Contextual Document Embeddings
논문 정보
- Date: 2025-03-04
- Reviewer: 상엽
- Property: Retrieval, Embeddings
Introduction
-
Statistical approaches: BM25 → Neural method: dual encoder
-
neural model에 없는 Statistical approach만이 가진 장점: prior corpus 통계치를 알 수 있다는 것
- prior term을 통해 context-dependence를 가짐.
- Domain: Wikipedia, sports article, televised events
- IDF는 NFL, draft, annual 등에 더 높은 가중치를 부여할 수 있음.
- 연구 목표: dense encoder를 통한 contextualization of document embeddings
- Contextual training procudure
-
Fast query-document clustering: contrastive learning 과정에서 배치 내 이웃 문서 (neighboring documents) 정의
-
이웃 문서로만 배치학습 진행 ← most challenge contexts를 구별할 수 있게 하기 위함.
- Architecture
-
임베딩 동안에 contextual document를 주입하는 새로운 encoder 설계
-
Contextual Document Embedding (CDE): BERT-style encoder에 aggregated document-level information about neighboring documents를 제공
-
사전에 계산된 corpus-level 통계치를 제공 → 동일한 임베딩 사이즈 유지
Background
Text retrieval
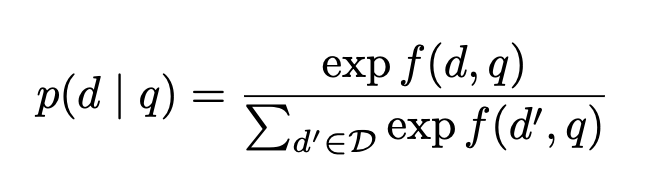
-
Vector retrieval methods
- f(d,q) → \phi(d) \cdot\psi(q) (documenct 임베딩의 경우 사전에 계산→ fast computation 가능)
-
Statistical Retrieval
- \phi(d;D) \cdot \psi(q;D): Document/Domain 정보를 활용 → Context 활용
Method
일반적인 Retrieval 모델 학습은 여러 도메인을 가진 대량의 데이터를 활용하게 되므로 특정 도메인의 통계적 특성을 모델이 알 수가 없음.
Contextual Training with Adversarial Contrastive Learning
-
일반 도메인에서 NFL은 적은 문서에 등장하여 가치가 있는 단어일지라도 검색 대상 데이터가 Sports 도메인일 경우 해당 단어는 상대적으로 흔한 단어가 됨. → 가중치가 낮아짐.
-
Meta-learning-style objectives: 도메인 선정 → 관련 예시를 샘플링
- Training dataset (\mathcal{D}_T)를 각각의 pseudo-domain을 나타내는** (**\mathcal{B}^1, …, \mathcal{B}^B**) 그룹들로 분할**
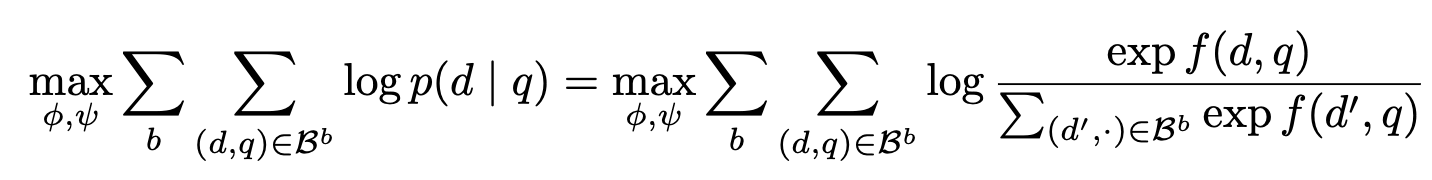
- Hard negatives (\mathcal{H}) 없음!
-
Group이 최대한 challenge하기 위해 다음의 최적화 문제를 풀 수 있음.
- Zhang & Stratos (2021) show that increasing the partition term improves the contrastive approximation to the maximum likelihood the gradient.
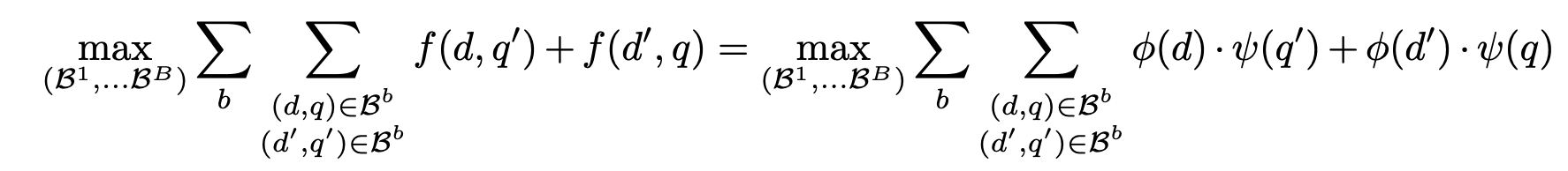
- target query의 d, q pair가 아닌 Group 내 다른 d', q' pair와의 유사도가 최대가 되게 → 정답이 아닌 것도 유사도가 가장 높아지는 배치 그룹 구성 → 가장 Challenge한 그룹 구분
- 현재 수식은 Intractable → 클러스터링을 통해 근사
1. **maximize → minimize 변환**
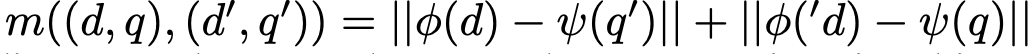
- dot products를 L_2를 활용해 다음과 같이 변환 가능
- 유사도를 높이자. == 거리를 줄이자. (normalized embeddings에서는 같은 의미)
1. **유클리디안 거리는 any other pair ****m****에 대해 다음 ****triangle inequality를 만족**
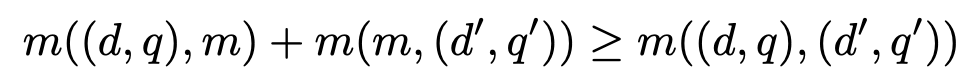
1. **이를 통해 Upper-bound를 얻을 수 있음.**
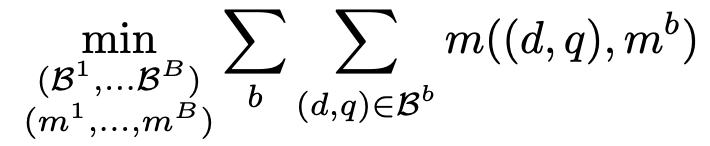
- 이미 정해진 B에 대해 이건 **비대칭 K-Means 클러스터링** 문제로 볼 수 있음. (그룹에 속한 샘플들의 거리를 가장 줄이는 방향으로 그룹을 묶자.)
- L_2 변환식을 볼 경우, m을 활용한 거리 계산은 \phi(d) \oplus \psi(q)와 같이 각각의 임베딩을 concat해서 빠르게 계산 가능!
- 클러스터링 과정은 임베딩 모델 학습 이전에 사용하기 때문에 sparse 임베딩과 GTR 활용
1. **Filtering Flase Negatives**
- **False Negative가 동일 배치 내에 포함될 수 있으므로 특히나 민감함.**
- MS Marco의 경우 70% 이상일 때도 있더라…
- Equivalence class 계산
- **다음의 surrogate function 활용**
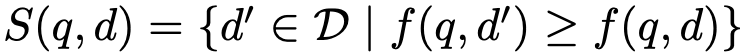
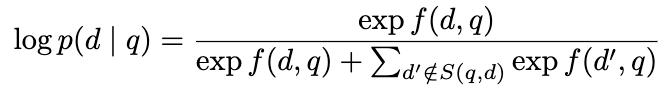
- 정답보다 더 가까운 유사도를 보이는 다른 문서들을 제거
- True negatives를 제거하게 될지라도 성능에 더 좋았음.
1. **Packing**
- equal-sized batches를 만들자.
- 아래 두 방법을 고려, 큰 그룹은 나누고 작으며 가까운 그룹은 합침.
1. random partioning
1. cluster-level traveling salesman
- 이 방법은 학습 때 마다 그룹 배치에 randomness를 줌으로써 도움이 되었음.
Contextual Document Embedding (CDE)
-
contextualization을 architecture에 직접적으로 주입하자.
-
Sparse retrieval 모델과 같이 corpus에 직접적으로 접근할 수 있는 encoder 모델을 만들자.
-
BM25와 같이 Corpus의 통계치만을 제공하자.
-
전체 문서에 대한 접근 권한을 가지되 cross attention과 같은 형태로 문서를 선별하자. (Garnelo et al., 2018: small scale) ← Large dataset에서 한계
→ corpus statistics를 배우되 효과적으로 계산할 수 있는 middleground 방법을 제안
-
Morris et al., 2023의 연구에서 documnet embeddings이 충분한 lexical inforamtion을 갖고 있음.
-
corpus subset을 미리 임베딩해 만들어 활용한다면 lexical 정보를 encdoing에서 활용하는 것이 아닌가?
-
Two-stage process를 통해 contextualized embedding을 생성
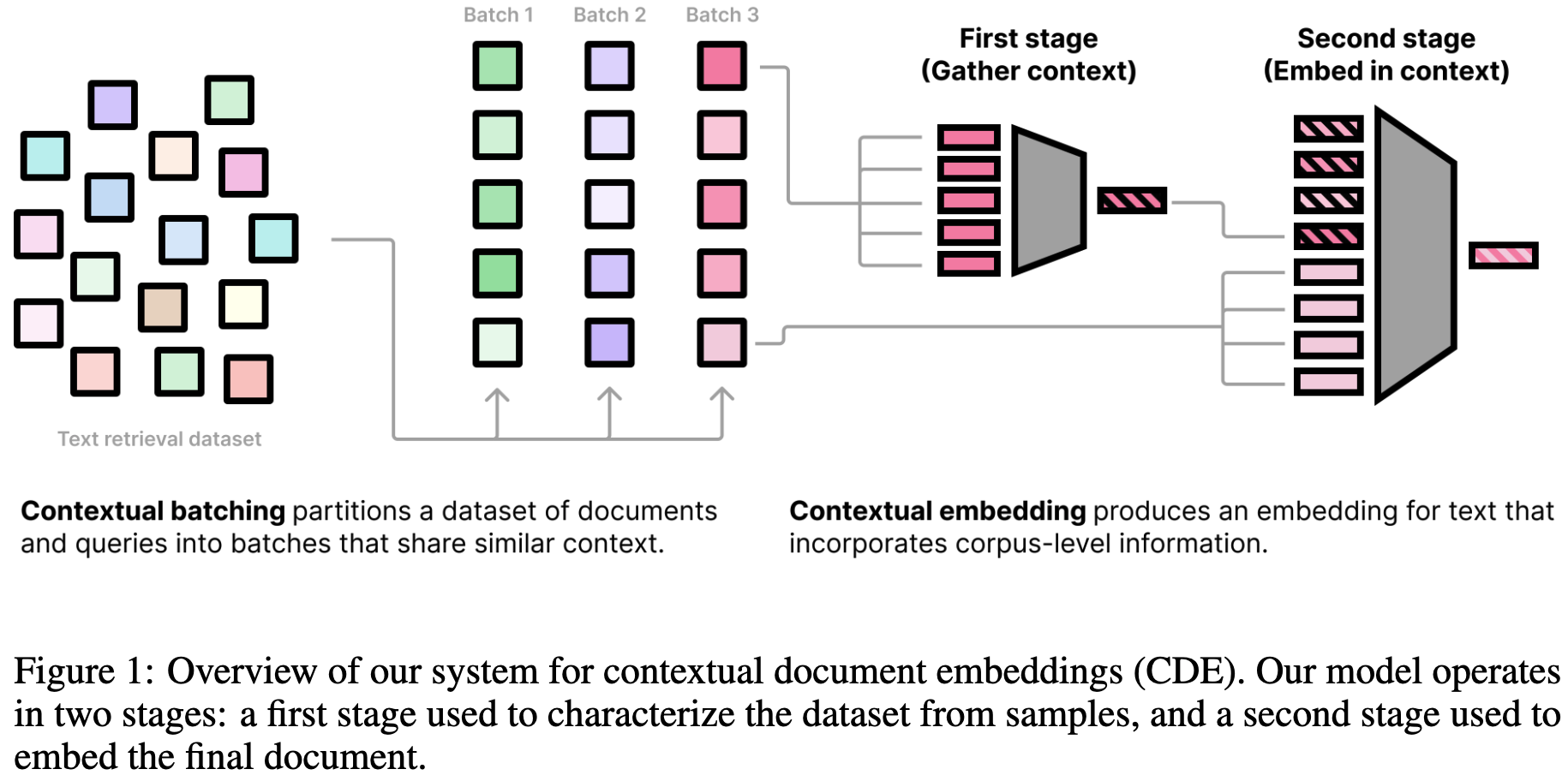
First stage: *Gather and embed context*
- Context documents: d^1, …, d^J \in \mathcal{D}가 있을 때, 임베딩 모델을 사용해 만든 임베딩을 concat하여 Embedding sequence M_1(d^1)…M_1(d^J) 획득
Second stage: *Embed document with additional context tokens*
- document d’의 임베딩을 일 계산하기 위해 contextual embedding sequence와 결합하여 다음을 계산
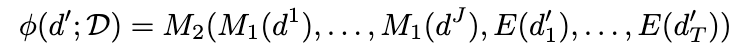
-
M_2: second-stage encoder model
-
E: token embedding matrix of M_2
-
Query도 유사하게 계산
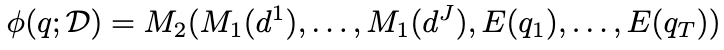
-
Contextual embedding implementation
-
매 배치에서 M_1 계산을 하는 것은 J에 비례해 많은 시간이 걸리는 작업
-
배치 내에서 M_1(d^1)…M_1(d^J)을 공유함으로써 계산을 한 번만하고 caching해서 사용
-
Embedding without context
-
Training 시, 모델의 generalization을 향상하기 위해 p 확률로 특정 context embedding M_1(d^*)을 null token으로 바꾸는 sequence dropout을 활용.
-
Test 시, context를 활용할 수 없을 경우 null tokens을 활용
Position-agnostic embedding
-
Document의 순서는 무관하기에 모든 postionality를 제거
-
\mathcal{D}에 상응하는 position에 positional embedding을 뺌.
Two-stage gradient caching
- GradCache의 two-stage version을 이용 → 더 큰 batch와 sequence를 활용 가능
-
first-stage와 second-stage를 gradient 없이 각각 계산 → Loss 계산
-
Second-stage에 대해서만 gradient 계산
-
Gradient 계산을 활성화하여 Second-stage 재실행 → Second-stage 업데이트
-
Gradient 계산을 활성화하여 First-stage 재실행 → First-stage 업데이트
Experimental Setup
-
적합한 세팅을 찾기 위해 BEIR의 truncate 버전을 활용해 small setting을 구성
-
6-layer transformer
-
maximum sequence length: 64
-
maximum number of the additional contextual tokens: 64
-
Batch size: {256, 512, 1024, 2048, 4096}
-
Cluster size: {64, 256, 1024, 4096, …, 2097152, 4194304}
-
-
Large setting에서도 small setting에서 찾은 하이퍼파라미터를 이용
-
Sequence length와 contextual token은 512개의 documents 사용
Training Data and Metrics
-
텍스트 임베딩 학습: 웹 (레딧, 위키피디아)에서 크롤링한 24개의 datasets 활용
-
Unsupervised training: 웹 (레딧, 위키피디아)에서 크롤링한 200M data 활용
-
Supervised training: 1.8M human-written query-document pairs
Implementation
배치 partioning 때,
-
GTR: documents와 queries 인코딩
-
Faiss: clustering, 100 step, 3 attempts
-
NomicBERT: pre-trained model backbone (137M) for filtering
Training
-
M_1, M_2 : nomic-embed-text-v1 ( Nussbaum et al., 2024) including flash attention
-
Adam optimizer
-
warmup: 1000 steps
-
lr: 2 x 10^{-5}
-
3 epochs
-
-
Contrastive loss, \tau: 0.02
-
sequence dropout: 0.005
Results
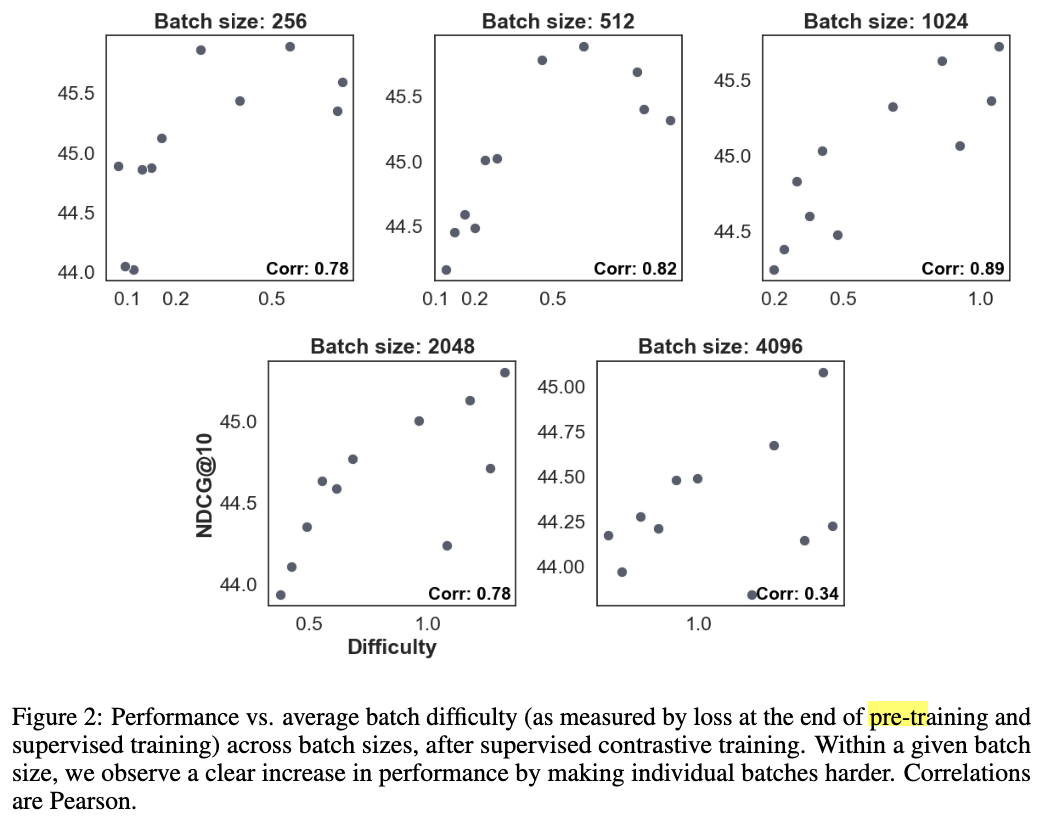
Contextual batching
-
클러스터링을 통한 batch 그룹 생성과 false negative filtering 이후, batch의 difficulty와 NDCG의 강한 상관관계 확인
-
batch의 document reoredering 역시 difficulty를 올렸으며 성능에 긍정적 영향을 줌.
Contextual architecture
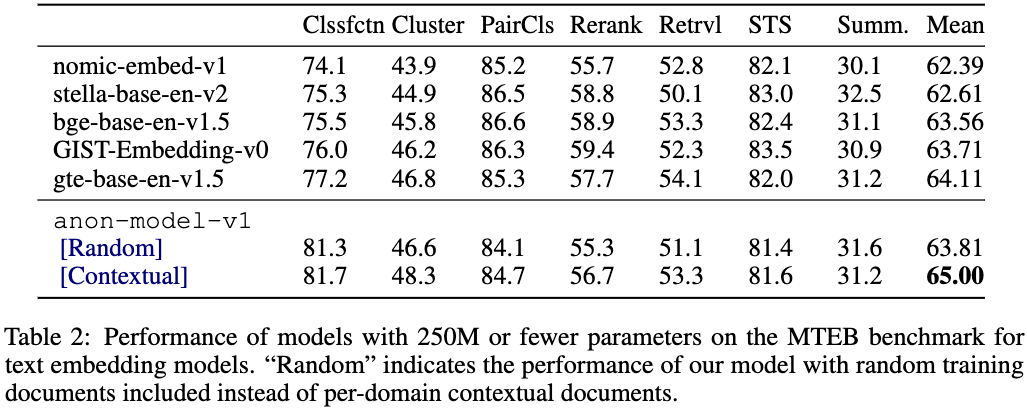
- Archictecture에서도 Contextual을 넣는 것이 일반적으로 더 좋았음.
Analysis
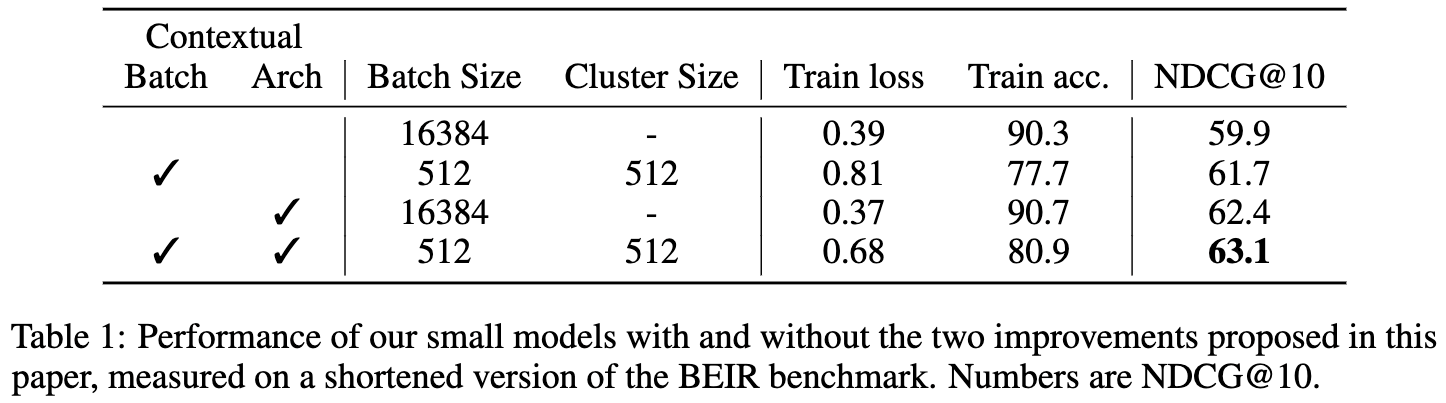
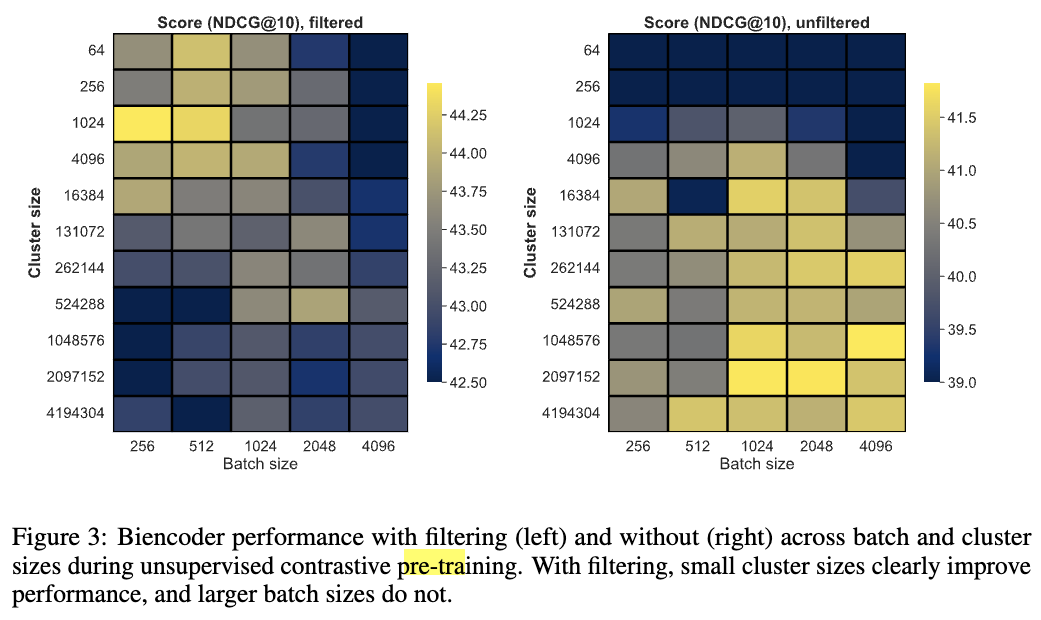
How hard are our clusters?
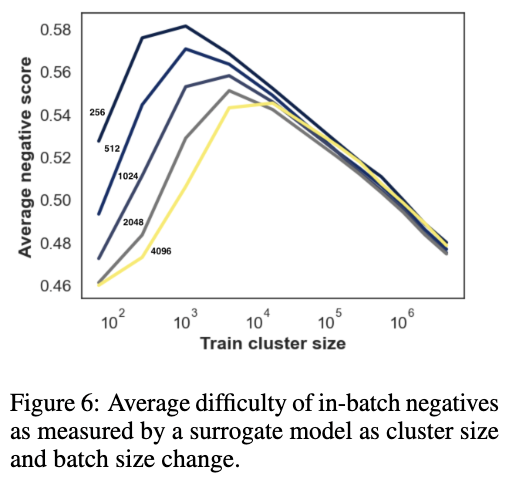
-
큰 배치는 더 쉬운 non-negative example을 가져옴 (난이도가 낮음.)
-
cluster size를 감소시키는 것은 난이도를 높임.
Which contextual documents help?
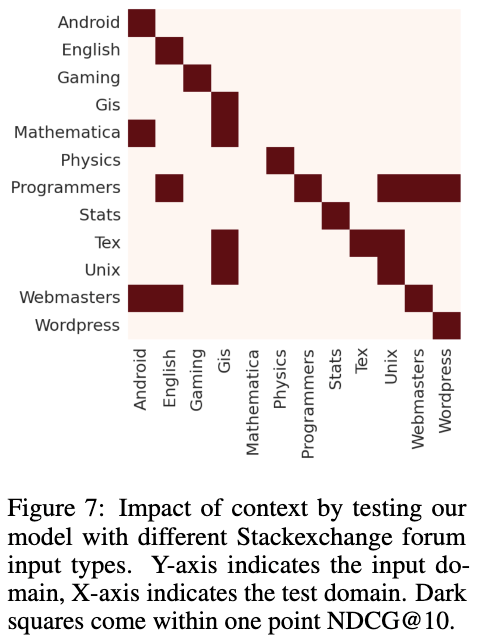
-
Contextual Documents 도메인을 다르게 해서 실험 진행. (Y-axis: input)
-
NDCG 값이 기존 최고 점수와 1%p 이내의 경우, 하이라이트
-
당연히 도메인이 같을 경우 즉 동일한 도메인 문서를 context로 받을 경우, 성능이 더 높음.
-
몇몇 도메인에서는 교차 상호작용도 있었음!
-
-
글에 에러가 좀 많음.
-
앞부분에는 흥미로웠는데 뒤에 힘이 너무 빠진 느낌.
-
이론과 성능을 다 얻기란 참 어렵다.
-
MTEB은 너무 수렴해버린 거 같음.