Training diffusion modelse with reinforcement learning
논문 정보
- Date: 2024-04-30
- Reviewer: 전민진
- Property: Evaluation Metric, RL
한 줄 요약 : diffusion모델을 강화학습으로 원하는 obejective(그림 실사화, 압축 잘되는 그림 등)에 바로 최적화하자!
Abstract
-
diffusion models은 log-likelihood objective를 근사시켜 학습하는 flexible generative models
-
diffusion모델로 사람들이 원하는 목표는 human-perceived image quality or drug effectiveness와 같은 downstream objective
- 하지만 log-likelihood objective를 근사화하는 것으로 학습됨
⇒ 이를 해결하기 위해(=원하는 objective에 optimize하기 위) 강화 학습을 접목하자!
-
denoising과정을 multi-step decision-making problem으로 보고, policy gradient algorithm을 접목하는 방법론을 제안, 이를 DDPO(denoising diffusion policy optimization)이라 명명
-
해당 방법론을 적용할 경우, prompting으로 표현하기 어려운 image compressibility나 human feedback에서 파생되는 aesthetic quality를 objective로 adaptation 가능
Introduction
-
diffusion model의 핵심 아이디어는 sequential denoising process를 통해 단순한 prior distribution을 여러 번 변형시켜서 target distribution으로 만드는 것
-
하지만 대부분의 diffusion model 활용 사례는 likelihood에 직접적인 관련이 있지 않고, 오히려 downstream objective과 연관이 있음
-
따라서, 본 논문에서는 data distribution을 matching하는 것보단 이러한 objective를 바로 만족하도록 diffusion model을 학습하는 문제에 초점을 둠
-
이 문제의 어려운 점은 diffusion model의 정확한 likelihood 계산이 불가능하다는 것에서 기인, 대부분의 RL알고리즘을 적용하기 어려움
- RL에서는 결국 최적의 정책, 최대 보상을 얻을 수 있는 정책을 찾는 것이 목표인데, diffusion에서 정책은 결국 데이터의 likelihood이기 때문
-
-
denoising을 multi-step decision-making task로 보는 방법론을 제안, 전체 denoising process 과정을 근사한 likelihood를 사용하는 것이 아니라 각 denoising step에서의 정확한 likelihood를 사용
- 해당 방법론을 이용해, black-box reward function만으로 downstream task에 diffusion model을 최적화할 수 있음
-
본 논문의 저자들은 큰 text-to-image diffusion model을 finetuning하는데에 해당 알고리즘을 적용
-
처음엔 prompting으로 규정하기 어려운 image compressibility, 혹은 human feedback에서 파생되는 aesthetic quality와 같은 task에 초점을 두고 평가
-
하지만 관심 있는 대부분의 reward function이 프로그래밍적으로 명시하기 어렵기 때문에, finetuning 절차는 사람의 라벨링 작업에 의존하게 됨
-
본 논문에서는 labeling대신 VLM모델의 feedback을 사용하는 방법론을 제안, LM을 finetuning하는 RLAIF방식과 유사하게 사용
-
이를 통해 추가적인 human annotation이 필요한 reward functino에 대해 diffusion model를 adapt할 수 있게 함
-
절차를 unusual subject-setting composition에 대해서 prompt-image alignment를 향상시키기 위해 사용
-
-
-
본 논문의 contribution은 다음과 같음
-
DDPO의 derivation과 conceptual motivation을 제시
-
다양한 reward function의 설계를 문서화, reward-weighted likelihood method와 비교하여 DDPO의 효과성을 증명
-
unseen prompt에 대한 제안 방법론의 fine-tuning generalization ability를 증명
-
Related Work
-
Diffusion probailistic models
-
denoising objective는 보통 likelihood를 근사하는 것에서 파생되지만, diffusion model의 학습은 일반적으로 maximum likelihood와 여러 가지 면에서 다름
-
likelihood를 더 strict하게 최적화하도록 objective를 수정할 경우, 종종 이미지 품질을 악화시킨다는 연구가 있었음
-
likelihood가 visual qulity에 대해 faithful proxy가 아니기 때문
-
-
⇒ 본 논문에서 diffusion model이 downstream objective에 바로 최적화될 수 있는 것을 보여줌
-
Controllable generation with diffusion models
-
이전에 diffusion 모델의 controllability와 quality를 향상시키기 위해 여러 방법론이 제안됨
-
한정된 유저 제공 데이터에 finetuning
-
새로운 concept에 대한 text embedding 최적화
-
composing model
-
adapters for addtional input constraint
-
inference-time techinque
-
classifier
-
classifier-free
-
-
-
-
Reinforcement learning from human feedback
-
다양한 세팅에서 human feedback을 사용해 최적화하는 연구들이 있었음
-
simulated robotic control
-
game-playing
-
machine translation
-
citiation retrieval
-
instruction-following
-
alignment with specifications
-
-
최근에 reward-weighted likelihood maximization을 기반으로 한 방법론을 사용해 human preferences로 text-to-image diffusion model의 alignment를 연구한 논문도 있음
-
해당 논문의 경우, RWR method를 한번 interation하는 것과 같음
-
실험 결과, DDPO가 RWR-style의 opimization의 여러 반복보다도 훨씬 뛰어난 성능을 보
-
-
-
Diffusion models as sequential decision-making processes
-
이전에도 diffusion model을 policy gradient로 학습하는 논문이 있었음
-
해당 방법론은 data distribution matching에 집중
-
reward function 고려한건 GAN과 같은 discriminator뿐이었음
-
-
본 논문과 비슷한 시기에 나온 논문으로 DPOK가 존재
-
policy gradient algorith을 사용해 text-to-imagae diffusion model이 human preference와 더 잘 align되도록 함
-
DPOK역시 하나의 preference-based reward function만을 고려
-
부가적으로, KL-regularlization을 연구, 각 프롬프트마다 다른 diffusion model을 학습
-
하지만 본 논문에서는 많은 프롬프트를 한번에 학습, 학습 데이터셋 외의 더 많은 프롬프트에 대해서도 일반화가 잘 된다는 것을 보임
-
또한 DDPO는 human feedback을 넘어서 다양한 reward function에 적용 가능함
-
-
Preliminaries
-
Diffusion models
-
본 논문에서는 conditional diffusion probailistic models를 고려, 해당 모델은 데이터셋의 샘플 \mathbf{x}_0와 그에 상응하는 context \mathbf{c}에 대한 distribution p(\mathbf{x}_0 \mathbf{c})로 나타냄 -
해당 분포는 데이터에 반복적으로 노이즈를 더하는 Markovian forward process q(\mathbf{x}_t \mathbf{x}_{t-1})의 역과정으로 모델링 됨 - forward process의 역과정은 아래 objective로 neural network \mathbf{\mu}_\theta(\mathbf{x}_t,\mathbf{c},t)를 학습하는 것으로 구현
-
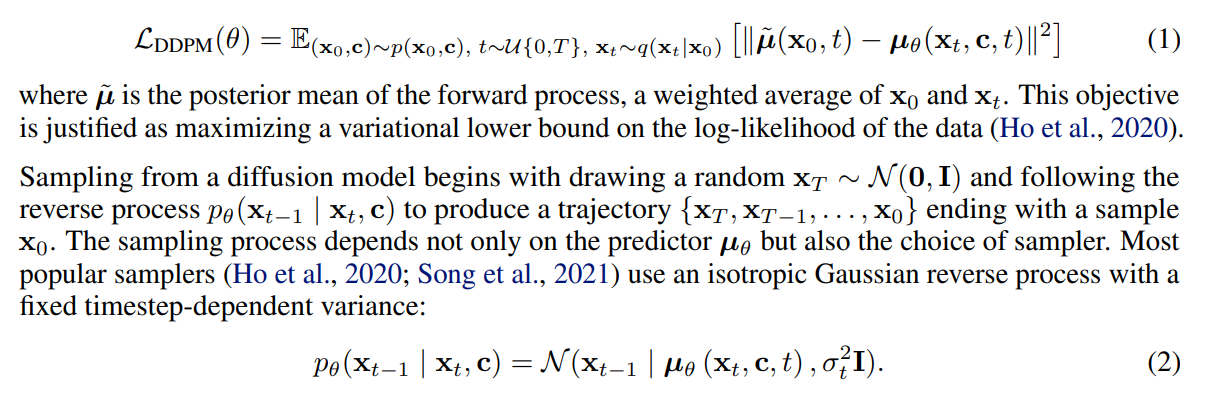
-
t시점의 이미지와 context, 특정 시점 t를 바탕으로 각 step의 평균을 모델링 특정 시점 t와, 원본 이미지가 주어졌을 때의 forward process의 mean과의 차이가 줄도록 학습
-
sampling process는 predictor \mu_\theta뿐만 아니라 sample의 선택에 의존
- 보통 sampler로 isotropic Gaussian reverse process를 씀
-
Markov decision processes and reinforcement learning
-
MDP는 (S,A,p_0 ,P,R)로 정의됨
-
S : state space
-
A : action space
-
p_0 : distribution of initial states
-
P : transition kernel
-
R : reward
-
-
각 timestep t마다, agent는 st \in S를 관찰, a_t \in A를 취하고, 보상 R(s_t,a_t)를 획득, 새로운 state s{t+1} \sim P(s_{t+1} s_t,a_t)로 이동 -
agent는 policy \pi(a s)에 따라 행동 - RL objectve는 아래의 식을 최대화 하는 것
-
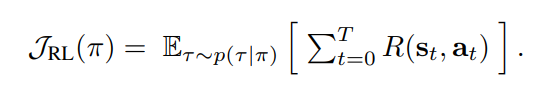
Reinforceement learning training of diffusion models
-
Problem statement
-
이미 diffusion model이 있다고 가정, model은 pretrain되거나 randomly initialized.
-
fixed sampler를 가정하고, diffusion model은 sample ditribution p_{\theta}(\mathbf{x}_0 \mathbf{c})을 유발 -
denoising diffusion RL objective는 각 sample과 context로 정의된 reward signal r을 최대화 하는 것이 목표
- 여기서 context distribution p(\mathbf{c})는 선택하면 됨
-
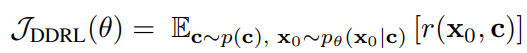
-
Reward-weighted regression
-
standard diffuion model 학습 시 적은 변화로 J_{DDRL}에 최적화하기 위해서, [Lee et al, 2023]에서는 diffusion model에 대한 sigle-round version을 서술
- 일반적으로 이 방법은 sampling과 training을 번갈아가면서 수행되기 때문에 online RL방법으로 가능
-
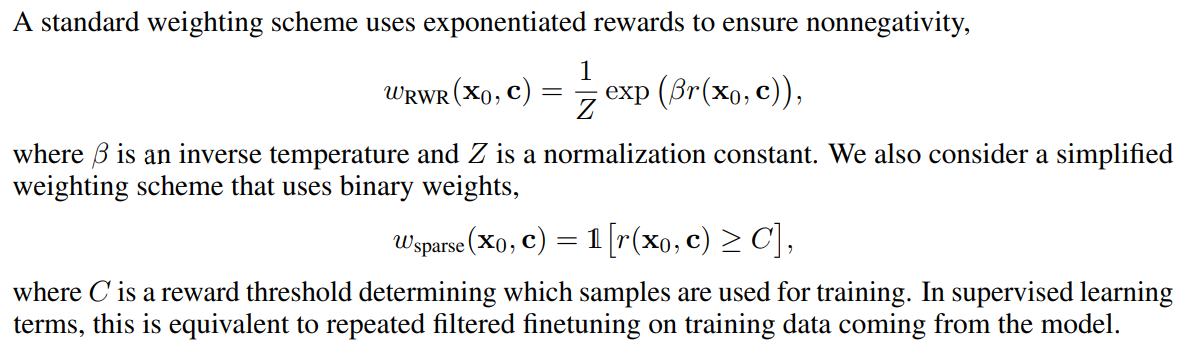
- weight scheme은 위와 같이 정의
- Z에서 바로 X를 생성하는 확률을 근사, reward로 가중치를 두고 학
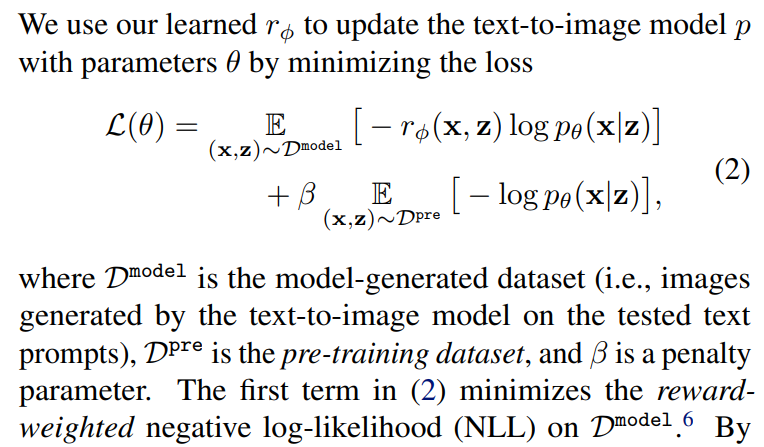
- w_sparse의 경우 특정 threshold를 바탕으로 해당 샘플을 학습에 쓸지 말지를 결정, 이는 repeated filtered finetuning과 동일
-
Denoising diffuion policy optimization
-
RWR는 denosiing process의 sequential한 특성을 무시하기 때문에 approximate log-likelihood에 의존
-
denoising process를 multi-step MDP에 치환하는걸 보임
-
이는 policy gradient를 통해 J_{DDRL}을 바로 최적화하도록 함
-
이는 이전 논문에서 유도한 것을 따르며, 그들의 방법과 reward가 GAN-like discriminator인 policy gradient algoritm간의 등가성을 증명
-
-
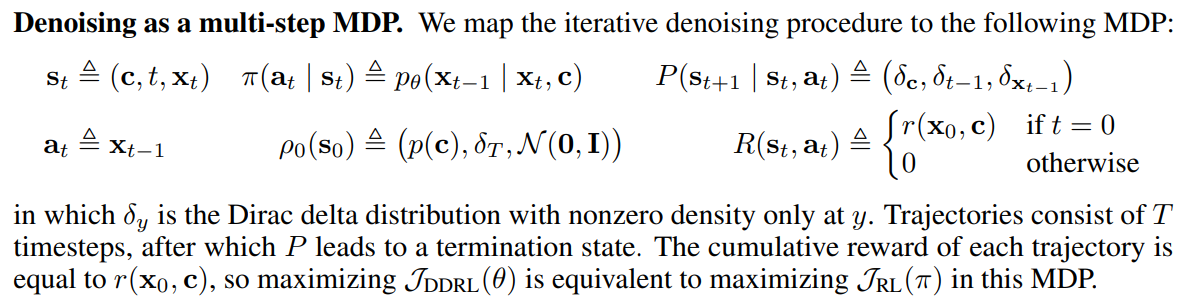
-
state : text, time step t, image of time step t
-
action : image of time step t-1
-
policy : reverse process given imag of time step t and text
-
distribution of initial states : distribution of text, dirac delta distribution of time step t, standard gaussian(X_T는 여기서 샘플링되니까)
-
transition kernel : dirac delta distribution of text, time step t-1, image of time step t-1
-
reward is computed given \mathbf{x_0}, \mathbf{c}
-
policy gradient estimation
-
likelihood와 likelihood gradient에 접근할 수 있다면, 우리는 \nabla J_{DDRL}의 직접적인 Monte Carlo estimate가능
-
RWR처럼, DDPO는 샘플링을 통해 denoising trajectories {\mathbf{x}T,\mathbf{x}{T-1},…,\mathbf{x}_0}을 수집, gradient descent로 parameter update
-
DDPO의 첫번째 버전을 DDPO_SF라 하고, score function policy gradient estimator(aka REINFORCE algorithm)를 사용
-
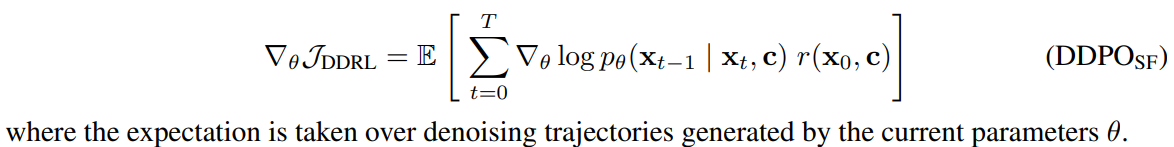
- 하지만 이 방법의 경우 data collection마다 한번의 optimization만 가능(데이터 재사용 불가능)
- gradient가 현재 파라미터로 생성된 데이터에 의해 계산되어야 하기 때문
-
여러 번의 optimization을 할 수 있게, importance sampling estimator를 사용(DDPO_IS)
- 구현시, p{\theta}가 p{\theta_{old}}와 너무 멀어져서 estimator가 부정확해지는 것을 막기 위해 clipping을 통해 trust region을 구현(PPO처럼)

Reward functions for text-to-image diffusion
-
Compessibility and Incompessibility
-
text-to-image diffusion modeld의 capabilities는 학습 데이터 분포에 있는 text-image의 co-occurrences에 제한
-
예를 들어, file size에 대한 caption이 붙어 있는 경우가 적다면, 원하는 file size를 prompting으로 명시하는 것이 불가능
-
이러한 제한으로 인해 file size를 기반으로 한 reward function이 보편적인 사례 연구
- 계산하긴 쉽지만, likelihood maximation과 prompt engineering을 통해 조절할 수 없음
-
-
본 논문에서는 diffusion model sample의 resolution을 512x512로 제한, 각 파일 크이는 오로지 image compressibility에 결정됨
-
저자들은 파일 크기에 기반해 2가지 task를 정의
-
compressibility
- JPEG compression 후의 최소화된 파일 크기
-
incompressibility
- 같은 측정이 최대화
-
-
-
Aesthetic quality
-
human user에게 유용한 reward function을 포착하기 위해, perceived aesthetic quality기반한 task를 정의
-
LAION aesthetics predictor를 사용, 176000 human image rating에 학습된 모델
-
predictor는 CLIP embedding 위에 linear model을 얹는 것으로 구현됨
-
annotation은 1-10사이, 점수가 높은 이미지는 artwork를 포함
-
aesthetic quality predictor는 human jugments로 학습되기 떄문에, 이 task는 human feedback 바탕의 reinforcement learning을 구성
-
-
Automated prompt alignment with vision-language models
-
text-to-image model을 학습하는 범용적인 reward function은 prompt-image alignment
-
하지만 일반적인 prompt alignment를 파악하는 reward를 specifying하는 것은 어려움
- large-scale human labelingh efforts가 필요
-
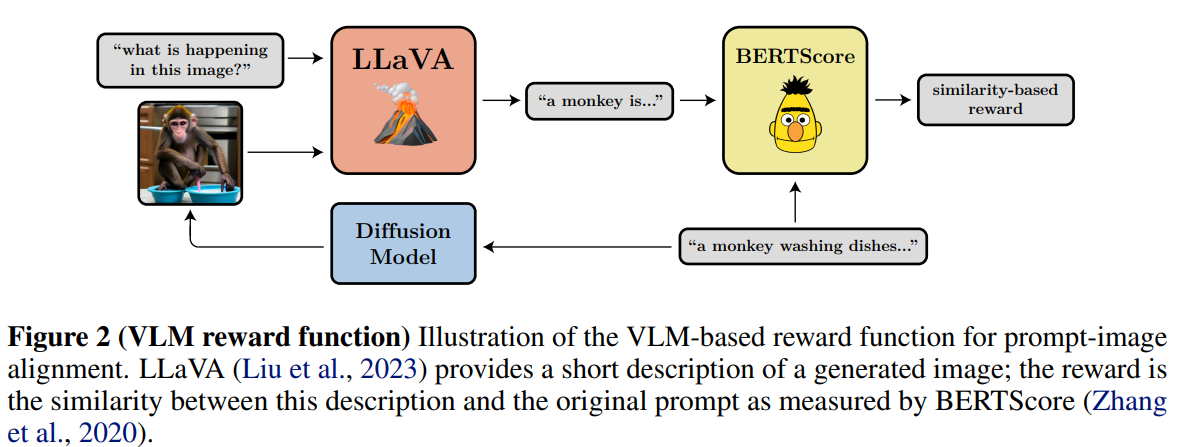
본 논문에서는 기존의 VLM을 사용하는 방법론을 제안
-
RLAIF연구에서 영감을 받음
- 언어 모델이 자체 피드백을 통해 개선
-
-
SOTA VLM인 LLaVa를 사용해서 image에 대한 description을 생성, image를 생성할 때 사용한 text와 BERTScore를 계산, 이를 reward로 사용
- BERTScore recall metric 사용
Experimiental evaluation
실험의 목표는 RL algorithm을 사용해 diffufsion model을 다양한 user-specified objective와 align이 되도록 finetuning, 그 효과를 평가하는 것
-
DDPO의 여러 버전과 RWR의 비교
-
VLM을 manually하게 명시하기 어려운 reward를 최적화 하는데 사용할 수 있는가?
-
RL finetuning의 효과는 finetuning시에 보지 못한 prompt에 대해서도 적용될 수 있는가?
-
Experiment details
-
Stable Diffuion v1.4를 사용
-
compressibility와 incompressibility prompt는 ImageNet-1000에서 모든 398개의 동물에서 uniform하게 샘플링
-
aesthetic quality prompt는 45가지 common animals에서 unifromly하게 샘플
-
-
Algorithm comparision
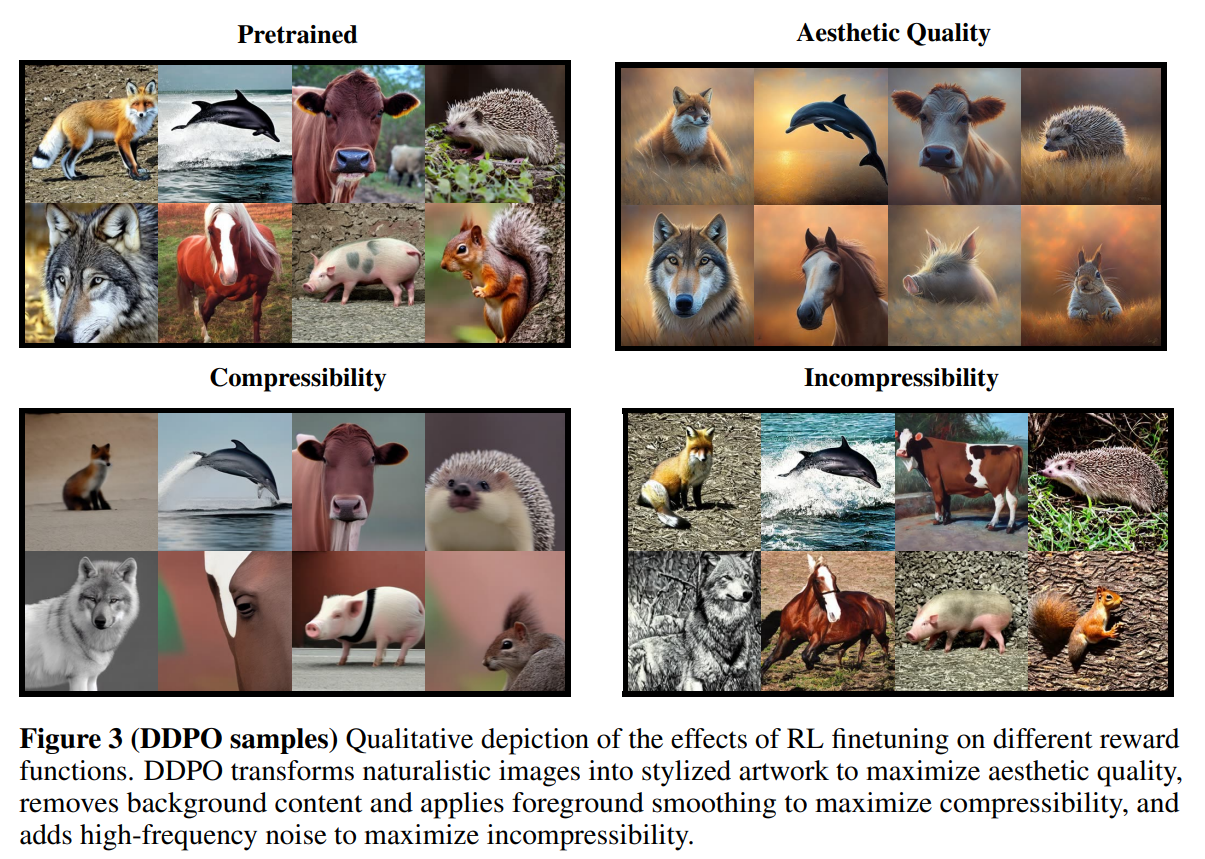
-
위의 결과를 보면, DDPO는 추가적인 data curation없이 reward function 명시만으로 pretrained model을 효과적으로 adapt
-
각 reward를 최적화 하기 위해 찾은 전략이 nontrivial함
-
예를 들어, LAION-predicted aesthetic quality를 최대화 하기 위해, DDPO는 자연스러운 이미지를 artistic drawing을 생성하도록 모델을 변형
-
compressibility를 최대화 하기 위해, DDPO는 background를 제거, 남아있는 것에 smoothing을 적용
-
incompressibility를 최대화 하기 위해, DDPO는 JPEG compression algorithm으로 인코딩하기 힘든 artifact를 찾음
- high-frequency noise, sharp edges
-
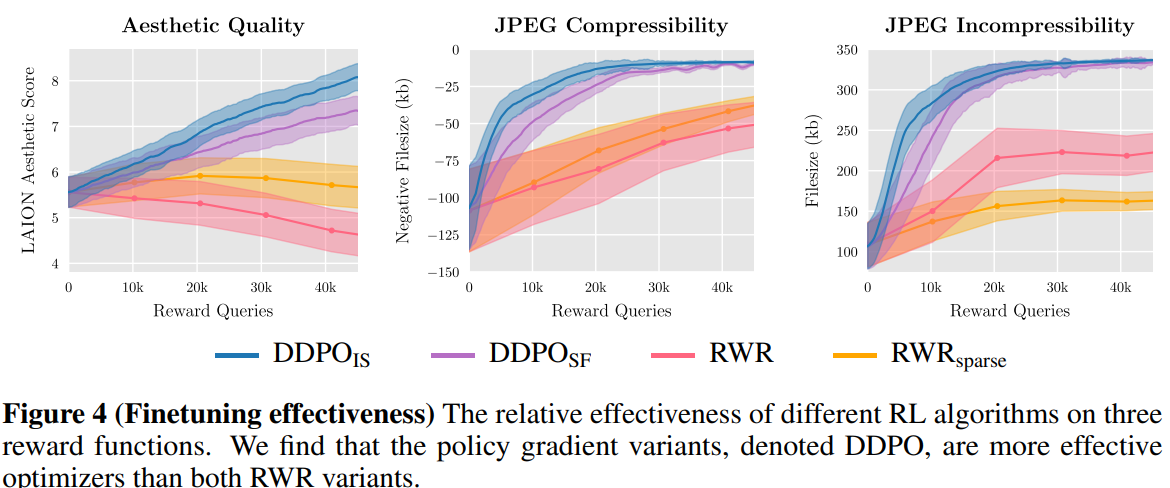
-
양적인 비교는 위의 그래프에 나와 있음
-
DDPO가 확실히 RWR보다 우월한 성능을 보임
-
즉, denoising process를 multi-step MDP로 formulating하고 policy gradient로 바로 최적화하는 것이 log-likelihood에 대한 reward-weighted variational bound에 최적화하는 것보다 훨씬 효율적
-
DDPO끼리 비교하면, importance sampling estimator가 약간 성능이 우수, 이는 opimization step이 늘어났기 때문
-
-
Automated prompt alignment
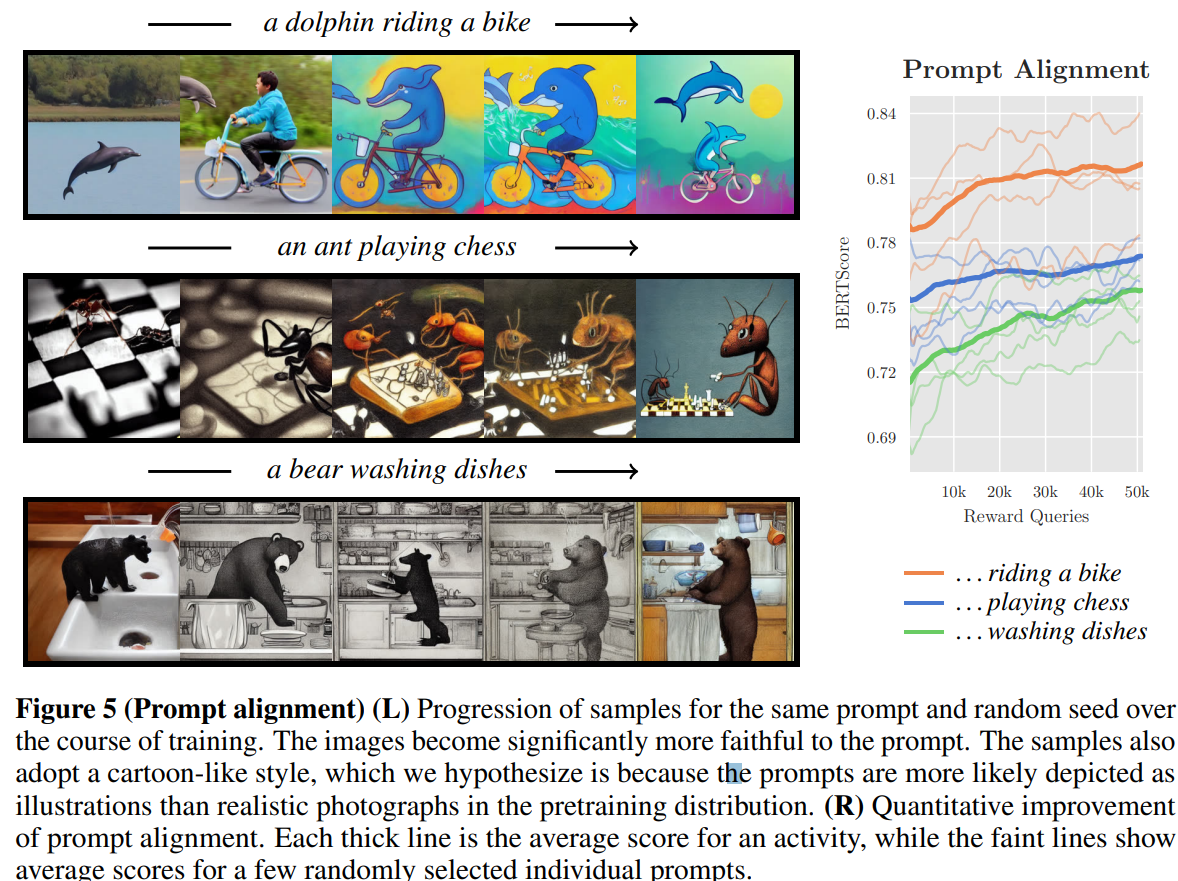
-
DDPO_IS를 바탕으로 실험 진행
-
해당 task에 대한 prompt로 “a(n) [animal] [activity]”형태를 사용
-
동물은 45개 list에서 선택
-
activity는 “riding a bike”, “playing chess”, “washing dishes”중 하나 선택
-
-
finetuning set의 일부 prompt의 경우(돌고래가 자전거를 타고 있는 모습)엔 pretrained모델로 아예 생성하지 못했는데, adaptation후에는 잘 생성되는 것을 볼 수 있음
-
대부분의 이미지가 cartoon-like 혹은 artistic하게 변화하는 것을 볼 수 있음
-
본 논문의 저자들은 pretraining distribution의 function 혹은 reward function 때문인 것으로 추정
-
예를 들어, 일상적인 활동을 동물이 하는 것은 photorealistic보단 cartoon-like로 묘사됐을 것
-
혹은 LLaVA모델이 간단한 cartoon-like image를 인식하기 용이했을 것
-
-
-
Generalization

-
LM에서와 비슷하게 finetuning의 효과가 일반화 되는 것을 발견
-
학습 분포 밖의 동물, 비동물(일상적인 물건)에 대한 generalization evidence를 발견했고, prompt-image alignment의 경우 새로운 활동 “tasking an exam”에 대해서도 생성이 가능했음
Discussion and Limitations
-
denoising diffuion model을 바로 다양한 reward function에 최적화할 수 있는 RL기반의 framework를 제안
-
iterative denoising procedure를 multi-step decision-making problem으로 보고, policy gradient algorithm을 설계, 효율적으로 diffusion model을 학습
-
DDPO는 prompt로 명시하기 어렵고, 프로그래밍 적으로 평가하기 어려운 taks에 대해서 매우 효과적으로 최적화 하는 방법론
-
향후 과제로,
-
VLM에 input으로 들어가는 질문을 확장할 수 있고, prompt를 기반으로 관련 질문을 생성하는 언어모델을 사용할 수 있음
-
prompt distribution의 다양성도 확장 가능
-
overoptimization에 대해선 다루지 않음
- RL finetuing시 모델이 기존 분포에서 너무 멀어져 발산하는 문제
-