Cognitive Behaviors that Enable Self-Improving Reasoners, or, Four Habits of Highly Effective STaRs
논문 정보
- Date: 2025-03-11
- Reviewer: 준원 장
- Property: RL, Reasoning
1. Introduction
-
Motivation
-
기존의 RL 방법론들은 몇번의 iteration 이후에 reasoning 성능 향상이 saturation된다.
- 왜 Qwen2.5-3B랑 Llama-3.2-3B에 같은 RL training을 했는데 전자에만 test-time scaling 효과가 적용될까?
-
→ 논문에서는 ‘change in self-improvement’가 base-llm의 ‘key cognitive behaviors’유무에 따라 다르게 발현된다고 함
-
문제를 풀기 위해서 4개의 cognitive behaviors가 있다고 정의
-
verification (systematic error-checking)
-
backtracking (abandoning failing approaches)
-
subgoal setting (decomposing problems into manageable steps)
-
backward chaining (reasoning from desired outcomes to initial inputs).
-
-
Findings of work
-
Llama에 synthetic reasoning traces을 priming (인공지능 모델에 특정 형태의 입력이나 예시를 미리 제공)하면 RL후 성능증가
-
1.에서 Incorrect solution이 주어져도 무방
-
targeted modification of the pretraining distribution으로 cognitive behavior induce 가능
-
2. Related Works
-
Improving Reasoning Capabilities
-
External Search for Reasoning.
-
incorporate search process itself to improve the underlying reasoning model
-
(operate without awareness of previously explored solutions)
-
In-Context Search and Self-Improvement.
-
enabling models to search sequentially in language. (enable llm to think in rationale)
(in-context examples, finetuning on linearized search traces, training on self-correction examples)
-
Reinforcement Learning for Reasoning.
-
RL (e.g., GRPO) → emergence of in-context search behaviors.
3. Identifying and Engineering Self-Improving Behavior
Initial Investigation: A tale of two models
-
Pilot Test: Countdown
-
Input: 25, 30, 3, 4, Target:32, Arithmetic operations (+, −, ×, ÷)
-
Solution: 32: (30 − 25 + 3) × 4
-
-
Why Countdown? (아래를 반영할 수 있는 task)
-
mathematical reasoning
-
planning
-
search strategies (general problem solving)
-
분석가능한 restricted search space이 있는 task
-
-
BaseLLM
-
Qwen-2.5-3B
-
Llama-3.2-3B
-
-
RL-Training
-
PPO (superior stability across hyperparameter)
-
250 steps training, 4 trajectory sampling
-
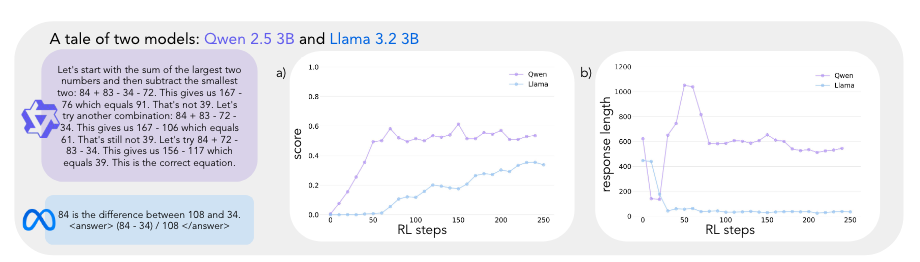
→ Qwen 30 step부터 성능 증가, 60% accuracy 달성. Llama 최종 30% accuracy 달성.
→ Qwen 초기에 explicit verification statements → implicit solution checking
(‘verbose하게 verification하다가 올바른 답을 찾을 때까지 순차적으로 다른 해결책을 시도를 하는 방식으로 바뀜)
RQ: what underlying capabilities enable successful reasoning-based improvement?
A Framework for Analyzing Cognitive Behaviors
-
Backtracking or the explicit revision of approaches when errors are detected: 백트래킹 또는 오류가 감지되었을 때 접근 방식의 명시적 수정(예: ‘이 접근 방식은 다음과 같은 이유로 작동하지 않습니다…’)”
-
Verification or the systematic checking of intermediate results: 검증 또는 중간 결과의 체계적인 확인 (예: ‘이 결과를 다음과 같은 방식으로 검증해 봅시다…’)”
-
Subgoal Setting: 하위 목표 설정, 복잡한 문제를 관리 가능한 단계로 분해하는 것(예: ‘이를 해결하기 위해, 우리는 먼저 다음이 필요합니다…’)”
-
Backward Chaining: 역방향 연쇄, 목표 지향적 추론 문제에서 원하는 결과에서부터 역으로 해결책을 찾아가는 것(예: ‘75라는 목표에 도달하기 위해, 우리는 다음으로 나눌 수 있는 숫자가 필요합니다…’)”
→ Countdown때문에 설정한 behavior
⇒ gpo-4o-mini를 활용해 각 training step에서 model output이 위의 behaviors를 포함하는지 분류
The Role of Initial Behaviors in Self-Improvement
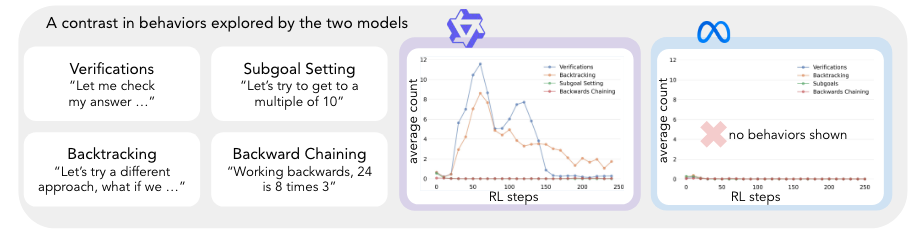
→** Qwen의 performance improvements지점과 emergence of cognitive behaviors의 지점이 거의 일치함 (30~130steps)**
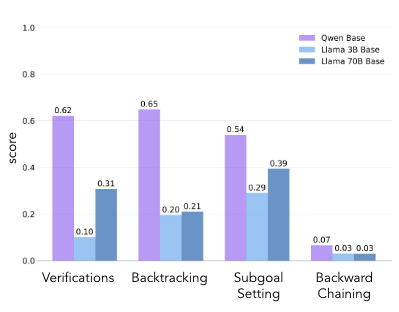
→ General한 분석을 위해 Qwen-2.5-3B, Llama-3.2-3B, Llama-3.1-70B에 대한 분석 진행 (PPO model output)
→ Qwen-2.5-3B가 Llama들에 비해 4가지 행동 모두에서 상당히 높은 비율 기록
-
Takeway
- initial policy가 test-time scaling의 실현시키는데 중요한 사전조건으로 작용한다.
(그림 오른쪽 참고)
- increased model scale로 behavior의 contextual activation이 가능하다.
(논문에 구체적으로 적어놓진 않았지만, successful trajectories에 나타나는 behavior만 증폭이 가능하다고 하다. 그리고 장표를 보면 Backward Chaining의 경우 llama는 scaling up해도 전혀 개선이 안되는 것을 확인할 수 있음)
Intervening on initial behaviors
RQ: targeted intervention을 통해 인위적으로 ‘cognitive behavior’를 발현시킬 수 있을까?
-
Claude 3.5 Sonnet으로 ‘cognitive behavior’를 반드시 포함하는 reasoning path를 생성하도록 함
-
이때, 각 reasoning path는 특정 ‘cognitive behavior’를 가지도록 controlled setting (system message)
(To create datasets rich in only the targeted behaviors and determine causal efficacy, we instructed Claude** to use exclusively the specified cognitive behavior while prohibiting all others.**)
-
Controlled reasoning path [Correct Answer]
-
all strategies combined
-
backtracking only
-
backtracking with verification
-
backtracking with subgoal setting
-
backtracking with backward chaining
- Claude 3.5 Sonnet도 Correct Answer의 비율이 높지는 않음
-
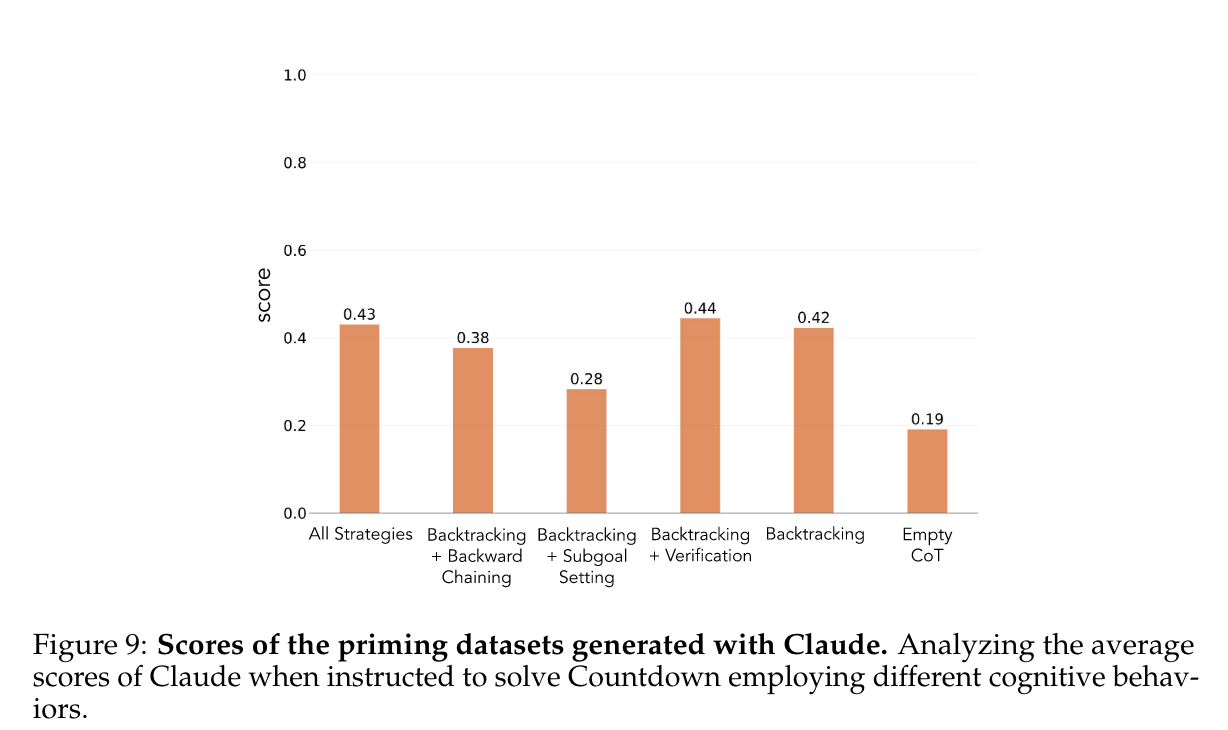
-
Empty-CoT
-
length-matched (all strategies combined 길이 맞춰서 placeholder tokens 채우는 setting → 길이만 길어진다고 test-time computing이 발현될까?)
- In-Correct Answer
-
Experimental Setting
-
Correct Answer만 가지고 SFT - EXP1
-
InCorrect Answer만 가지고 SFT - [ EXP2 ]
-
-
Result
** [ EXP1 ]**
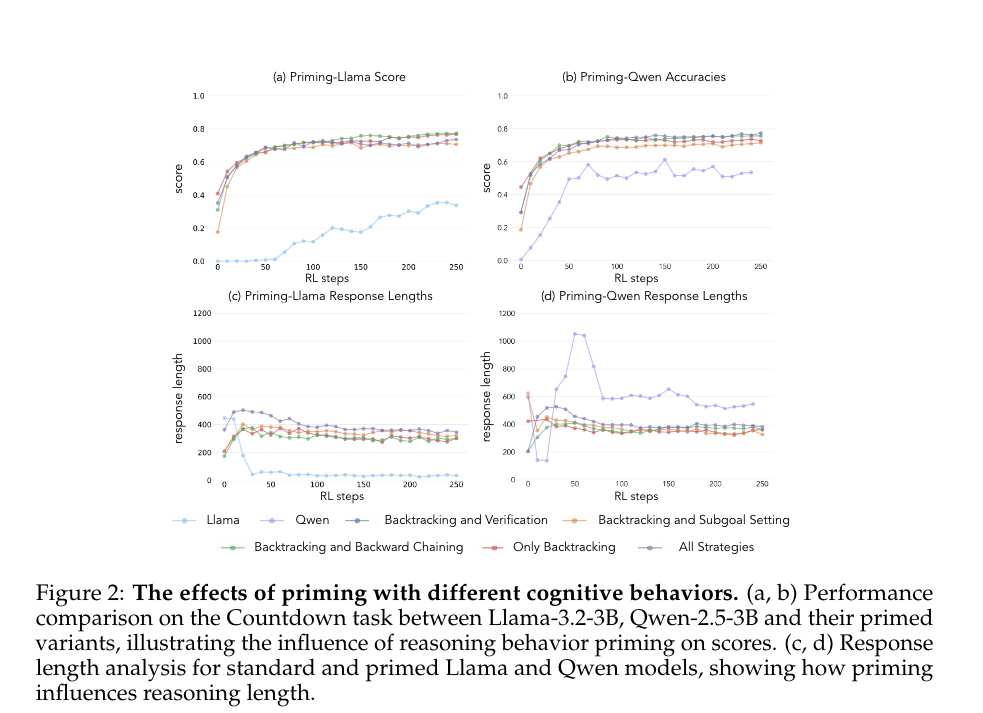
→ Llama와 QWEN 모두 priming (SFT)의 효과를 보아 RL때 성능이 증가한다.
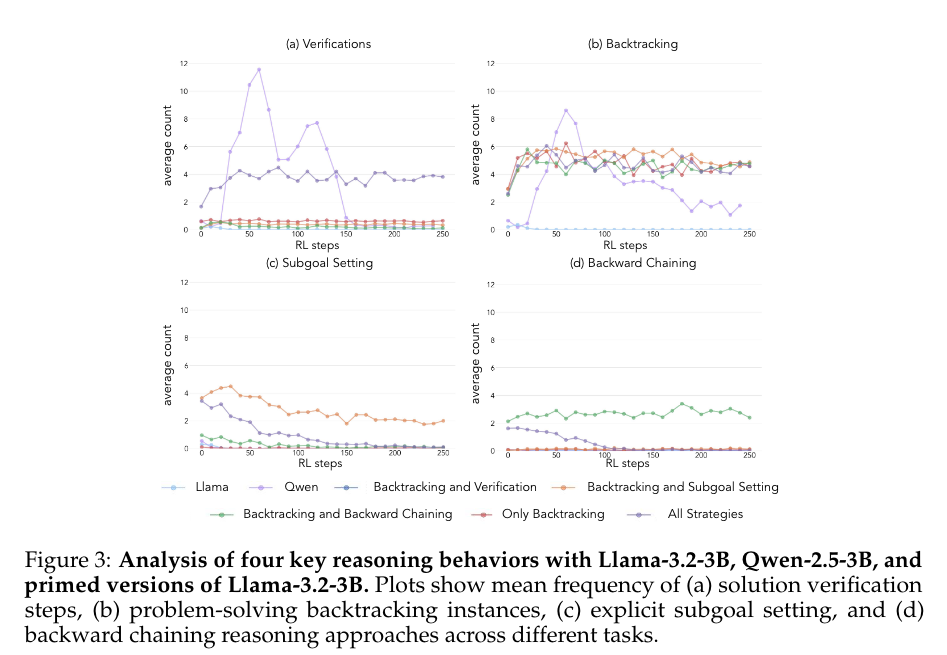
→ priming (SFT)된 LM의 model output을 분석해보면 (primed llama), all strat에서는 verification과 backtracking이 선택적으로 사용되지만 subgoal이나 backward chaining은 사용되지 않도록 RL이 진행되는 것을 실험적으로 확인, 그러나 또 각각은 backtracking이랑 paired되면 RL에서 발현
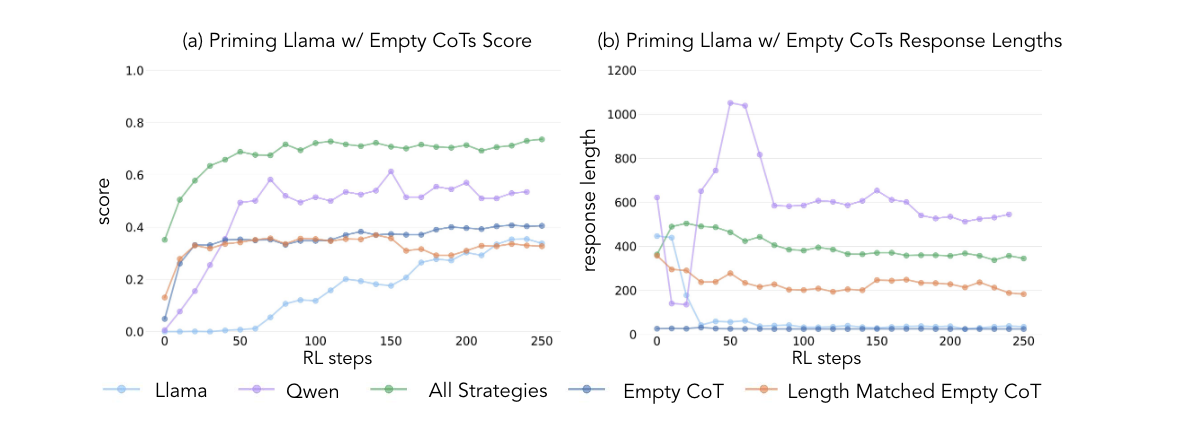
→ Empty CoT priming은 당연히 어떠한 ‘cognitive behavior’도 실현시키도록 학습시키지 못하고, 의미없는 긴 토큰으로 학습하는것은 test time scaling에 전혀 도움이 안되는 것을 score상으로 확인
** [ EXP2 ]**
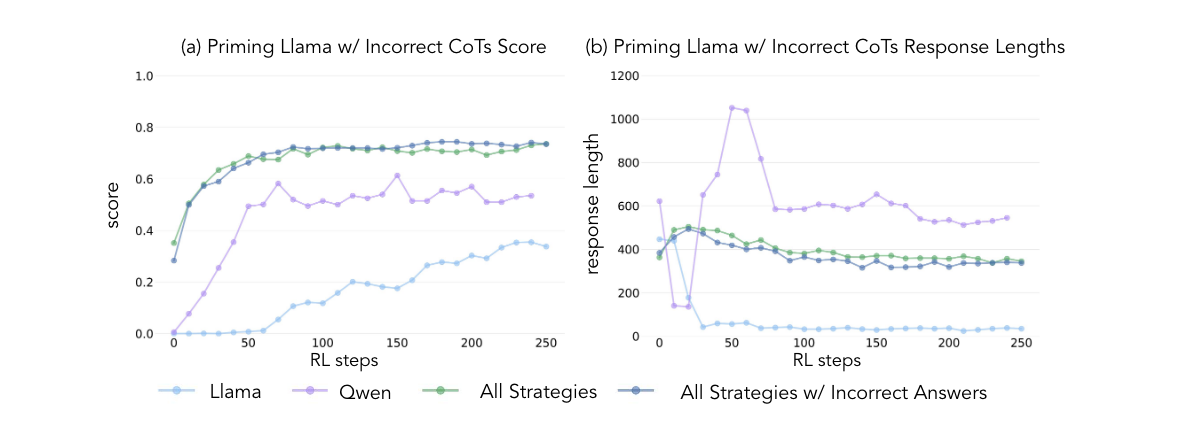
→ incorrect answer 해당여부는 ‘cognitive behavior’를 발현시키는데 전혀 상관이 없음
→ RL에서 LM의 self-improvement를 이끌어내는데 중요한것은 정답보다는 풀이과정에서의 정확한 사고방식 방법이다.
Behavioral Augmentation of the Pretraining Data.
- 이전까지 진행했던 priming 실험은 Countdown-specific실험
RQ: LM의 pre-training distribution을 RL때 self-improvement하도록 수정하는 방법은 없을까?
(Generalization)
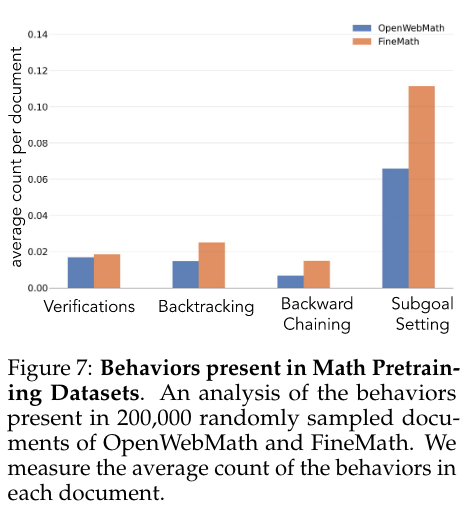
- 바로 OpenWebMath나 FineMath에 Qwen-2.5-32B를 classifier로 두고 ‘cognitive behavior’가 있는지 검수해봤는데 비율이 많지는 않더라 (200K)
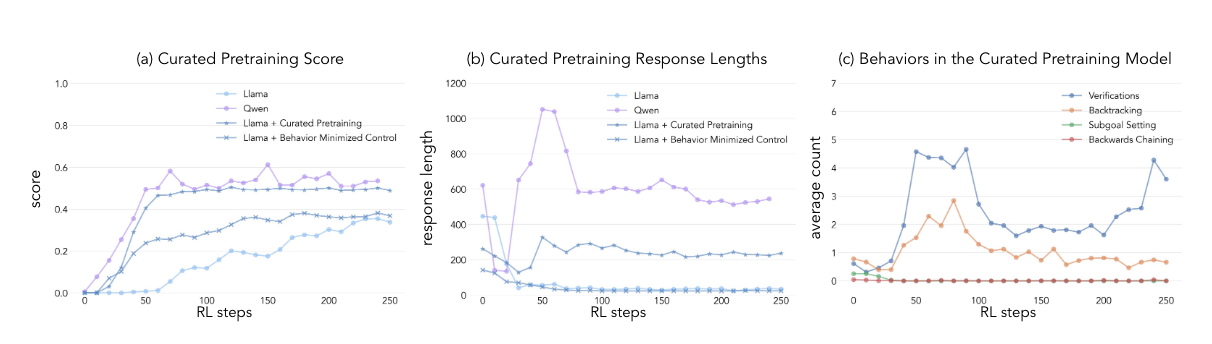
-
OpenWebMath에서 ‘cognitive behaviors’가 있는 부분을 추출해서
-
question-thought-answer format변환
-
‘cognitive behaviors’가 있는 부분 없는 부분 (curated vs minimized curated)
-
CL → PPO
- ‘cognitive behaviors’가 발현되도록 RL training이 가능하며 output에서 verification과 backtracking을 하는 것으로 드러남
4. Discussion
-
RL후에 발현되는 test-time scaling은 base-model이 가지고 있는 (엄밀히 말하면 실현시킬 수 있는) ‘cognitive behaviors’에 따라 다르다.
-
논문에서는 QWEN은 cognitive behaviors가 있고 Llama3은 ‘cognitive behaviors’이 없다고 실험적으로 보여줌
-
‘cognitive behaviors’의 포함여부가 correct answer유무보다 RL시 self-improvement에 있어서 더 중요한 인과관계를 가짐
-
‘cognitive behaviors’가 rich한 pre-training data를 curation해 CL하면 RL후 test-time scaling을 달성할 수 있음
-
논문에서 검증한 ‘cognitive behaviors’가 task-dependent하다.
(‘cognitive behaviors’라는게 problem space에 따라 sequential, deliberate하게 정해질 수 밖에 없음. e.g., code, create writing에서 어떻게 적용될진 미지수)