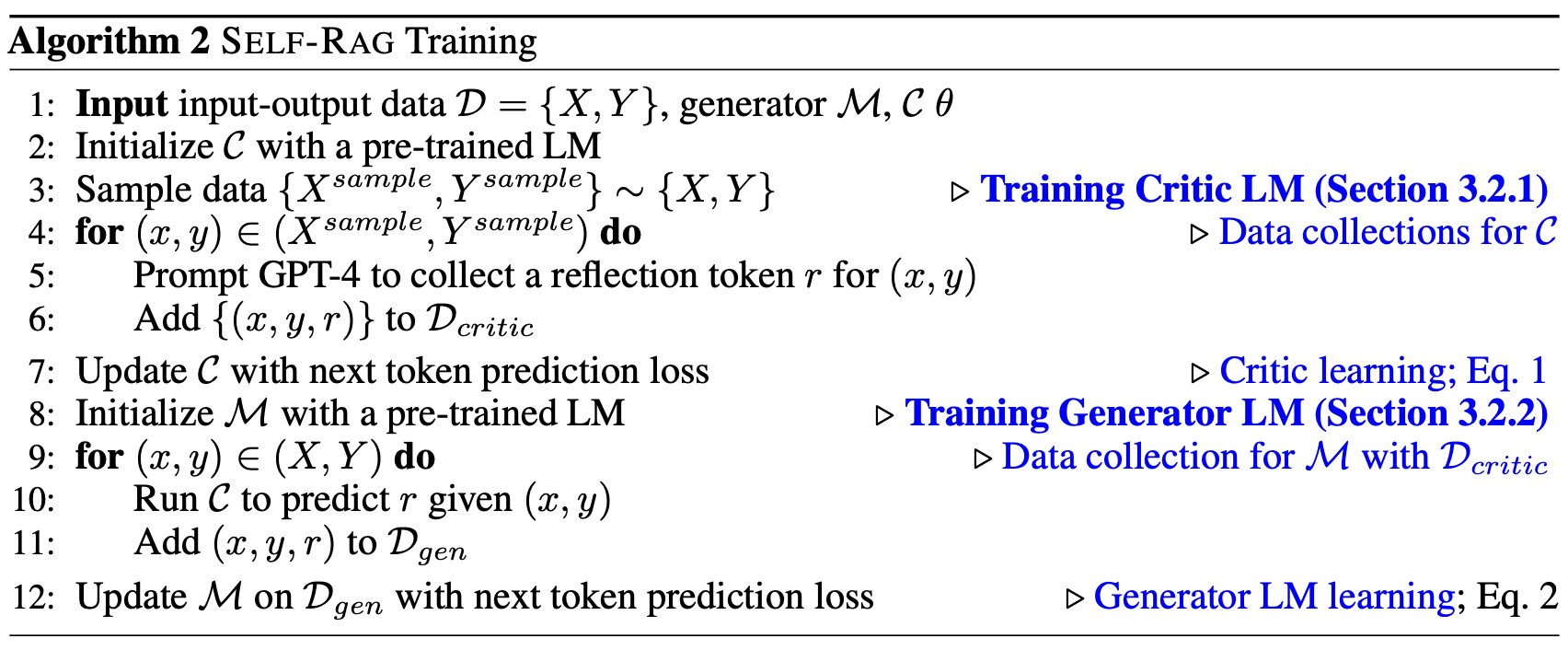
-
Data collections (\mathcal{D_{critic}}) : GPT-4를 이용해 reflection token을 포함한 데이터 수집
-
Learning critic model \mathcal{C} : \mathcal{D_{critic}} 데이터를 이용해 reflection token 생성 학습 (일종의 reward 모델)
-
Training generator \mathcal{M} : critic model을 이용해 input에 reflection token 생성 (offline으로 사전에 진행)한 데이터를 이용해 일반적인 generation task 학습
SELF-RAG TRAINING
TRAINING THE CRITIC MODEL
-
Data collection for critic model : \mathcal{D_{critic}}
-
human annotation은 너무 비싸기 때문에 GPT-4를 이용
-
특히, 전체 내용을 segment 단위로 나눠서 매번 evaluation을 해야하기 때문에 API 비용 역시 비쌈.
-
→ GPT-4를 이용해 supervised dataset을 일부 만들고 이를 이용해 critic model을 학습하자.
-
각 reflection token에 대해 데이터 랜덤 샘플링, {X{sample}, Y{sample}} \sim {X, Y}
-
각 token의 정의에 맞는 prompt 구성 후, few-shot example 제공해서 학습 데이터 생성
-
critic model을 이용해 P(r I, x, y) 학습
-
4k ~ 20k supervised training data 수집
-
실제 휴먼 annotation과 상당히 높은 일치율을 보였음.
-
학습 데이터 예시
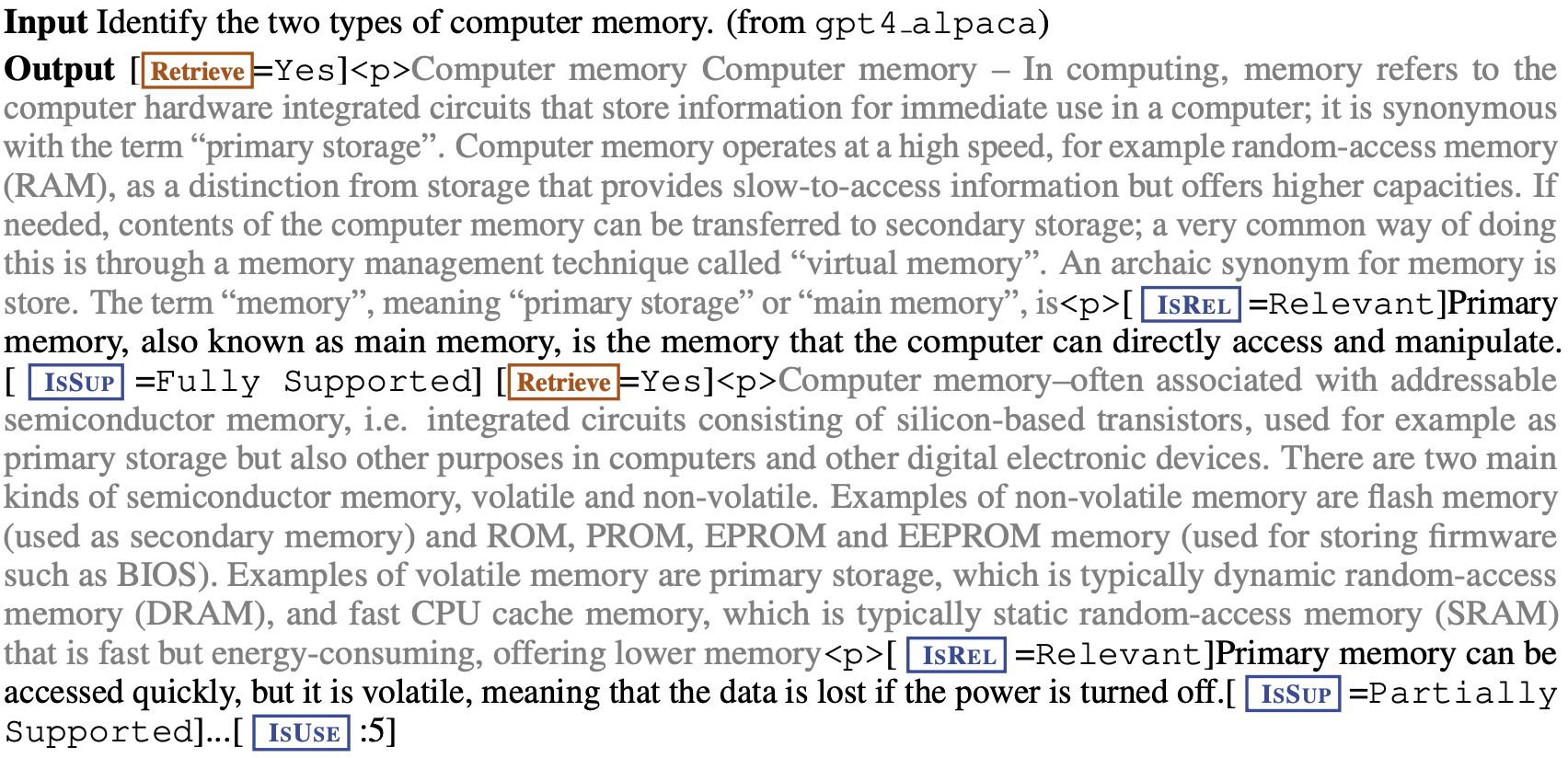
-
Critic learning
-
generator와 동일한 모델 사용
-
critic 모델은 GPT-4와 상당히 높은 일치율을 보임.
-
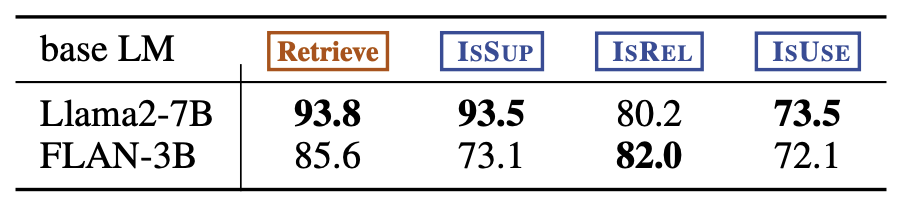
TRAINING THE GENERATOR MODEL
-
Data collection for generator : **\mathcal{D_{gen}}**
-
critic 모델을 이용해 output y에 대해 reflection token을 추가한 데이터를 생성
-
retrieval이 필요한가 아닌가? → Yes
-
Retrieve=Yes special token 추가 → top-k passage retrieval
-
각각의 passage segment에 대해 critic model을 이용해 IsRel, IsSUP 평가, 마지막 segment 이후 IsUse 평가
-
-
-
Generator learning
- reflection token을 포함한 generation 학습
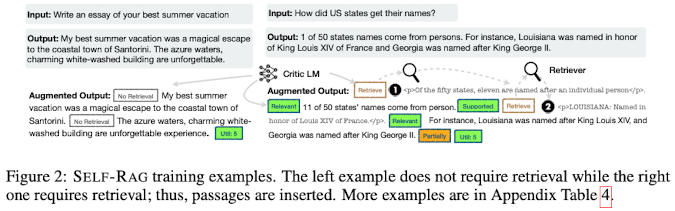
- training 동안 <p>, </p>로 쌓인 retrieved text chunk는 masking해서 진행
SELF-RAG INFERENCE
-
reflection token을 이용한 SELF-RAG는 controllable함.
-
task의 특징에 맞춰 retireval의 빈도를 조절할 수 있음.
- factuality가 중요하다면 검색 빈도를 증가시키고 open-ended task에서는 검색 빈도를 줄인다. (뒤에서도 언급.)
Adaptive retrieval with threshold
-
retrieval 여부에 대한 threshold를 설정
- 모든 output 토큰에 대해서 normalized 된 Retrieve score를 계산, 값을 넘을 경우 retrieval 적용
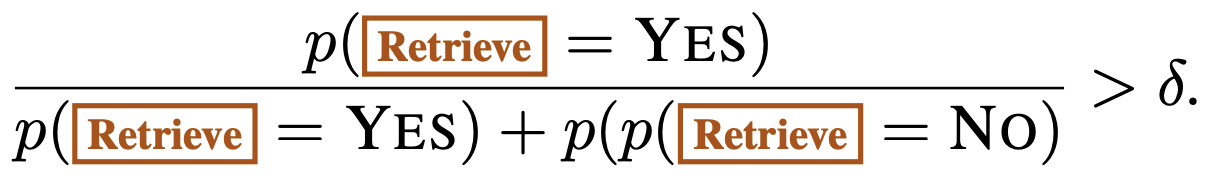
Tree-decoding with critique tokens
-
매 Segment에 대해 Retrieval 결정 → K개의 passage retrieval 진행 → \mathcal{M}을 K개 passage에 병렬적으로 적용.
-
segment-level beam search 진행
-
각 segment의 score는 다음과 같이 계산
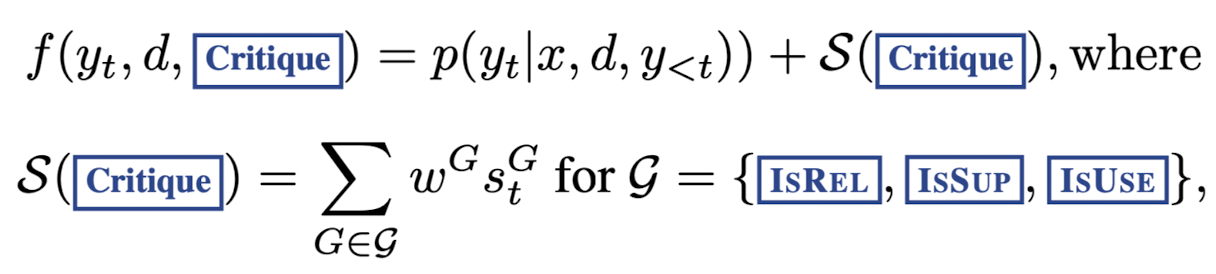
- linear weighted sum of the normalized probability of each
w^G : weight hyperparameter
st^G=\frac{p_t(\hat{r})}{\sum{i=1}^{N^G} p_t\left(r_i\right)}
G : critique token type
\hat{r} : desriable reflection token
N^G : different possible values for G
- w^G를 조절함으로써 재학습없이 inference 단계에서 모델 조절 가능
Experiments
Task and Datasets
다양한 모델과 downstream task 비교 overall correctness, factuality, and fluency.
zero-shot evaluations 진행
- experiment details
training: 4 Nvidia A100 with 80GB memory
epochs: 3
batch size: 128
learning rate: 2e-5 (3% warmup steps, and linear decay afterward)
max token: 2,048 for the 7B model, and 1,524 for the 13B model
**Deepspeed stage 3 **(Rajbhandari et al., 2020) to conduct multi-GPU distributed training, with training precision Bfloat16 enabled.
FlashAttention (Dao et al., 2022) is used to make the long-context training more efficient.
inference: 1-2 Quadro RTX 6000 GPUs with 24GB memory.
Closed-set tasks
-
fact verification dataset **about public health (PubHealth**; Zhang et al. 2023)
-
multiple-choice reasoning dataset **created from scientific exams (ARC-Challenge**; Clark et al. 2018).
→ test set 정확도로 평가
Short-form generations tasks
two open-domain question answering (QA) datasets (factual knowledge에 대한 질문에 답변)
-
PopQA (Mallen et al., 2023)
- long-tail subset 이용 : wikipedia 조회수가 100회 미만인 1399개 쿼리
-
TriviaQA-unfiltered (Joshi et al., 2017)
- 11,313 test queries : Min et al., 2019; Guu et al., 2020의 연구와 동일
→ gold answer가 생성한 정답에 포함되어 있는지 여부로 평가 (following Mallen et al. (2023); Schick et al. (2023).)
Long-form generation tasks
biography generation task
- FactScore (Min et al., 2023)로 평가
long-form QA task
-
ALCE-ASQA dataset
-
correctness (str-em), fluency based on MAUVE, citation precision and recall
BASELINES
**Baselines without retrievals. **
-
Llama2 (7B,13B), Alpaca (7B,13B), Chat- GPT, Llama2-chat (13B).
-
CoVE (65B) 이용 (iterative prompt engineering to improve the factuality)
**Baselines with retrievals. **
-
standard RAG baselines
-
위의 LLM 모델, LLaMA-FT
-
Ret-ChatGPT and Ret-Llama2-chat, perplexity.ai (private data로 train)
-
-
concurrent methods
-
retrieved passage와 함께 학습
-
SAIL, Toolformer (pre-trained an LM with API calls (e.g., Wikipedia APIs))
-
EXPERIMENTAL SETTINGS
Training data and settings.
-
Training data
- Open-Instruct processed data (Wang et al., 2023) and knowledge-intensive datasets (Petroni et al., 2021; Stelmakh et al., 2022; Mihaylov et al., 2018)에서 sampling을 통해 15만개 추출
-
model
-
generator : Llama2 7B and 13B
-
critic : Llama2 7B
-
retriever model : Contriever-MS MARCO (Izacard et al., 2022a), 각 input에 대해 10개까지 retrieval
-
Inference settings.
-
IsRel : 1.0, IsSup : 1.0, IsUse : 0.5 사용
-
retrieval threshold 0.2
-
vllm 이용
-
segment level : beam width of 2
-
token level : greedy decoding
-
Contriever-MS MARCO에서 5개, biographies and open-domain QA의 경우 웹 서치 엔진에서 5개 retrieval해서 사용.
Results and Analysis
Main Results
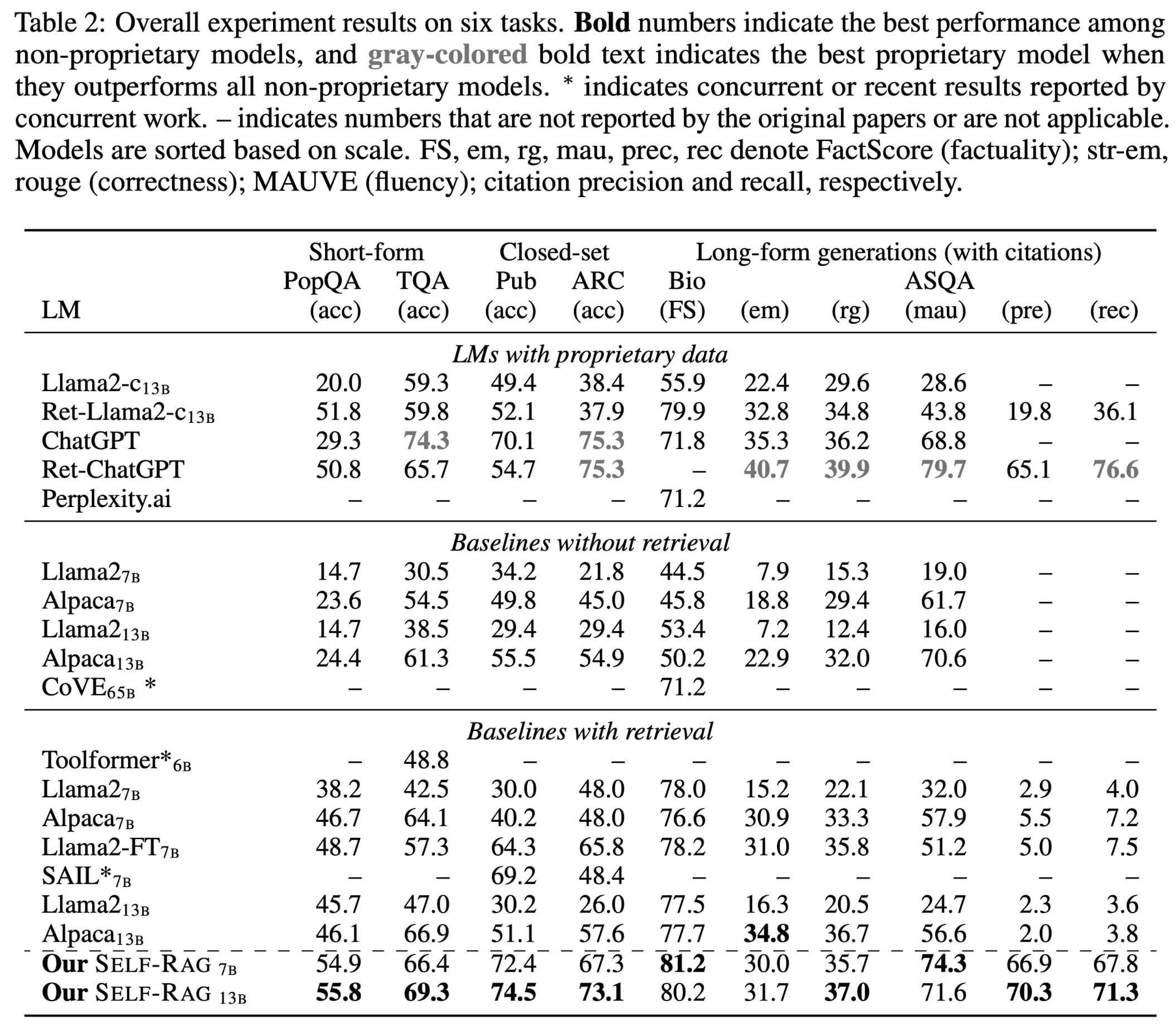
-
without retrieval 모델
-
제안 모델이 월등히 뛰어난 성능
-
ChatGPT보다 뛰어난 성능을 보이는 경우도 있음. (PubHealth, PopQA, biography generations, and ASQA (Rouge and MAUVE))
-
CoVE보다도 압도적으로 좋음. (iterative prompt engineering)
-
-
with retrieval 모델
-
RAG를 이용한 모델보다는 모든 task에서 뛰어난 성능
-
PopQA, Bio에서는 모든 모델 통틀어 최고 성능
-
On ASQA, citation accuracy 측면에서 다른 retrieval 성능이 떨어지는 것과 대비해 높은 성능을 보임.
-
Llama2-FT 7B는 SELF-RAG와 동일한 데이터셋으로 학습함에도 큰 성능 차이가 남을 확인할 수 있음. → 이것은 SELF-RAG framework가 효과가 있음을 의미함.
-
Analysis
아래 항목들에 대한 Ablation studies 진행
Training phases
-
No Retriever : retrieval 없이 일반적인 instruction-following 방법으로 학습. (더 구체적인 내용은 없어서 critique 여부는 모르겠음.)
-
No Critic : top-1 retrieved 결과만 이용. (SAIL 방법과 유사)
Inference phasese
-
No retrieval : inference 시에 retreival 사용하지 않음.
-
Hard constraints : Retrieve token이 YES일 때, retrieval (threshold 사용하지 않음.)
-
Retreive top 1 : 항상 top-1 retrieval (기존 RAG 방식)
-
Romove IsSup : IsSup token을 제외하고 critique score 계산
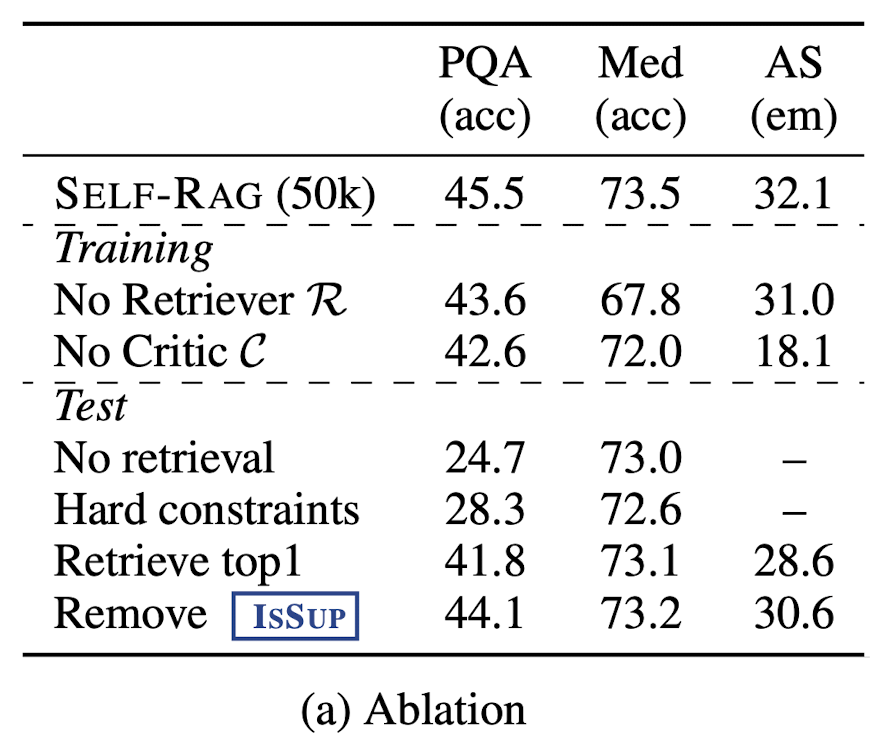
-
50000개 데이터만 사용
-
데이터셋에 대해서만 평가 PopQA, PubHealth, and ASQA
-
모든 component는 중요한 역할을 한다.
-
Training 단계에서 추가한 component가 성능에 더 큰 기여를 한다.
-
Retrieve top 1 (conventional RAG) : PopQA and ASQA에서 큰 폭의 성능 하락
-
removing ISSUP : ASQA에서 큰 폭의 성능 하락. - > SELF-RAG가 support를 고려해 retrieval하는 것의 효과 (신중히 고르는 것의 효과)
Effects of inference-time customization.
-
SELF-RAG은 critique type의 가중치를 조절함으로써 generation 성능을 제어할 수 있음.
-
7B model, ASQA 데이터셋을 이용해 평가
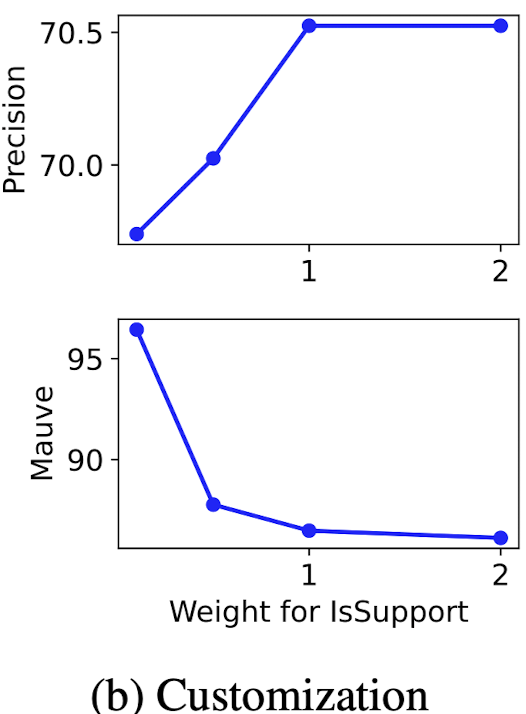
-
IsSup의 가중치를 증가시킴에 따라 모델 precision은 향상 ← 모델 generation 시 evidence에 의해 support 되는지를 더 중점적으로 보기 때문
-
반대로, Mauve 결과는 하락 ← generation이 길어지고 더 유창해줄수록 완전히 support 되지 않은 citation 확률이 증가함.
→ 상황과 목적에 따라 training 없이도 weight 조절을 이용해 효과적으로 쓸 수 있다.
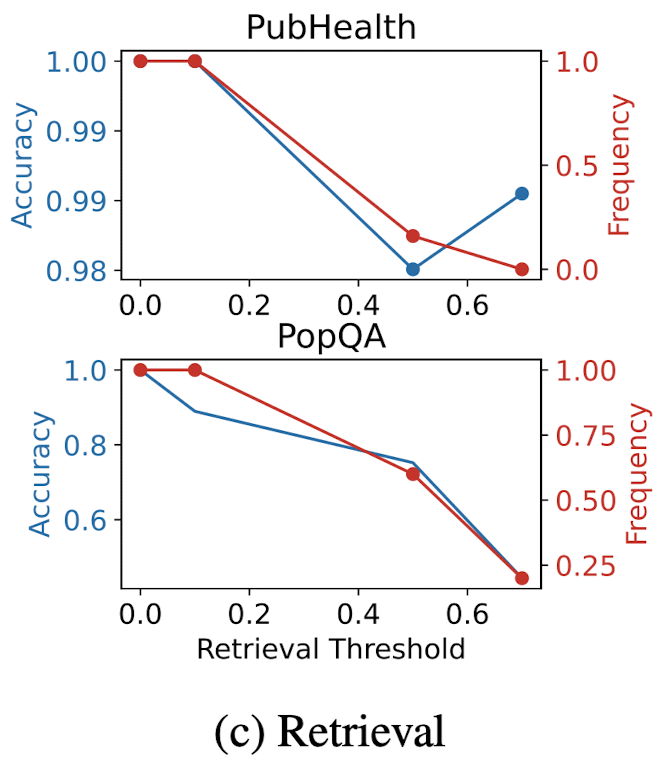
Efficiency and accuracy trade-off
-
SELF-RAG은 얼마나 빈번히 retrieval을 할지 조절할 수 있다.
-
Adaptive threshold가 정확도와 retrieval 빈도에 미치는 영향을 평가
-
threshold δ (larger δ results in less retrieval), PubHealth and PopQA 데이터셋을 이용
Effects of training data size
-
데이터셋의 크기가 모델의 성능에 미치는 영향을 평가
-
SELF-RAG 7B 모델 이용, randomly sampleed 5k, 10k, 20k, and 50k개의 데이터셋 이용
-
PopQA, PubHealth, and ASQA (citation precision) 데이터에 대해 평가
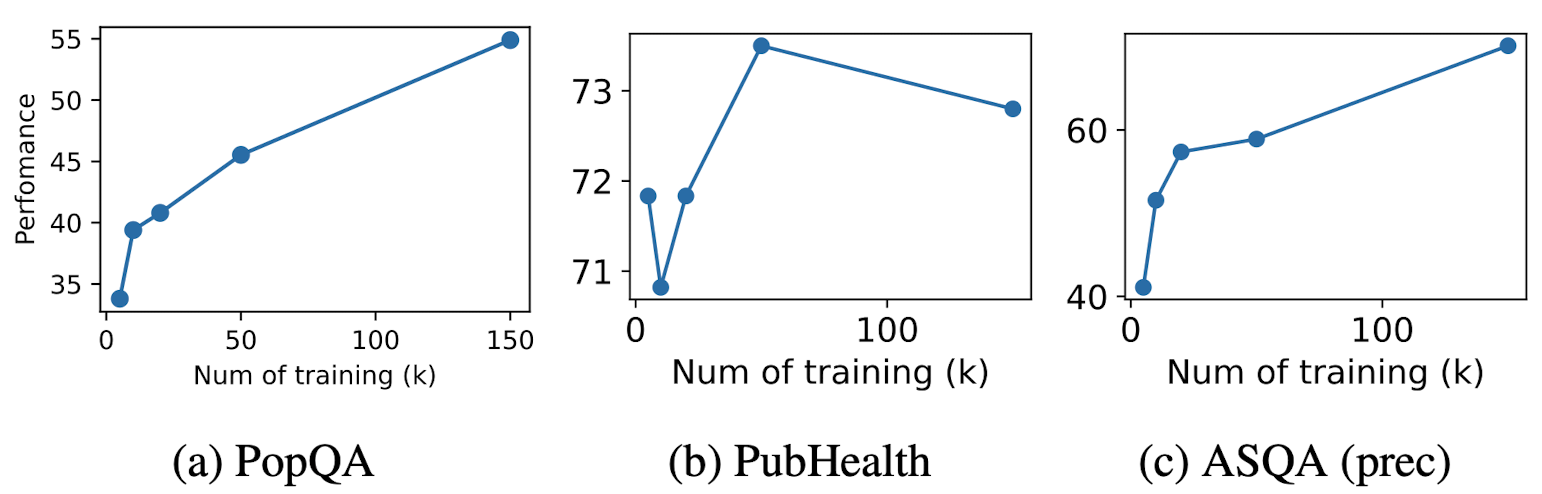
- 데이터셋의 증가는 대체로 성능향상을 보임. (특히, PopQA, ASQA)
→ 데이터셋 더 확보하면 더 큰 성능 향상을 보일 것.
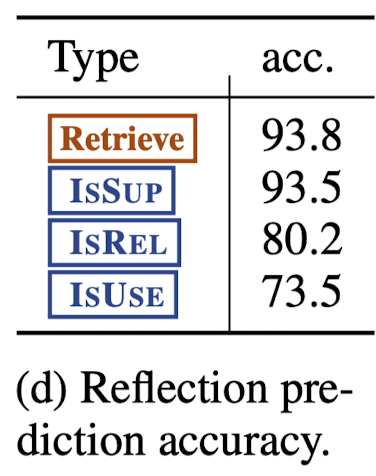
Reflection token prediction performance
-
reflection token 예측 확률 평가, (its agreement against GPT-4 predictions)
-
높은 정확도를 보임.
-
IsUse의 경우 two highest cases (5 and 4)에서 사람 역시 구별을 어려워 함.
CONCLUSION
-
retrieval on demand and self-reflection을 이용한 SELF-RAG로 quality and factuality를 모두 향상 시킴.
-
original corpus에 reflection 토큰을 추가한 후 학습 → retrieve, generate, and critique text passages
-
inference에 맞춰 weight을 조절함으로써 쉽게 다양한 task에 적용 가능.
-
평가를 통해 conventional RAG 대비 큰 성능 향상을 보임.
의견
- ablation study 항목들이 너무 쉽고 많은 부분이 빠진 건 아닌가?