SUPER: Evaluating Agents on Setting Up and Executing Tasks from Research Repositories
논문 정보
- Date: 2024-09-23
- Reviewer: yukyung lee
- Property: Autonomous-Agents, Code Generation
1. Introduction

-
Can LLMs automate theset up and execution of tasks in research repositories?
-
Experimentation frequently requires substantial effort to setup and execute them
-
installing the environment:
-
configuration changes
-
resolv-ing outdated package dependencies
-
fixing bugs
-
determining the correct execution commands
-
-
-
-
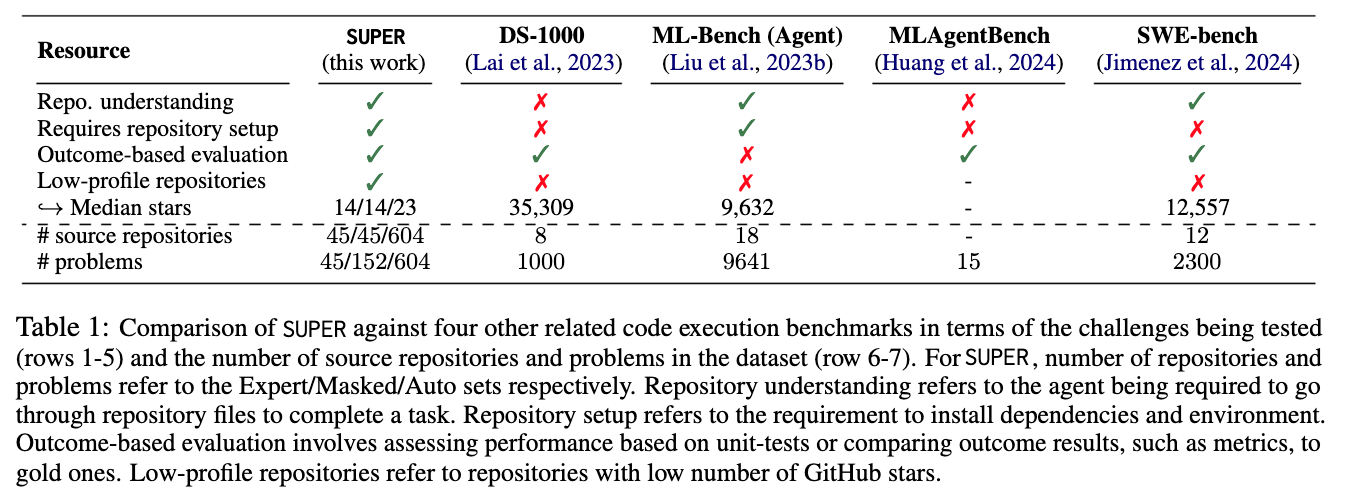
both setting up and executing experiments using research repositories in-the-wild
2. Related work
1) Coding benchmarks
-
Contributions
- In contrast to these works,SUPER focuses onthe end-to-end task of setting up and executingresearch tasks in lower-profile repositories, pre-senting a unique set of challenges, with tasks thatrequire repository comprehension and reasoning,editing multiple files, setting up the repository en-vironment for execution while interactively run-ning commands in the environment
2) LLM Agent
- Our benchmark introduces an importantnew domain that encourages the development ofLLM-based agents to assist researchers in their end to end research tasks with arbitrary repositories
3. Benchmark Construction
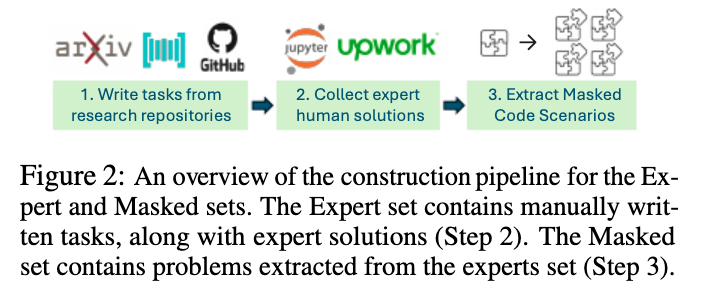
-
SUPER benchmark (3 setting)
-
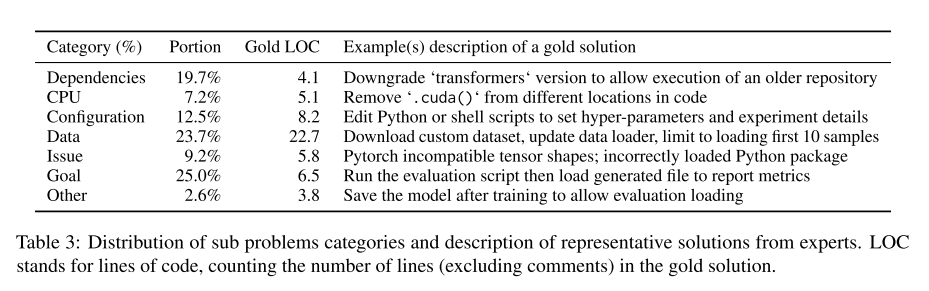
Expert set - contains manuallywritten problems, solved by experts.
-
Masked set - contains sub-problems extracted from the Expert set using the gold solution, which pro-vide easier and more focused sub-problems.
-
Auto set - contains automatically generated problemswhich can be used for development and improve-ment of agents
-
-
Environment setup : Jupyter notebook as engine
-
Execute cells: system shell command & stateful python command
-
Each execution returns an observation string
-
https://modal.com
- 2-3 cents per problem in Modal (not including API costs)
-
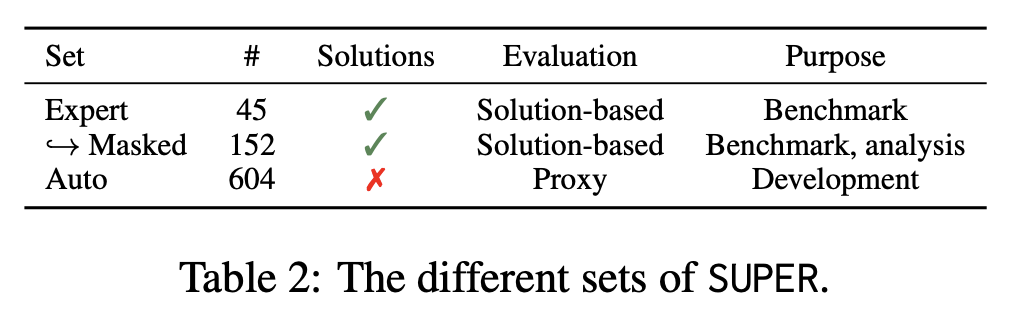
Expert: 45 end-to-end
-
Manually written by “expert” programmers
-
Ask for git commit hash, and any exceptional implementation decisions they had to make (which are specified to agent)
-
Check that solutions are reproducible (up to error of 10-2)
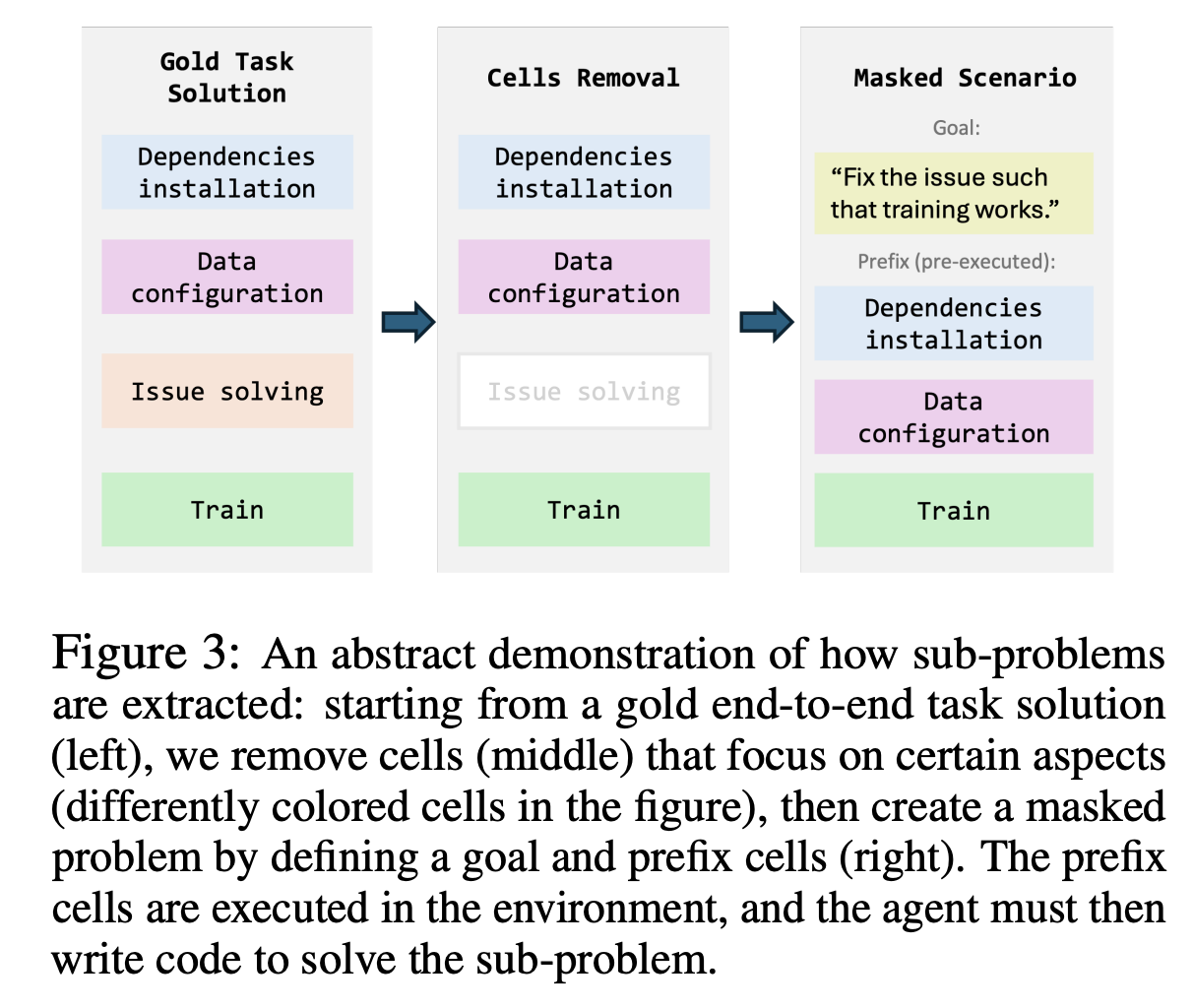
Masked: 152 sub-problems from Expert
-
Removes parts of expert-written code (“masks” them)
-
Pre-execute existing cells and pass as history - code to be written by model not required to fit “in between” existing cells, can follow sequentially
- In prompt history as [pre-executed by the user]
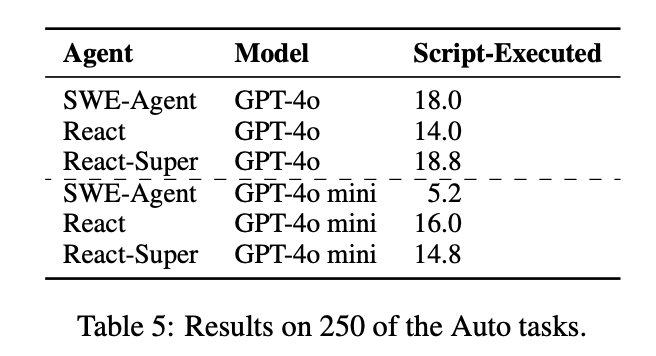
Auto:** **604 auto-generated examples
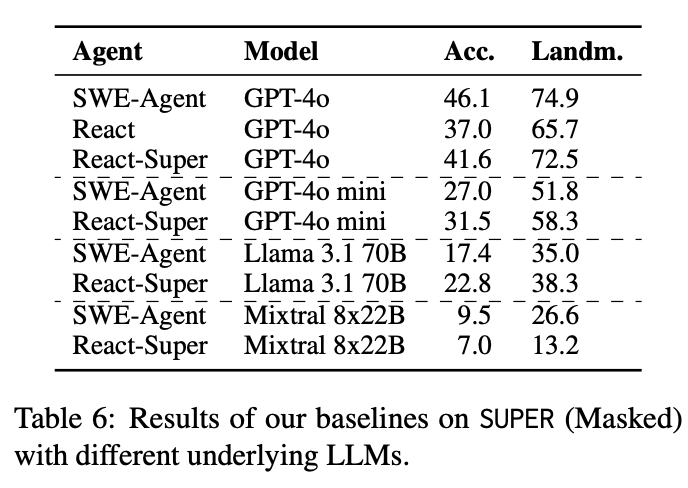
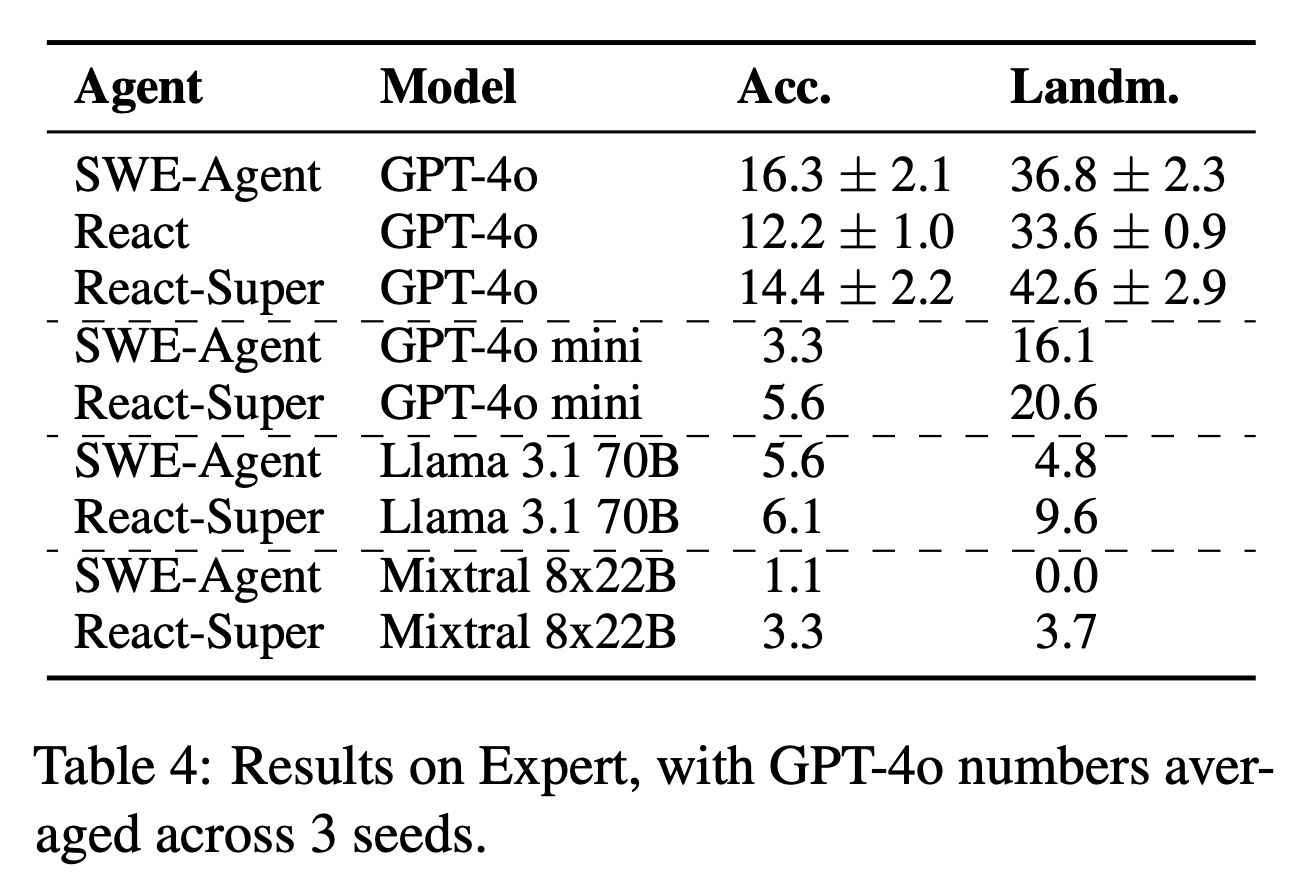
- state-of-the-art approaches struggle to solve these problems with the best model (GPT-4o) solving only 16.3% of the end-to-end set, and 46.1% ofthe scenarios.
4. Evaluation
-
replication of metrics
-
Partial credit through “landmarks” (points in code signalling sub-completion, e.g. training stage done)
- E.g., the explicit output string “_training completed _” or the string “Loading data… 100%”
-
Auto-generated: check no exceptions when running script (for a minimum duration)
- use 10 seconds based on gold expert solutions
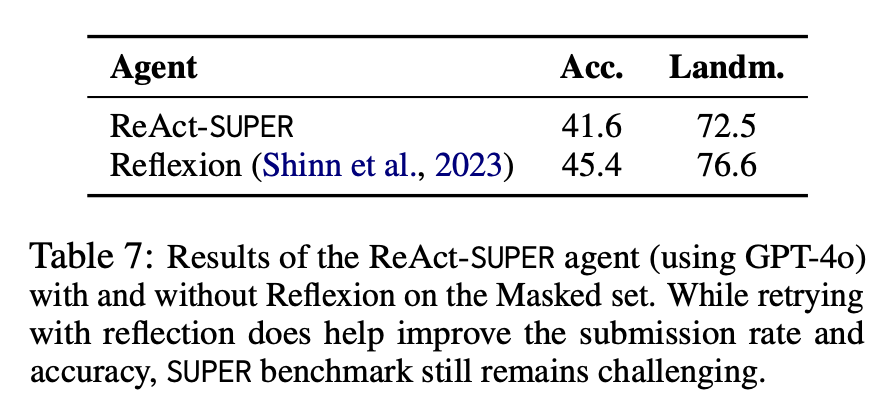
“Open-source models substantially lag behind on both the sub-problems and end-to-end tasks.”
“agents are better at resolving well-specified sub-problems, such as solving exceptions, bugs, and other issues, than tasks requiring repository and file exploration to understand code structure”
LLMs
GPT-4o (gpt-4o-2024-08-06)
GPT-4o mini (gpt-4o-mini-2024-07-18)
Mixtral-8x22B-Instruct
Llama 3.1 70B
Agents
- Execute and submit commands
- ReAct
<thought, action, observation>
Truncation strategies to keep context in limit (e.g. reduce size of training file output)
- For the last step, we provide the 50k last characters, which is usually enough for the entire observation. For earlier steps, we shorten the observations to show the last 500 characters.
- ReAct-SUPER
- Result
Edit action
- “ Specifically, the edit command accepts three parameters: the name of the file, the exact content of the lines to be replaced, and the content to replace it with.”
{filename}